

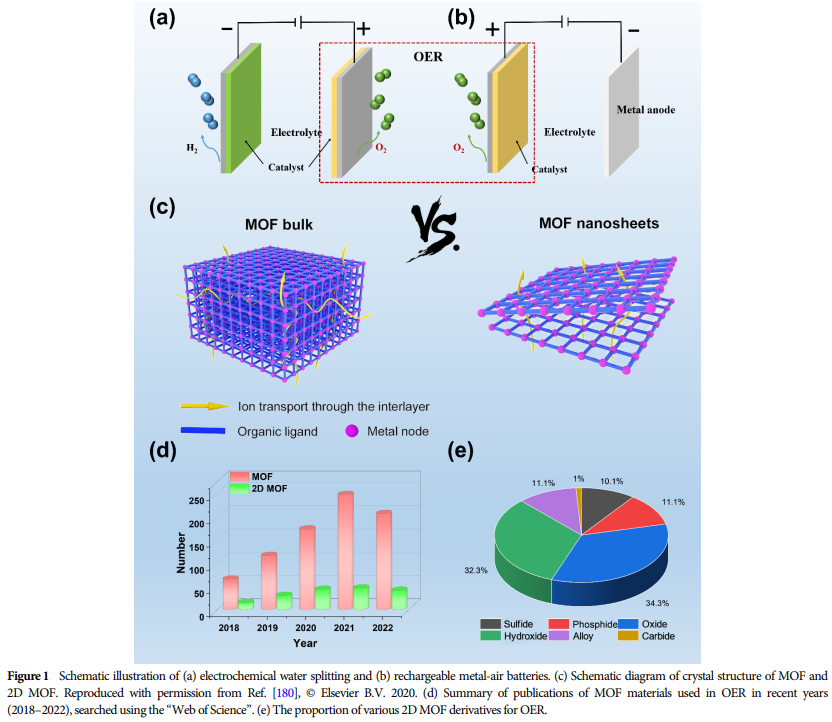
Advantages of 2D MOFs: They have abundant coordinatively unsaturated metal nodes, large specific surface area, and tunable structures, making them a new class of efficient OER electrocatalysts.
02 Reaction Mechanism of OER
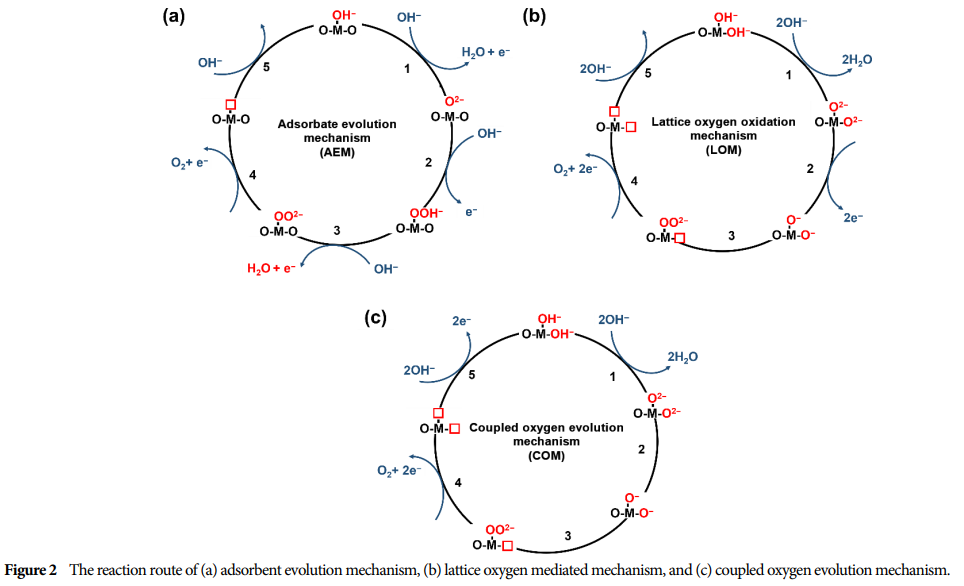
Traditional Mechanism: Includes the Adsorption Evolution Mechanism (AEM) and Lattice Oxygen Mediated Mechanism (LOM).
New Mechanism: Xi et al. proposed a coupled oxygen evolution mechanism.
03 Evaluation Parameters of OER
Overpotential (η): Ideally, OER requires a voltage of 1.23 V to proceed, but due to inherent kinetic barriers, additional potential is needed in practice to initiate the reaction.
Other Parameters: Literature may also involve other parameters used to evaluate OER catalyst performance, such as current density, Tafel slope, etc. (specific data not explicitly mentioned in the abstract).
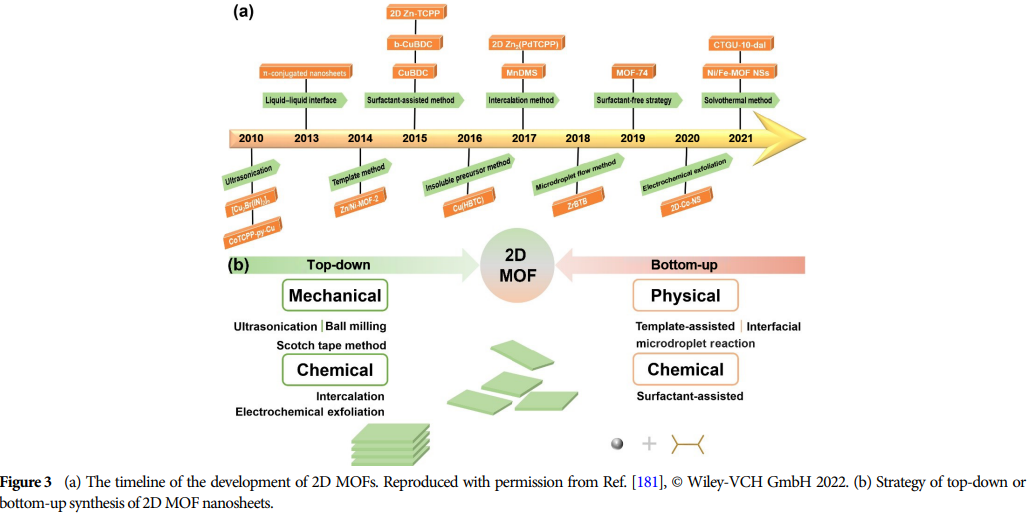
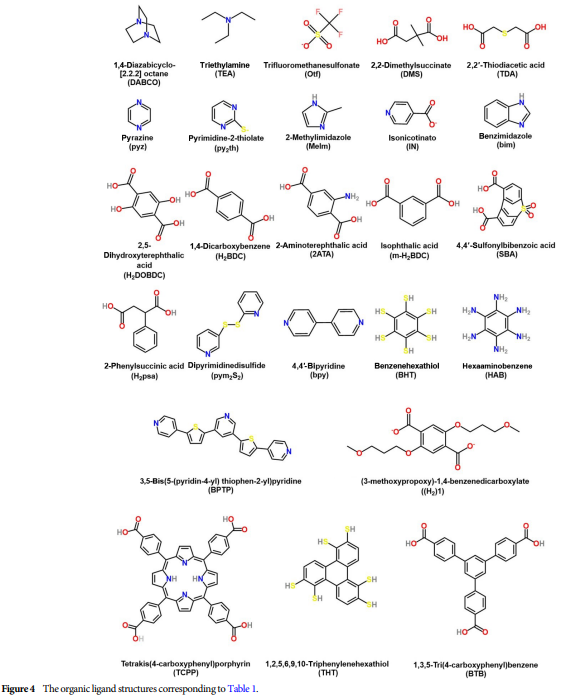
04 Synthesis Methods of 2D MOFs and Their Derivatives
Diverse Synthesis Strategies: Such as coordination modulation, liquid exfoliation, top-down fabrication, etc., used for synthesizing two-dimensional NiFe metal-organic frameworks.
Case Study: For example, synthesizing two-dimensional NiFe metal-organic frameworks through coordination modulation to enhance electrocatalytic water oxidation.
05 Characterization Techniques of 2D MOFs
Types of Techniques: Various characterization techniques mentioned in the literature are used to determine the structure and properties of 2D MOFs.
Purpose: To ensure that the synthesized 2D MOFs have the expected structure and performance, thus serving as effective OER electrocatalysts.

06 Applications of 2D MOFs in OER
Efficient Catalysts: 2D MOFs and their derivatives exhibit high performance as OER electrocatalysts.
Case Study: For example, two-dimensional ultrathin metal-organic framework nanosheets as high-performance oxygen evolution catalysts, and enhancing oxygen evolution reaction performance in two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks by incorporating bimetallic electrocatalysts.
07 Modification of 2D MOFs
Modification Methods: Modifying 2D MOFs by introducing other elements or compounds to improve their OER performance.
Effects: Modified 2D MOFs demonstrate higher activity, stability, and selectivity in OER.
08 Illustrated Guide

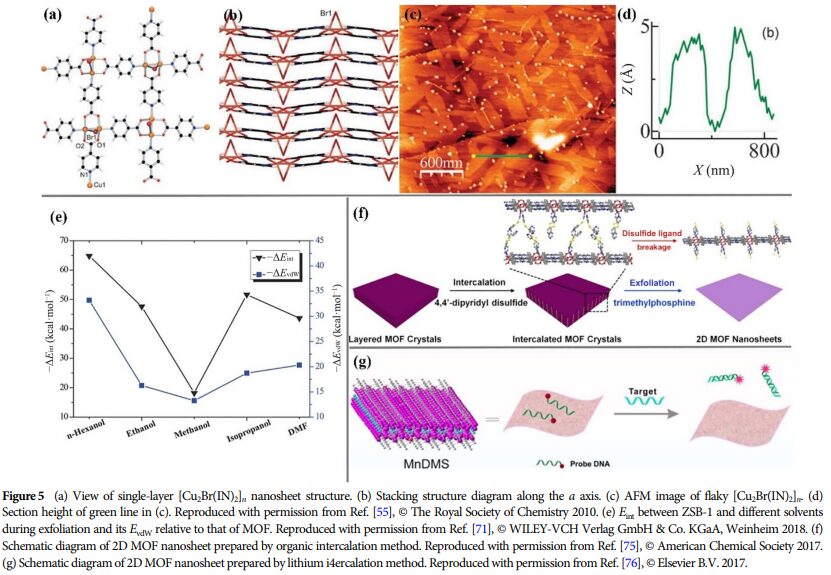
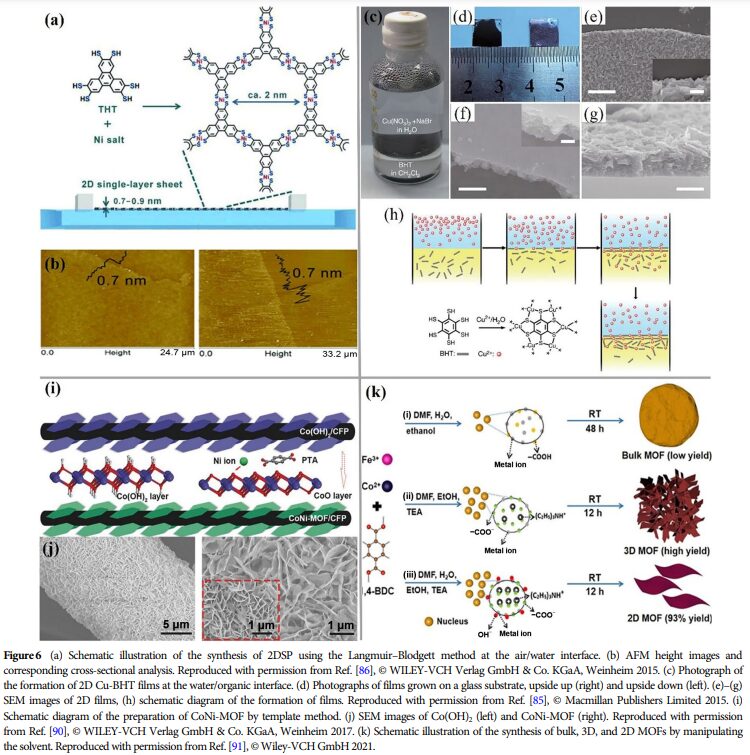
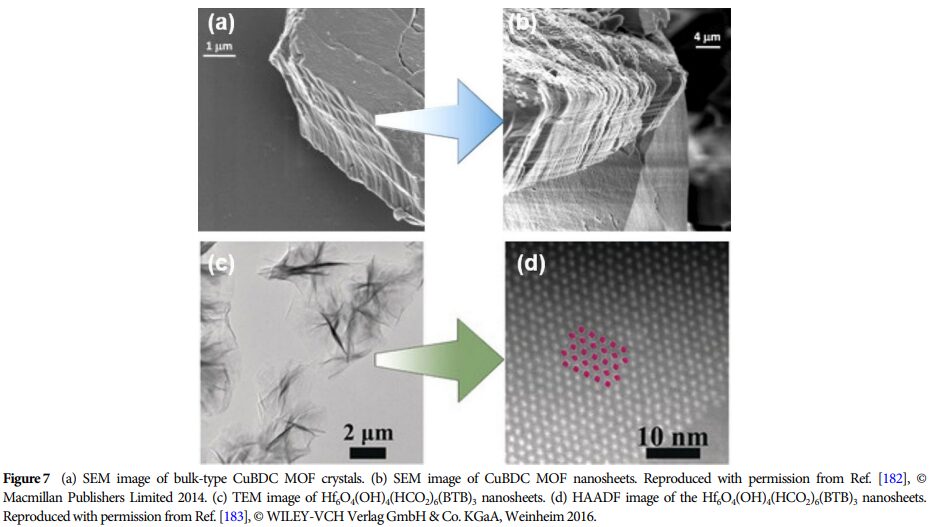
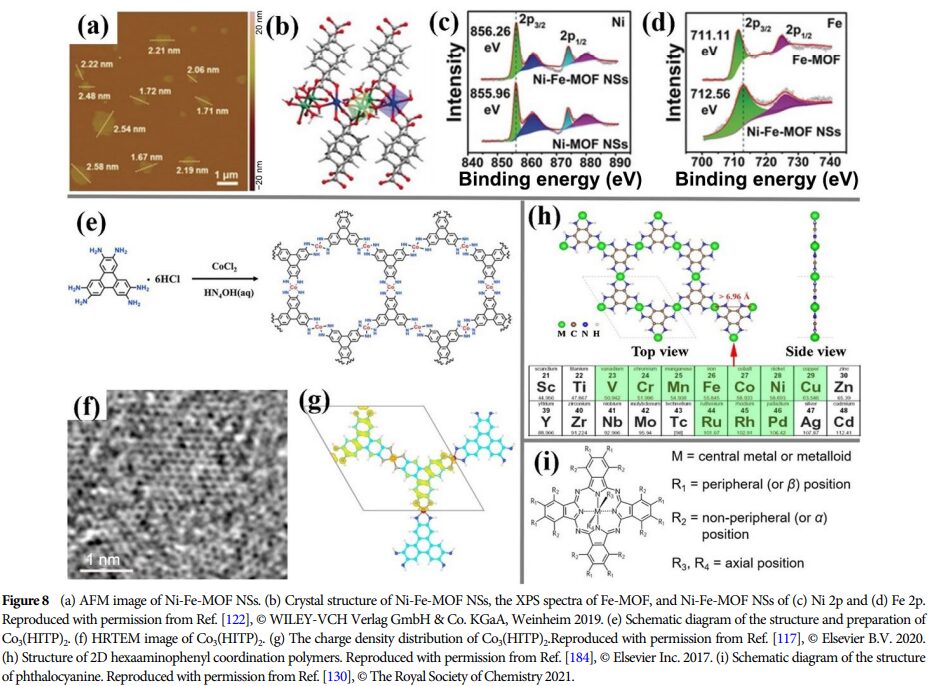

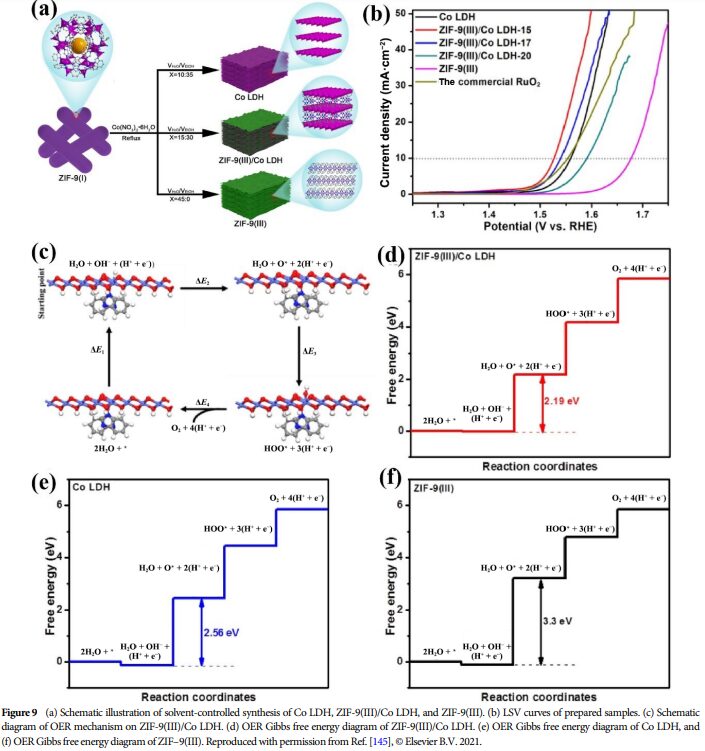
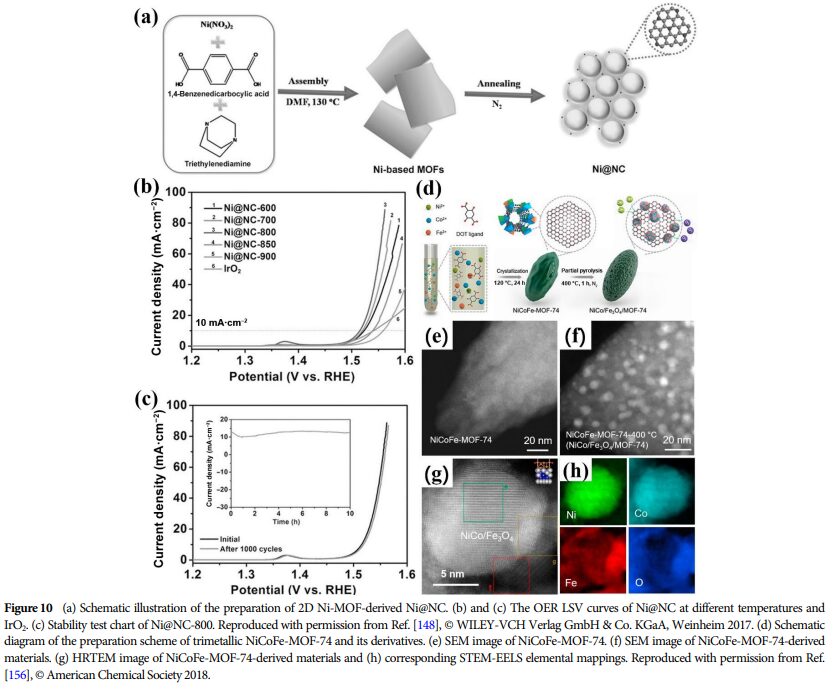
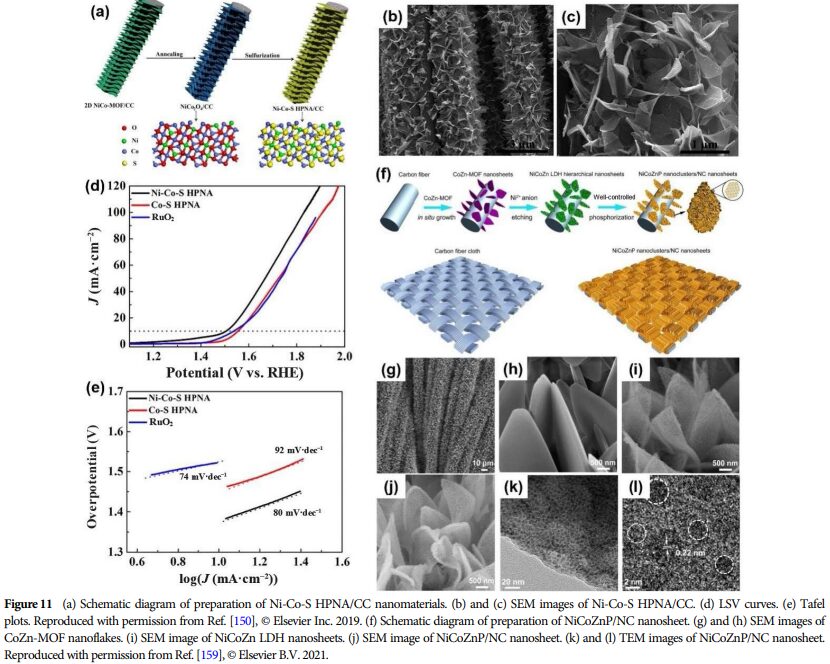
09 Future Outlook
Research Direction: Continue exploring new synthesis methods, characterization techniques, and modification strategies to improve the performance of 2D MOFs as OER electrocatalysts.
Application Prospects: 2D MOFs have broad application prospects in water splitting, metal-air batteries, and other related fields.
10 Conclusion
-
This article comprehensively reviews the latest advances of two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks (2D MOFs) in the oxygen evolution reaction (OER).
-
From reaction mechanisms, evaluation parameters, synthesis methods, characterization techniques to specific applications and modification strategies, this article elaborates on the advantages and challenges of 2D MOFs as OER electrocatalysts.
-
In the future, as research continues to deepen, the application prospects of 2D MOFs in OER will be even broader.
