The development path of the Internet of Things (IoT) is connection – perception – intelligence. Currently, we are in the first stage of IoT development, which is characterized by the rapid growth of IoT connections. By 2018, the number of global IoT connections is expected to exceed the number of mobile phone connections.
First Stage of IoT Development:This stage marks the large-scale establishment of IoT connections. More and more devices are being connected to the network through communication modules using mobile networks (LPWA, GSM, 3G, LTE, 5G, etc.), WiFi, Bluetooth, RFID, ZigBee, and other connection technologies. In this stage, the construction, management, and intelligence of network infrastructure and connections are core. Ericsson predicts that by 2021, the number of global mobile connections will reach 27.5 billion, of which IoT connections will reach 15.7 billion, and mobile phone connections will be 8.6 billion. Areas such as smart manufacturing, smart logistics, smart security, smart power, smart transportation, vehicle networking, smart homes, wearable devices, and smart healthcare will see exponential growth in connections. The largest investment opportunities in this stage mainly lie in network infrastructure construction, communication chips and modules, various sensors, connection management platforms, and measuring instruments.
Second Stage of IoT Development:In this stage, the status of devices connected to the network is perceived, generating a massive amount of data and forming IoT big data. Sensors, meters, and other devices become further intelligent, and diverse data is perceived and collected, aggregated to a cloud platform for storage, classification, processing, and analysis. At this point, IoT becomes one of the largest businesses on cloud computing platforms. According to IDC’s forecast, by 2020, the total amount of global data will exceed 40ZB (equivalent to 40 trillion GB), which will be 22 times the amount in 2012, with a compound annual growth rate of 48%. In this stage, cloud computing will rapidly develop alongside IoT. Major investment opportunities in this stage lie in AEP platforms, cloud storage, cloud computing, and data analysis.
Third Stage of IoT Development:Initial artificial intelligence has been realized, and intelligent analysis of data generated by IoT will demonstrate its core value in IoT industry applications and services. Gartner predicts that by 2020, the output value of IoT applications and services will reach $262 billion, surpassing the market size of the IoT infrastructure sector by four times. In this stage, IoT data achieves maximum value as enterprises analyze sensor data and use the results to build solutions for commercial monetization, while operators benefit from a large amount of user data, significantly improving their revenue through data monetization. Major investor opportunities in this stage lie in IoT solution providers, artificial intelligence, and machine learning vendors.
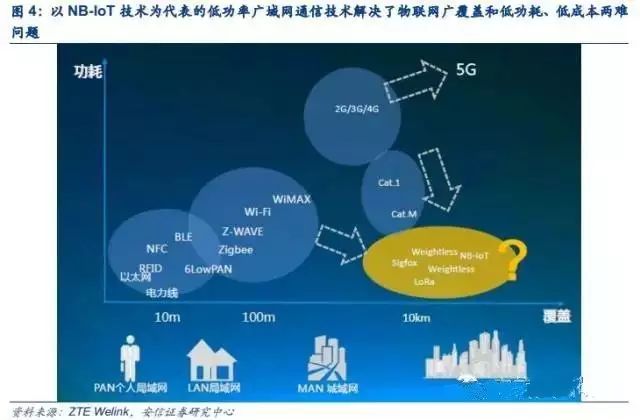
Before the emergence of LPWA communication technology, achieving wide coverage and low power/low cost in IoT connections was challenging, leading to slow growth in IoT connections. The foundation for the interconnection of all things is the use of communication technology to connect people to things and things to things. Currently, communication technologies applied to IoT include short-range wireless communication technologies like WiFi, RFID, Bluetooth, ZigBee, and long-distance mobile cellular communication technologies like GSM, 3G, 4G/LTE.
Short-range communication technologies, while having low deployment costs, low power consumption, and high transmission rates, can only meet local area network communication scenarios and are generally used in smart homes, industrial data collection, and automated office settings. GSM/3G/4G cellular communication technologies were primarily designed for communication between people; although they cover wide distances, they have disadvantages such as high power consumption and high deployment costs. Therefore, currently, only 6% of the total number of connections globally is carried on mobile cellular networks.
The majority of terminals still rely on short-range communication technologies like WiFi and Bluetooth. The relatively low proportion of operator network connections is mainly due to the insufficient carrying capacity of mobile networks (single sectors cannot support large numbers of terminal connections, and considerations of power consumption and cost). To solve the dilemma of wide coverage and low cost/low power, communication technology specifically designed for IoT connections, LPWA (Low Power Wide Area), was born, which has also driven the rapid growth of IoT connections.
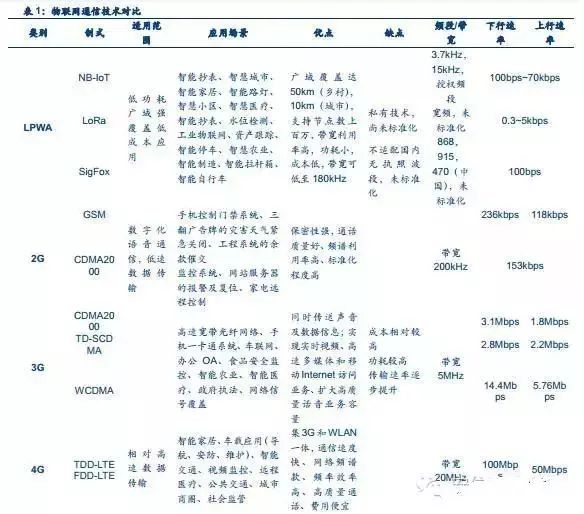
The industry chain jointly promotes, with NB-IoT as a representative, LPWAN technology leading to rapid growth in connections
LPWA connection technology, represented by NB-IoT, has solved the barriers to the popularization of mobile IoT. After large-scale deployment of LPWA, it will promote rapid growth in IoT connections. Compared to traditional short-range communication technologies and existing cellular communication technologies, LPWA represented by NB-IoT has four significant advantages, making it very suitable for IoT application scenarios that require long-distance data transmission, low communication data volume, and long battery life. For example, the four advantages of NB-IoT are:
(1) Wide coverage: NB-IoT coverage is 20dB better than traditional GSM networks. In terms of coverage area, a single base station can provide 10 times the area coverage;
(2) Massive connections: Under a frequency of 200KHz, a single base station can provide 100,000 connections using NB-IoT;
(3) Low power consumption: NB-IoT communication modules can operate independently for ten years without needing to recharge;
(4) Low cost: The cost of an NB-IoT module is less than $5. Additionally, NB-IoT is based on cellular networks and can be directly deployed on existing GSM, UMTS, or LTE networks, resulting in lower deployment costs for operators and enabling a smooth upgrade to 4.5G.
LPWA communication technology is particularly suited for two types of IoT applications: one is fixed-location, relatively concentrated scenarios, such as smart water meters in buildings, warehouse management, or other device data collection systems. Although cellular networks have been applied in these areas, signal penetration has always been a shortcoming; the other type is long-distance applications that require battery power, such as smart parking, asset tracking, and geological and hydrological monitoring. In the future, the number of connections to the IoT through LPWA connection technology is expected to exceed 50% of the total number of connections. GSMA predicts that by 2020, the number of connections in China’s machine-to-machine (M2M) market will reach 1 billion, with LPWA technology represented by NB-IoT providing 730 million connections.
IoT will become a fundamental business for operators. At the end of 2016, Huawei and the three major operators began large-scale deployment of NB-IoT IoT solutions. In the next two years, the growth rate of M2M connections in China will exceed 100%, marking the true high-speed development phase of the IoT industry. On June 30, 2016, Huawei announced the end-to-end NB-IoT solution, ranging from NB-IoT communication chips and base station equipment to connection management platforms, at the Shanghai IoT Summit. The new products were officially launched in September 2016, with large-scale commercial use expected to start by the end of December. China Unicom plans to launch NB-IoT outdoor scale network trials based on 900MHz and 1800MHz in more than five cities this year, with more than six business application demonstrations, including key areas like Shanghai Disneyland for trial use.
China Unicom plans to advance the commercial deployment of NB-IoT in key cities by the end of 2016 and early 2017, and will begin nationwide commercial deployment in 2018. China Mobile is reportedly also set to start the commercialization process in 2017. China Telecom signed an innovation research cooperation agreement with Huawei in June 2016 for NB-IoT. Meanwhile, major chip manufacturers globally, including Qualcomm, Intel, and Huawei, are launching NB-IoT layout plans, aiming to introduce NB-IoT chips and modules before 2017. Domestic operators plan to begin large-scale construction of low-power wide-area IoT in 2017, marking the true entry of the IoT industry into a high-speed development phase. It is expected that by 2017, the number of mobile IoT connections in China will increase from 140 million at the end of 2016 to 300 million, a year-on-year growth of 114%, significantly higher than the 50% connection growth rate in 2016.
In the next three years, global M2M IoT connections will grow rapidly, with China maintaining the largest number of IoT connections globally, greatly promoting the robust development of upper-layer applications in the domestic IoT sector. According to GSMA statistics, by the end of 2015, the number of IoT M2M connections in China had reached 74 million, accounting for 23.1% of the global IoT M2M connections, ranking first globally, far exceeding those in the United States and Europe. China has the largest population globally, and its manufacturing, transportation, and logistics industries are highly developed. As the demand for automation in China increases, so does the demand for smart manufacturing, smart logistics, smart retail, and smart communication, leading to continuous robust development of upper-layer application demands in China’s IoT sector, creating significant commercial value.
The future 5G will meet the diverse needs of advanced IoT applications, achieving ultimate interconnection of all things
In the future, LTE will evolve towards 5G from both high-speed and low-speed directions, coexisting with LPWA technology to meet the diverse needs of IoT applications and promote the robust development of upper-layer applications in the industry. In fact, there are low-speed technologies like LTE Cat.M and LTE Cat.1 within LTE networks that will coexist with NB-IoT, providing communication support in low-speed, low-cost areas of IoT and meeting the needs of different niche markets. Compared to NB-IoT, LTE Cat.M is better compatible with GSM networks and easier to replace GSM applications, offering advantages in certain niche fields. Complex upper-layer applications like autonomous driving, VR, and remote surgery require high bandwidth, significant data transmission, and ultra-low latency, posing new demands on network technology that can only be met through large-scale deployment of 5G.
5G provides better performance than 4G, supporting user experience rates of 0.1 to 1Gbps, a connection density of one million connections per square kilometer, millisecond-level end-to-end latency, tens of Tbps traffic density per square kilometer, mobility over 500Km/h, and peak rates of tens of Gbps. In the future, LTE cellular technology will evolve towards 5G from both low-speed and high-speed directions, coexisting with LPWA technology to achieve continuous wide-area coverage, high-capacity hotspots, low-power large connections, and low-latency high reliability requirements for upper-layer applications, thus realizing the ultimate interconnection of all things in the 5G era.
Future IoT applications will derive diverse applications around government, enterprises, and consumers, creating significant social value. The service targets of IoT can be divided into three categories: government, enterprises, and consumers.
Government IoT applications include public resource/energy management, intelligent transportation, safe city initiatives, smart governance, and smart agriculture. Comparing the IoT application demands of governments in recent years in China, the US, and Europe, the primary goal is to solve increasingly tense energy consumption, pollution, and urban safety issues. Therefore, future applications related to urban life, such as intelligent transportation, smart metering, and smart street lighting, will be the first areas to realize IoT applications. For example, in Sweden’s smart transportation solutions, after equipping vehicles with electronic license plates and connecting them to a traffic big data platform, intelligent traffic management and congestion fee collection were implemented, reducing traffic congestion by 20-25%, decreasing traffic queue time by 30-50%, and reducing traffic emissions in central urban areas by 14%, with total emissions in the Stockholm area decreasing by 2.5% and greenhouse gas emissions like CO2 dropping by 40%.
Enterprise IoT applications include comprehensive upgrades to Industry 4.0 (remote management of equipment, data management, automation, etc.), smart logistics, and using machine learning and artificial intelligence to predict and solve business problems. More and more enterprises are connecting their devices to the cloud for unified management and seeking to improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and increase sales from production manufacturing, logistics, sales, and after-sales data. In 2012, due to GE’s successful remote diagnostics, Spring Airlines saved over $210,000 in maintenance costs and avoided several unscheduled engine disassemblies and downtimes.Wind turbine manufacturer Vestas improved the layout of wind turbines by cross-analyzing weather data and customer turbine instrument data, thereby increasing the power output of wind turbines and extending their service life. In the future, the transition from equipment management and data analysis to machine cognitive learning to help solve problems is expected. For example, AbleCloud achieved a 30% energy saving by training a water dispenser to automatically heat, insulate, and power off after three months of machine learning.
In the consumer sector, vehicle networking, wearable devices, smart homes, and complex entertainment will become key application areas for IoT. Currently, vehicle networking mainly focuses on navigation, remote information collection, and vehicle system upgrades. In the future, with the popularization of vehicle entertainment systems, ADAS, and autonomous driving, integrated management of vehicle smart hardware is expected to be realized. In smart communities and smart home fields, safe communities and safe homes are expected to achieve breakthroughs first. The original community video surveillance system will be expanded into an IoT platform that combines community and home sensors, wearable devices, and community entrance management systems, providing infrastructure solutions for modern community management and intelligent big data applications. In the event of illegal intrusion, fire, gas leaks, and other anomalies, smart sensors will send out alarms and notify security personnel through the community property management center, alarm center, and residents’ mobile phones to ensure timely arrival at the scene for handling. Residents can also remotely monitor and visually communicate through mobile devices like smartphones and tablets.
The IoT platform connects the upper and lower tiers, acting as the key lever for the IoT ecosystem
The IoT platform acts as the hub of the IoT industry chain
The technical system of IoT mainly includes four levels: perception and control layer, network layer, platform service layer, and application service layer. The IoT platform is the hub of the IoT industry chain, connecting the dispersed IoT sensing layer below, aggregating sensing data, and providing a foundational platform for application developers and a unified data interface for the underlying network. It supports specific IoT applications based on sensing data. Currently, IoT platforms can be deployed on private clouds of enterprises and public clouds of IoT vendors.
Perception and Control Layer:This layer obtains environmental, asset, or operational status information from sensors, meters, and other devices, processes it appropriately, and transmits the data through sensor transmission gateways. Simultaneously, it receives control command information through sensor receiving gateways and transmits it locally to control devices, achieving the purpose of controlling assets, devices, and operations. In this layer, the management of perception and control devices, transmission and reception gateways, and local data and signal processing are important technical areas.
Communication Network Layer:This layer transmits information, data, and instructions between the perception control layer and the platform and application layers through public or private networks using wireless or wired communication methods. It is mainly composed of various wide-area IP communication networks provided by operators, including ATM, xDSL, fiber optics, and mobile communication networks such as GPRS, 3G, 4G, and NB-IoT.
Platform Service Layer:The IoT platform is a key link in the IoT network architecture and industry chain. It not only achieves integrated management of terminal devices and assets but also connects to the perception layer below and provides application development capabilities and unified interfaces to application service providers above. It offers common service capabilities to various industries, such as data routing, data processing and mining, simulation and optimization, business process and application integration, communication management, application development, and device maintenance services.
Application Service Layer:Diverse applications are the ultimate goal of IoT. In the future, based on government, enterprise, and consumer categories, diverse IoT applications will be derived, creating significant social value. According to business needs, relevant IoT applications will be established on top of the platform service layer, for example: analysis and prediction of urban traffic conditions; monitoring and analysis of urban asset statuses; environmental monitoring, analysis, and early warning (e.g., wind, rainfall, landslides); health status monitoring and medical plan recommendations, etc.
The IoT platform is the core of the overall IoT solution. More and more cloud computing vendors and IoT solution providers are acquiring IoT platform vendors to include them in their ecosystems to form end-to-end IoT solutions. Due to the pivotal role of the IoT platform, it provides important functions such as device management, network connection management, application development, data services, intelligent analysis, and interconnection with third-party systems. At the same time, the IoT platform connects underlying devices, enterprise business needs, application developers, and other IT systems within the enterprise (CRM, ERP, etc.), making it the core of the entire IoT solution.
Major IoT solution providers are also increasingly focusing on IoT platform business, most of which have acquired IoT platform capabilities through external mergers and acquisitions. This is also the reason for the accelerated mergers and acquisitions in the IoT platform field in recent years. Representative companies include Cisco, Ericsson, PTC, Bosch, Sierra Wireless, and LogMeIn. Cloud computing vendors choose to build a strong IoT platform ecosystem through extensive cooperation, with representative companies like IBM, AWS, and Microsoft collaborating with mainstream IoT platform providers.
Introduction to IoT Platform Functional Classification
IoT platforms provide four major functions in a logical relationship from the lower layer to the upper layer: Device Management (DMP), Connectivity Management (CMP), Application Enablement (AEP), and Business Analytics (BAP). Therefore, IoT platforms can be divided into four major types from bottom to top: Device Management Platform (DMP), Connectivity Management Platform (CMP), Application Enablement Platform (AEP), and Business Analytics Platform (BAP). So far, no platform company has been able to provide end-to-end services from terminal management monitoring, connection management to application development and data analysis. Each platform provider has its own focused field and unique advantages.
1) Device Management Platform (DMP):DMP platforms perform remote monitoring, configuration adjustment, software upgrades, system upgrades, fault diagnosis, and lifecycle management of IoT terminals. They can also provide real-time monitoring alerts for gateway and application statuses, supporting preemptive fault handling and improving customer service satisfaction. Open API interfaces can help customers easily integrate systems and develop value-added functions; all device data can be stored in the cloud.
Generally, DMP platforms are integrated into the entire end-to-end M2M device management solution. Solution providers work with partners to provide communication gateways, communication modules, sensors, device management cloud platforms (DMP), device connection software, and open interfaces for upper-layer application developers, offering end-to-end solutions. Manufacturers like Bosch, familiar with enterprise business processes, can also integrate enterprise business applications like CRM, ERP, and MES into the DMP, forming a more comprehensive device management solution.
The majority of DMP platform providers are also communication module and device suppliers, such as DiGi, Sierra Wireless, and Bosch, which possess products like connected devices, communication modules, gateways, and device management platforms, thus enabling them to help enterprises achieve comprehensive device management solutions. DMP is generally deployed as part of the entire device management solution, with overall pricing; there are also a few vendors that provide standalone cloud-based device management services, charging a certain operational management fee for each device per month.
2) Connectivity Management Platform (CMP):CMP platforms are typically used on operator networks to manage IoT connection configurations and fault management, ensuring stable terminal connection channels, managing network resource usage, connection fee management, billing management, plan changes, and number/IP address/Mac resource management, better helping mobile operators manage IoT SIMs. M2M IoT applications have several characteristics for mobile operators: large numbers of M2M connections, high SIM card usage, significant management workload, complex application scenarios, and a demand for flexible pricing plans, low ARPU values, and high cost management requirements.
Through CMP platforms, operators can comprehensively monitor the communication connection status, service activation, and subscription of IoT terminals; they can check the data usage and balance of their IoT terminals; they can self-diagnose and repair some faults. Meanwhile, the IoT connection management platform can push corresponding alert information based on user configurations, allowing customers to flexibly control their terminal’s data usage, status changes, etc.
CMP connection management platforms are connected to mobile operator networks, helping operators manage M2M IoT. CMP platform suppliers participate in the revenue sharing of the operator’s IoT mobile income. Using mobile networks (2G/3G/4G/NB-IoT), it is necessary to reasonably control data usage, split billing for multiple users, and dynamically monitor usage status and costs in real time. This makes CMP platforms collaborate with mobile operators, participating in the operator’s mobile income sharing, with a straightforward business model. Considering that multinational corporations prefer a single point of access for global use when connecting with CMP platforms, global CMP platforms are more competitive in serving large enterprises.
Currently, there are three major camps of CMP globally: Jasper platform, Ericsson DCP platform, and Vodafone GDSP platform. Jasper, as a leader in CMP, collaborates with over 100 operators and 3,500 enterprise customers globally, while Ericsson DCP and Vodafone GDSP platforms have fewer customers compared to Jasper. The CMP platforms of China’s three major operators include partnerships between China Unicom and Jasper, adopting a revenue-sharing model; China Mobile and Huawei collaborating on CMP, M2M modules, and terminal sales; and China Telecom recently signing a memorandum of understanding with Ericsson DCP for collaboration in CMP and terminal sales.
3) Application Enablement Platform (AEP):AEP platforms provide application development and unified data storage as two major functions of PaaS, built on top of CMP platforms. Specifically, AEP platforms offer a complete set of application development tools (most provide graphical development tools, even without requiring developers to write code), middleware, data storage capabilities, business logic engines, and APIs for integrating third-party systems. IoT application developers can rapidly develop, deploy, and manage applications on AEP platforms without worrying about underlying infrastructure expansion, data management and aggregation, communication protocols, and communication security issues, thereby reducing development costs and significantly shortening development time. Currently, world-renowned AEP platforms are gradually enriching their functions, adding features like terminal management, connection management, data analysis applications, and business support applications.
AEP platforms help enterprises significantly save time and costs in IoT application development. According to Aeris, developers using AEP platforms can save 70% of their time, allowing applications to reach the market faster while saving costs associated with hiring underlying infrastructure technical personnel. Another major issue solved by AEP platforms is the flexibility of upper-layer application expansion. Even as the scale of M2M management increases rapidly, using AEP platforms does not require concern about the underlying resources keeping pace with the expansion speed of connection devices.
4) Business Analytics Platform (BAP):The Business Analytics Platform includes fundamental big data analysis services and machine learning capabilities. Big data services: The platform classifies, processes, and visualizes various related data after aggregation, providing visualized data analysis results (charts, dashboards, data reports); through real-time dynamic analysis, it monitors device status and issues alerts.
The platform’s machine learning: By training historical data (both structured and unstructured), it generates predictive models, or customers can develop models themselves using tools provided by the platform, meeting predictive, cognitive, or complex analytical business logic. In the future, machine learning on IoT platforms will transition towards artificial intelligence, such as IBM Watson, which possesses IBM’s unique DeepQA system, combining neural systems to simulate the brain’s thinking process to summarize a progressively powerful question-and-answer system, which will help enterprises solve more business problems.
Currently, machine learning charges two fees: modeling fees and prediction fees. During the modeling phase, fees are charged based on the time spent on data analysis, model training, and evaluation, calculated based on the computing hours required for executing these operations; after modeling is complete, fees are charged based on the amount of information in the data results or the memory capacity required for calculations and predictions.
China’s IoT platforms are in the early stages of development, with enormous market potential
Current State of IoT Platform Development in China
As a key link in the IoT industry chain, IoT platforms play an important role. In the future, the AEP market will exceed that of CMP and DMP. According to Nokia’s prediction, by 2025, the total value of the entire IoT industry will reach 400 billion euros, with the IoT platform market accounting for 12.5% of the overall IoT market, meaning that the combined market of DMP, CMP, and AEP platforms will exceed 50 billion euros. According to First Analysis, by 2024, the AEP platform market share will reach 53% of the total market of the three platform types.
If CMP platform providers need to collaborate with operators and cloud computing vendors to jointly provide connection services and obtain more revenue-sharing income, for example, Jasper collaborates with operators and cloud computing vendors like AWS and Microsoft globally; the key to AEP vendors winning lies in providing an open platform and operating system, establishing a large application development community, making application development convenient, and launching their own cross-industry generic applications to accumulate more customers and connections. Due to the close integration of AEP platforms with upper-layer applications, as applications become more complex in the future, the service fees collected from each device by AEP platforms will gradually increase, enhancing the overall platform value.
Major IoT platform providers in China can be roughly divided into operators, cloud computing vendors, internet giants, and startups. Currently, the IoT cloud platform functions provided are relatively simple, and the ecosystem is still in need of improvement, with a certain gap compared to foreign IoT vendors. Since the operation of IoT platforms, ecosystem cultivation, and developer aggregation require a long time to accumulate, in the future, if traditional internet and IT companies want to enter the IoT platform field, acquiring excellent overseas and domestic startups or conducting in-depth industry chain collaborations will be a good choice.
(1) BAT and JD.com layout IoT platforms based on their traditional advantages, including cloud, big data, hardware management platforms, etc., creating third-party ecosystems while leveraging their strengths. The IoT business strategies of major internet companies are similar, with hardware networking as a foundational step, opening up data and ecosystems, technologies, and interfaces to build a collaborative ecosystem in the industry chain. Tencent has two major IoT platforms: QQ IoT and WeChat smart hardware, where its huge user base and social attributes are core advantages. On the WeChat platform, device manufacturers can open WeChat public accounts, connecting users with their smart devices through device function plugins within the public accounts, where each device will also have a WeChat ID. Meanwhile, device manufacturers can establish WeChat stores on public accounts to regularly provide purchase services for accessories and consumables based on device operating conditions.
Alibaba has integrated smart cloud, Taobao crowdfunding, and Tmall electrical city for its IoT business, forming a smart life division, helping smart hardware developers solve market sales challenges. Baidu’s advantage lies in its long-term accumulation in artificial intelligence, voice recognition, and deep learning technologies. In the future, the massive data generated on its IoT platform can be processed using Baidu’s deep learning and artificial intelligence capabilities to develop powerful upper-layer applications, potentially surpassing Tencent and Alibaba in machine learning and big data processing.
(2) The three major operators in China are highly focused on the development of IoT connection management platforms (CMP) and are collaborating with leading domestic and foreign platform companies to provide enterprise customers with one-stop global IoT connection services. In July 2015, Jasper and China Unicom launched the ControlCenter IoT management platform, which integrates seven major functions: API integration capabilities, lifecycle management, flexible pricing plans, device listing functions, network diagnostics, automated engines, and billing and reporting functions.In November 2014, China Mobile officially released the IoT open platform – OneNet, providing a complete set of solutions from underlying IaaS connections to upper-layer applications, establishing partnerships with numerous industry manufacturers.
On July 15, 2016, China Telecom signed a memorandum of understanding with Ericsson for cooperation in IoT connection management, jointly building global IoT connections to provide one-stop global IoT connection services for enterprise customers. As of May 2016, the number of IoT connections for China Mobile exceeded 60 million, with a target of reaching 100 million by the end of 2016; China Unicom’s IoT connections reached 13 million, with a goal of achieving 30 million IoT connections in 2016. China Telecom has not yet disclosed its IoT connection numbers, with a target of netting an additional 12 million IoT users in 2016 and achieving sales of 10 million IoT terminals.
(3) IoT platform startups are continuously setting financing records and are likely to emerge as unicorn companies. On June 29, 2016, Ayla Networks announced it raised $39 million in Series C financing; on August 31, 2015, JiZhi Cloud (Smart Cloud) secured 200 million RMB in Series B financing. The continuous financing record set by IoT platform startups reflects the opportunities recognized by major IT giants and investment institutions due to the rapid development of IoT.
Domestic IoT platform companies focus mainly on device management platforms and application enablement platforms, aiming to solve the difficulties faced by smart hardware manufacturers in application software development, high R&D costs, long development times, and lengthy sales cycles, helping other smart hardware manufacturers improve their survival capabilities. Domestic companies like JiZhi Cloud, Shanghai Qingke, and Ayla Networks (China branch) are among the leading startups, with a growing number of developers and partners forming a certain scale. In the future, with their deep exploration of traditional industries, integration of upstream and downstream resources in the industry chain, and continuous accumulation in the IoT field, they are likely to emerge as unicorn platform companies.
China’s AEP platforms are in the early stages, with enormous market potential
As the foundational platform for IoT application development, AEP platforms in China are still in their infancy, with the future market reaching hundreds of billions. According to GSMA forecasts, by 2020, the number of M2M connections in China (i.e., devices connected through cellular networks, satellite networks, and other LPWA technologies) will reach 1 billion. Assuming an average charge of 5 RMB per connection per month, the value of China’s AEP platform in 2020 will be at least 60 billion RMB. If we include other non-M2M IoT connections (which are three times the number of M2M connections), the total value of the AEP management platform will exceed 100 billion RMB.
Compared to foreign vendors, China’s IoT application development platforms started later and are still in the early stages of development. In the future, from the perspective of listed companies, acquiring domestic and foreign IoT AEP platform companies or conducting in-depth collaborations with excellent domestic and foreign IoT AEP platform companies will be the fastest and most realistic development path. Currently, some of the more outstanding IoT AEP platform companies in China include JiZhi Cloud, Shanghai Qingke, China Mobile’s OneNet, and Ayla Networks in China.
JiZhi Cloud is currently one of the largest smart hardware clusters in the country, gathering over 30,000 developers and researching over 30,000 smart hardware projects, with a decade of deep technological accumulation. Established over ten years ago, JiZhi Cloud provides developers with smart hardware PaaS and SaaS cloud services, including basic access services (intelligent development tools, M2M access, data storage and analysis, third-party data integration, OTA firmware upgrades, and cloud access services), post-access services (providing intelligent device access systems GDCS, intelligent device management systems GDMS, IoT time-sharing leasing platforms that can interface with mainstream ERP and CRM systems), and developer services (providing self-service development tools and technical support for smart hardware).
JiZhi Cloud has numerous partners throughout the entire industry chain and has proactively connected with over 70 mainstream chip and module manufacturers. Its future goal is to establish joint laboratories with domestic and foreign research institutions to study artificial intelligence, machine learning, and other technologies, laying a technical foundation for in-depth analysis of upper-layer applications in the future.
Shanghai Qingke collaborates with Alibaba to become a one-stop smart hardware solution provider, leading in the layout of industrial IoT and operating systems. Shanghai Qingke (MXCHIP) offers a comprehensive IoT solution that integrates device side, mobile side, and cloud side. Its core technologies, products, and services include the IoT operating system MiCO, wireless modules based on MiCO, mobile application (App) development, and cloud services across four domains. In July 2014, Shanghai Qingke and Alibaba Smart Cloud launched MiCO IoTOS, the first truly IoT operating system in China, designed for smart hardware, running on microcontrollers, and is a highly portable operating system and middleware development platform that reduces smart hardware development costs and improves development efficiency. It has been widely applied in smart appliances, lighting, healthcare, security, entertainment, and other IoT application markets.
The low power consumption, low cost, and security of the MiCO operating system are its greatest advantages, with over a million smart products successfully running on it. In April 2016, at the Alibaba Cloud Summit, a one-stop industrial IoT solution based on MiCO was released, enabling real-time feedback and diagnosis of equipment performance through precise data collection and analysis, allowing for intelligent remote control in the cloud. The valuable on-site experience and fault sample data will help industrial equipment manufacturers upgrade their products more effectively.
Ayla Networks has obvious global advantages and has achieved rapid breakthroughs in a short time after entering China. Established in 2010 and headquartered in Silicon Valley, California, Ayla Networks is a leading global IoT cloud platform (B2B/PaaS) service provider. It entered the Chinese IoT market in 2012 and has a branch in Shenzhen, being the only foreign enterprise with an ICP license.
The Ayla agile IoT platform consists of three main components: Ayla embedded modules, Ayla cloud services, and the Ayla application library. This is a complete solution that enables almost any device to connect to the cloud and App; it includes high-quality tools and services that allow manufacturers to manage, configure, and analyze devices. On the device side, Ayla collaborates with chip manufacturers like Qualcomm and Broadcom to embed connection control software in chips; on the cloud side, it connects with mobile applications, allowing consumers to directly control devices through the App, forming a closed-loop IoT system. At the same time, the Ayla platform integrates with various platforms, including Apple HomeKit, Google Thread, Tencent Open Platform, WeChat, and JD.com, helping enterprises share users with third-party platforms.
Ayla Networks, with its significant global advantages, has its own clouds in China, Europe, and the United States, capable of providing global cloud services and assisting Chinese appliance manufacturers in providing IoT services overseas. For instance, in May 2015, Ayla Networks signed a cooperation agreement with TCL Air Conditioning to initially collaborate in the US market, enabling American consumers to use the Ayla IoT platform to view and manage TCL smart air conditioners. At the same time, TCL can utilize the Ayla platform for data collection (user behavior analysis) and other intelligent analysis functions.
China Mobile’s OneNet aims to build a comprehensive IoT cloud from connection IaaS, application development PaaS, to upper-layer data analysis SaaS. The OneNet platform supports the rapid access of various sensors and smart hardware through adaptation to various networks and protocols while providing big data services. It also supports the development of various smart hardware and industry applications through APIs and application templates, reducing development and deployment costs for various IoT applications and meeting platform-level service needs in terms of device connection, protocol adaptation, data storage, data security, and big data analysis.
OneNet aims to save 70% of development time and costs for small and micro enterprises. As of May 2016, the number of registered users on OneNET exceeded 19,000, with over 2.3 million connected devices and more than 2,400 cooperating enterprises, including Qihoo 360, Huawei, Inspur, IBM, Intel, Sierra, Sinotrans, Jicheng Electronics, and San Chuan Water Meter.
Yitong Century: Improving the IoT platform layout, future expert in end-to-end IoT solutions
Yitong Century has accurately positioned itself in the IoT AEP platform layout, continuously improving the IoT platform architecture and providing more complete IoT solutions. In May 2016, Tianhe Hongcheng jointly established a subsidiary “Beijing Particle” to layout the IoT application enablement platform (AEP), continuously refining the large IoT application management platform layout. In the A-share company, following the CMP platform, it has perfectly positioned itself in the AEP platform layout, continuously enhancing its leading advantages in China.
In the future, AEP platforms will become the foundational platforms for IoT application development for enterprises, allowing the company to charge service fees based on the number of connected devices. Gradually, it will extract common needs from customer cases, develop cross-industry applications, profit from general applications, and accumulate more cross-industry customers. More importantly, the AEP platform is a key link in the overall IoT solution, enabling Yitong Century to integrate upstream and downstream resources in the industry chain, using its existing IoT platform to provide customers with complete IoT solutions from communication modules, device management, application development to system integration, thereby creating greater value.
More than 70% of the value in the IoT industry chain comes from the provision of IoT applications and end-to-end solutions. IoT solution providers will gain the most benefits in the industry chain, and Yitong Century will gradually transform into an end-to-end IoT solution provider. Since the end of 2015, Tianhe Hongcheng has begun providing end-to-end IoT solutions to customers, targeting the specific business characteristics of clients and providing a comprehensive structure across the perception layer, network layer, infrastructure layer, platform layer, and application layer. Through its independent sales channels and according to customer differentiation needs, it offers IoT industry system integration solutions that include basic IoT communication management, IoT application development, asset and hardware device management, data management, and more.
Currently, Tianhe Hongcheng has collaborated with chip, communication module, and sensor device suppliers, communication operators, cloud service providers, platform service providers, application developers, and other IoT industry chain service providers to build IoT systems at various levels for enterprises, providing demand research, solution design, construction installation, software development, personnel training, platform debugging, and subsequent technical services and operation and maintenance services to ultimately realize the implementation of IoT industry system integration solutions and the overall operation of customer IoT businesses.
Currently, Tianhe Hongcheng has collaborated with chip and communication module manufacturers to research IoT chips or communication modules with built-in platform software. Tianhe Hongcheng has signed cooperation agreements with companies such as Guangzhou Procter & Gamble Co., Ltd., Guizhou Gas Group Co., Ltd., Shanghai Yibest Information Technology Co., Ltd., Guangdong Kanglin Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Hangzhou Qundui Technology Co., Ltd., and Beijing Yaxin Data Co., Ltd., providing them with IoT industry system integration solutions.
Tianhe Hongcheng developed a drug integrated management platform for Guangzhou Kanglin Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., including a drug information-based security management platform, a drug safety comprehensive management platform, a drug public service platform, and a drug IoT application development platform. The drug IoT development platform is a model-based rapid development PaaS platform for internet applications. Compared to traditional development methods, it replaces traditional coding development with modeling development, allowing program developers to easily assemble new applications using existing modules, focusing their efforts on agile application construction rather than constantly troubleshooting code errors, thus significantly reducing program development time.
Introduction to Major Global IoT Platform Providers
Currently, the world’s major IoT platform providers have different focuses and advantages. By organizing the world’s leading IoT platform suppliers, we summarize the following development rules:
1) Establishing alliances between platforms and collaborating with integrators and upstream and downstream manufacturers is necessary to provide complete IoT solutions while continuously cultivating the IoT ecosystem. End-to-end IoT solutions are a massive and complex project, and the platforms can be divided into four major types. Almost no vendor can independently provide a complete solution from underlying connections to upper-layer application analysis, so extensive collaboration with other manufacturers in the industry chain is essential to cultivate the IoT ecosystem.
2) Open platforms attract more developers, continuously enhancing platform compatibility and the ability to connect with third-party systems and applications. AEP, DMP, and BAP platforms need to interface with numerous third-party systems and applications. By freely opening platform interfaces to community developers, enhancing platform connectivity and compatibility will continuously improve the platform’s scalability, attracting more customers.
3) Artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities will become the core competitiveness of business analytics platforms in the future. The ultimate goal of IoT is to optimize operations and processes, enhance efficiency, save costs, and increase revenue through data analysis, thereby improving business profitability. Therefore, after completing infrastructure construction, upper-layer intelligent analysis and machine learning capabilities will become the core competitiveness of business analytics platforms.
Introduction to DMP Leaders in Terminal Management Platforms
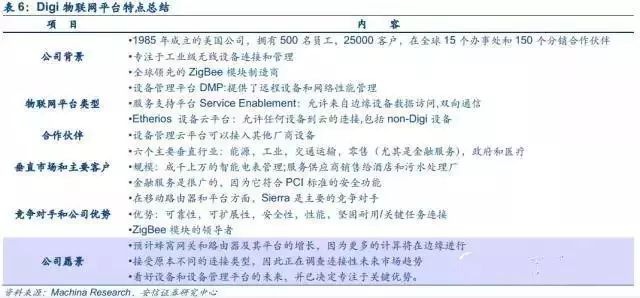
Digi and Nokia started early in the terminal management platform DMP and have formed powerful terminal management cloud platforms. Bosch later caught up, beginning in 2011 to develop its current IoT system and platform through external acquisitions. Due to its rich integration experience in industrial systems and partnerships with numerous global integrators, it has become a leader in device management IoT solutions. All three companies provide IoT connection devices, sensor products, and management cloud platform services, offering complete end-to-end solutions.
Digi’s cloud platform focuses on industrial 4.0 device management and is more compatible with other manufacturers. Nokia’s platform has a large user base and comprehensive functionality, providing customized applications for vertical industries such as vehicle networking, healthcare, and smart cities. Bosch currently has a strong alliance with Thingworx, where the Thingworx AEP platform can be directly built on Bosch’s device management and connection platform, providing a complete solution from device management to application development.
Bosch Software Innovations (BSI) is currently a leader in device management platforms. In addition to achieving the basic functions of device connectivity, it also provides various value-added services, such as security and integration with existing business systems (ERP, CRM, MES, etc.). In early 2016, PTC and Bosch announced a technical alliance to integrate the ThingWorx AEP platform and Bosch’s IoT suite, jointly offering IoT solutions to customers while allowing them to develop IoT applications for complex IT environments at low cost.
Digi, as an industrial M2M solution expert, combines industrial devices, modules, and cloud services to provide end-to-end solutions. Digi’s competitive advantage lies in offering complete solutions for industrial 4.0 IoT device management. On one hand, it provides embedded and non-embedded products such as enterprise cellular routers, gateways, wireless communication adapters (ZigBee, Wi-Fi, proprietary RF), serial servers, intelligent console servers, USB products, remote display products, cameras, sensors, and the globally best-selling serial card series. On the other hand, it offers a device management cloud platform.
Digi’s device management platform introduction: Digi merged Etherios with its existing iDigi device cloud to form the current Etherios device cloud platform. The functionalities provided by Etherios device cloud include: 1) Terminal configuration: Terminal configuration, software upgrades, and remote status monitoring through a web browser; 2) Device status alerts: Setting alert conditions, automatic alarms, and automatic firmware reboot settings; 3) Integrating data into third-party systems, such as Salesforce: Through the platform’s open API, device data can be pushed into any third-party application or build a custom M2M application. For example, using salesforce.com, the Salesforce AppExchange application seamlessly connects devices to the core business processes of the Salesforce platform, transforming raw data into actionable business information. 4) Security services: Providing data security value-added services.
(Source: Organized from the internet)
