Click on “The Voice of Waves” to make your voice heard



Smart Home
Opening a New Era of Intelligent Living
Smart home is, in short, a networked and intelligent home control system that integrates automation control systems, computer network systems, and network communication technologies. It uses the residence as a carrier to connect various devices in the home, such as lighting systems, electrical appliances, security systems, and environmental control devices, through certain technical means to achieve centralized management and remote control, creating an efficient, comfortable, safe, and convenient living environment for users.
The core of smart home is to provide more humanized services, making life easier and better. It can automatically adjust the operation status of home devices according to user habits and needs, for example, automatically turning on the air conditioning to adjust the room temperature before the user returns home, and automatically turning off lights and electrical devices after the user goes to sleep. At the same time, smart homes also have powerful security functions, capable of monitoring the safety status of the home in real-time and promptly alerting users in case of any abnormalities.
Working Principle

The smart home system mainly consists of four parts: sensors, controllers, actuators, and communication networks, with each part working together to achieve intelligent control of home devices.
Sensors
Sensors are the “perceptual organs” of the smart home system, responsible for real-time collection of various environmental information and device status information. Common sensors include temperature sensors, humidity sensors, light sensors, human infrared sensors, and door/window magnetic sensors. For example, a temperature sensor can monitor indoor temperature in real-time and relay information to the controller when the temperature is too high or too low.

Controller
The controller is the “brain” of the smart home system, receiving information from sensors and analyzing and processing it according to preset rules and algorithms, then issuing control commands to the actuators. The controller can be a dedicated smart gateway or an application installed on a smartphone or tablet. Users can remotely control and manage the smart home system through these terminal devices.

Actuator
The actuator is the “executive organ” of the smart home system, operating home devices according to commands from the controller. Common actuators include smart switches, smart sockets, smart curtain motors, and smart locks. For example, when the controller issues a command to turn off the lights, the smart switch will cut off the power and turn off the lights.

Communication Network
The communication network is the “nervous system” of the smart home system, responsible for connecting sensors, controllers, and actuators to achieve data transmission and sharing. Common communication networks include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, and Z-Wave. Different communication networks have different characteristics and applicable scenarios; for example, Wi-Fi is suitable for high-speed data transmission, Bluetooth is suitable for short-distance communication, and ZigBee and Z-Wave are suitable for low-power, large-scale device networking.

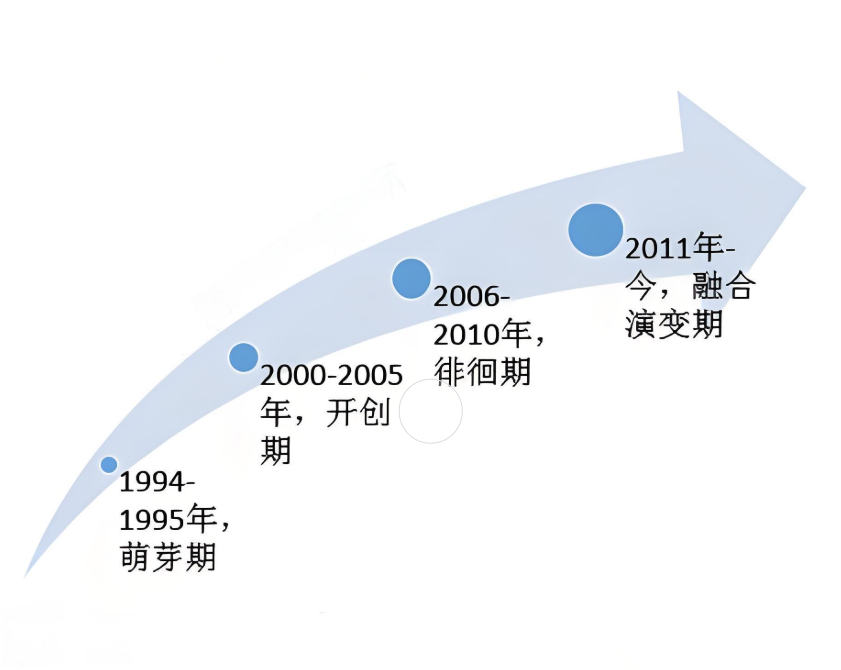
Development History


Initial Stage
1970s – 1990s
The concept of smart homes can be traced back to the 1970s when developed countries such as the United States and Europe began research and experimentation in home automation. During this period, smart home systems mainly focused on lighting control and appliance control, using simple switches and timers to control devices. Due to limited technology, these systems had relatively simple functions, were expensive, and had a very limited application range.

Development Stage
1990s – Early 21st Century
With the continuous development of computer technology, network technology, and communication technology, smart home technology gradually entered a development stage. During this period, smart home systems began to adopt computer control and network communication technology, achieving interconnectivity and remote control between devices. For example, users could remotely control lighting, appliances, and other devices in their homes via the internet. At the same time, the functions of smart home systems continued to enrich, adding security monitoring, environmental monitoring, and other features in addition to basic device control.

Popularization Stage
Early 21st Century – Present
Since the beginning of the 21st century, the rapid development of technologies such as the Internet of Things, big data, and artificial intelligence has provided strong support for the popularization of smart homes. During this period, the variety of smart home products has continued to increase, prices have gradually decreased, and user experience has greatly improved. Smart home products such as smart speakers, smart locks, and smart cameras have gradually entered thousands of households, becoming an indispensable part of people’s lives. At the same time, major technology companies have also begun to invest in the smart home field, promoting the rapid development of the smart home industry.

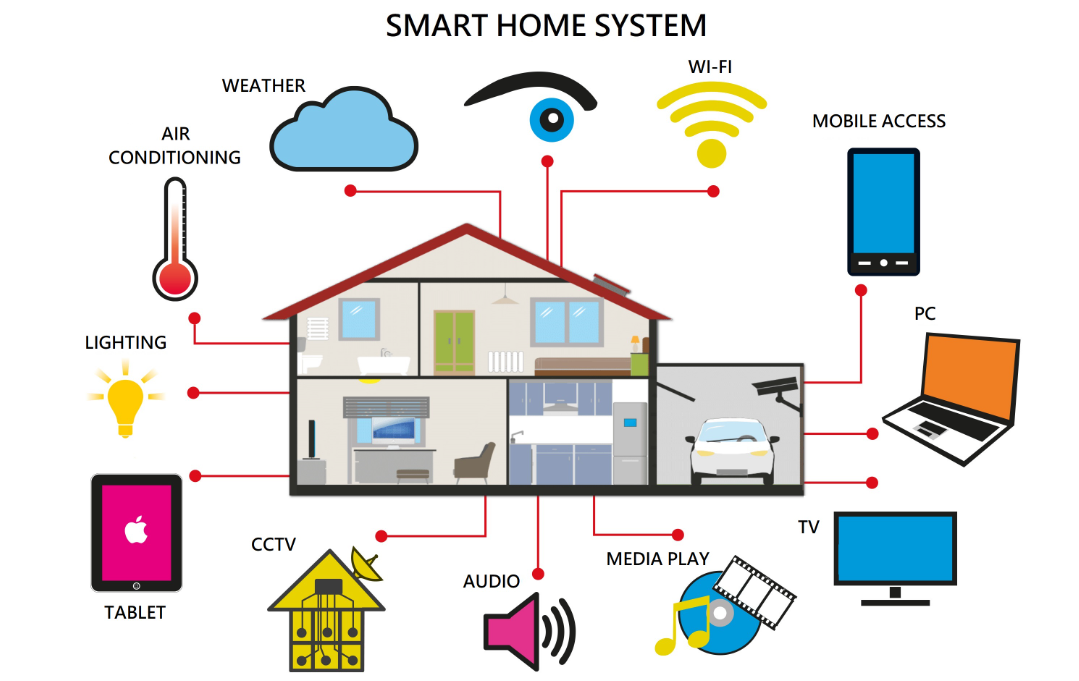
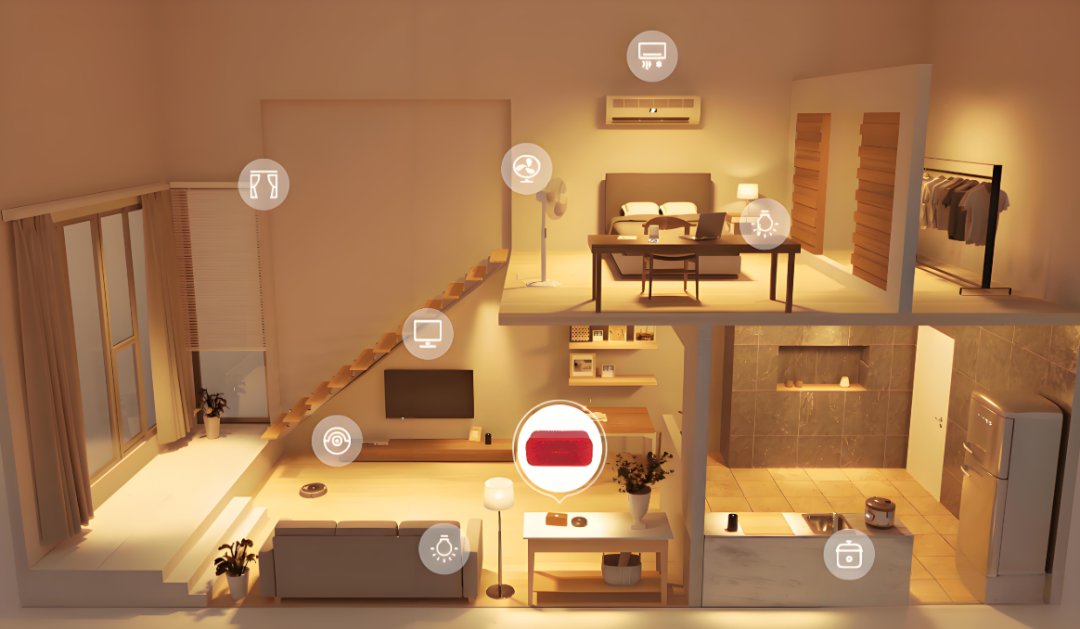
Application Examples


Smart Lighting System
The smart lighting system can automatically adjust the brightness and color of the lights based on factors such as ambient light intensity, time, and human activity. For example, in the morning when waking up, the lights will gradually brighten, simulating the natural sunrise process to help users wake up naturally; at night when going to sleep, the lights will automatically dim to create a comfortable sleeping environment. In addition, users can also remotely control the lights and set scenes through terminal devices such as smartphones and smart speakers, such as setting reading mode, party mode, etc.


Smart Appliance Control System
The smart appliance control system can achieve intelligent control of various household appliances. Users can remotely control the on/off state of appliances, adjust temperature, and set operating modes through terminal devices such as smartphones and tablets. For example, in the hot summer, users can turn on the air conditioning in advance while on their way home from work to adjust the indoor temperature; in the cold winter, users can turn on the water heater in advance to prepare hot water. In addition, smart appliances can also interact with other smart home devices, such as when a human sensor detects someone entering the room, the TV will automatically turn on; when the user leaves the room, the TV will automatically turn off.
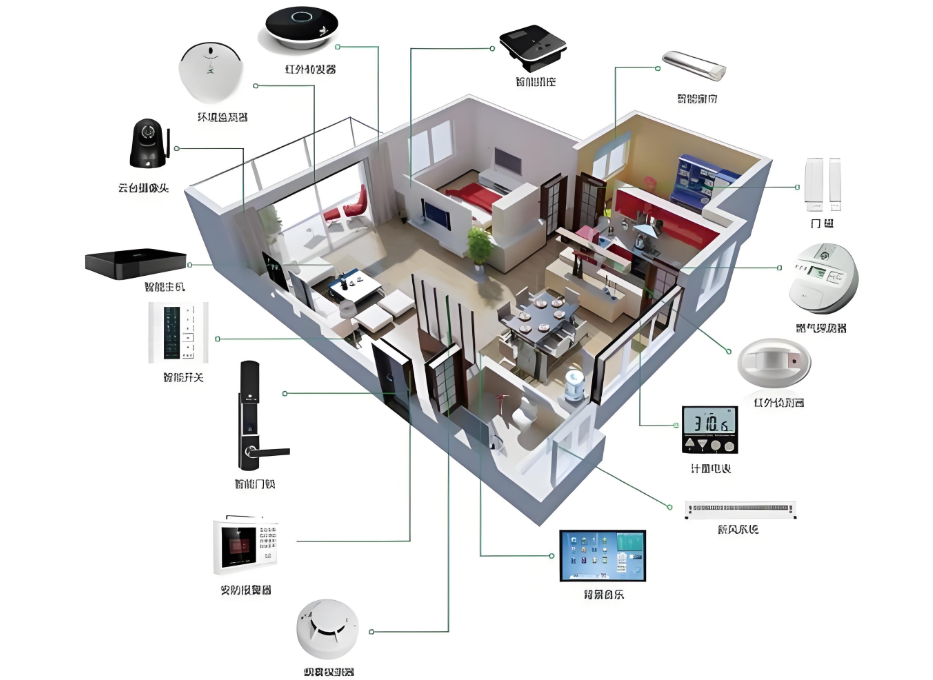

Smart Security System
The smart security system can monitor the safety status of the home in real-time, such as whether doors and windows have been illegally opened, whether there is smoke, or gas leaks. In case of any abnormal situation, the system will immediately issue an alarm and notify the user via mobile phone or SMS. At the same time, the smart security system can also interact with surveillance cameras to record monitoring videos in real-time, allowing users to check the situation at home at any time. For example, when someone illegally breaks into the home, the surveillance camera will automatically record video and send it to the user’s mobile phone.

Image | Luo Junhan, Science and Technology Innovation Department of the Youth League Committee
Text | Luo Junhan, Science and Technology Innovation Department of the Youth League Committee
Editor | Sheng Zheyuan
Chief Editor | Li Shoutao, Lu Qing, Wang Junbo, Gao Yunshu, Hua Feifan
Produced by the Media Center of the School of Information and Electrical Engineering