

1
Program Introduction
The Robotics Engineering program is one of the first specialized programs established in Guangdong Province, starting enrollment in 2017.
Robots are the “jewels at the crown of manufacturing”; their research and development, manufacturing, and application are important indicators of a country’s technological innovation and high-end manufacturing level. The development of the robotics manufacturing industry is based on “national needs, public demands, and market requirements.” This program cultivates talents with skills in robot application, programming, simulation, and debugging technology, mastering the ability to integrate applications, programming development, assembly debugging, operation maintenance, and organizational management, engaging in the design, development, maintenance, and management of robotic products in the field of intelligent engineering.
Students in this program possess good team organization and coordination abilities, comprehensive application capabilities, and a professional advantage that integrates multiple disciplines’ foundational theories and the combination of software and hardware. Graduates from this program have a wide range of employment opportunities, engaging in the fields of complete robots, core components, control systems, intelligent manufacturing and services, as well as scientific research, product and system design and application, technology development, application maintenance, and management work.
2
Faculty Introduction
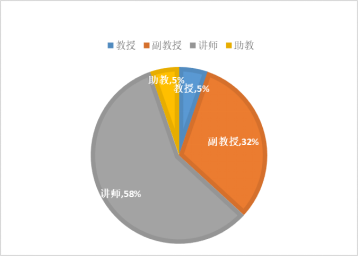
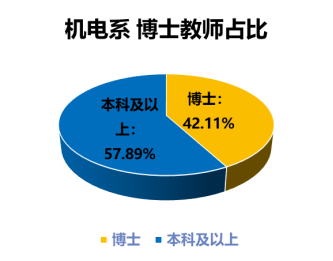
The Robotics Engineering program has 19 full-time teachers, including 1 professor, 6 associate professors (senior engineers), 11 lecturers (engineers), and 1 teaching assistant, with 10 dual-qualified teachers, accounting for 52.63%. The proportion of PhDs is 42.11%, and those with a bachelor’s degree or higher account for 57.89%.

High-level Talent and Key Representatives of the Teaching and Research Team
Luo Qingsheng:
Professor, doctoral supervisor, head of the Robotics Engineering program, professor in the Department of Detection and Control Engineering at Beijing Institute of Technology, a well-known expert in the field of special robots, and a recognized teaching expert in higher education in Beijing. He has presided over several key research projects funded by the Ministry of National Defense, with total research funding exceeding ten million yuan.
Ding Hongsheng:
Professor, doctoral supervisor. Mainly engaged in teaching, research, and discipline construction in mechanical design and theory, with a current research focus on “mechanisms and robotic mechanics.” He teaches multiple undergraduate and graduate courses and supervises doctoral, master’s, and engineering master’s students, as well as domestic visiting scholars. He has edited and co-edited several textbooks and has been responsible for and participated in multiple research projects and educational reform projects at the university, municipal, and national levels, publishing nearly 50 scientific research papers. He was awarded the “Patriotic Model Worker” in Beijing in 1999, the second prize for educational achievements in higher education in Beijing in 2001, the first prize for educational achievements in higher education in Beijing in 2004, and the second Beijing Higher Education Teaching Award in 2006. The engineering training center he led the construction of was recognized as a municipal-level experimental teaching demonstration center and a national-level experimental teaching demonstration center in 2006. Additionally, he has received various university-level achievement awards.
Wang Dandan:
Senior engineer with ten years of experience in state-owned enterprises, a dual-qualified teacher, mainly researching power plant control, gas turbine control, and wind power generation. In recent years, he has completed 10 national patents and published 3 papers. He teaches courses such as Fundamentals of Mechanical Control Engineering, Analog Electronic Technology, and Digital Electronic Technology.
Wu Mingyou:
Associate professor, senior engineer, and senior technician. His main research directions are CNC technology and robotics. He has presided over and participated in more than ten provincial, municipal, and university-level research projects. He has edited or co-edited over 20 publicly published textbooks related to CNC technology, CAD/CAM, and digital electronic technology. He has published 7 papers and has been engaged in teaching for 30 years, teaching courses such as CNC technology, circuits and motors, analog and digital electronics, EDA circuit design, and microcontroller principles and interface technology.
Teaching and Research Team (Partial):
Industrial Robot Teaching and Research Team: Cao Shaoyong, Liu Na, Cao Yanling, Han Huanqing, Wu Mingyou
Underwater Intelligent Robot Teaching and Research Team: Yin Xinyan, Liu Na, Han Huanqing, Li Dongqin
Control Engineering Teaching and Research Team: Wang Dandan, Huang Shiqing, Tang Weijie
PLC Teaching and Research Team: Tang Weijie, Mo Weiqiang, Chen Ting, Liu Hang
Machine Vision Teaching and Research Team: Deng Rongfeng, Cao Yanling, Han Huanqing
3
Talent Cultivation
1. Program Features:
The first specialized program in Guangdong Province, also a key and hot program in high demand. The Robotics Engineering program focuses on the mechanical structure, control systems, drive systems, robot operating systems, and programming application capabilities, emphasizing the integration of software and hardware. This program has leading experimental training equipment among similar institutions, with total assets exceeding ten million yuan, providing students with a good experimental training environment. The curriculum is closely aligned with engineering practice requirements, ensuring a balance between theoretical teaching and practical application, which is favored by many enterprises. This program integrates innovation awareness throughout the teaching process, incorporates technology innovation courses into the training plan, and integrates discipline competitions into course teaching to promote learning through competition and apply knowledge in practice.
Multi-support experimental auxiliary teaching model: Adopting a theory + practice teaching model to achieve practical implementation. The Robotics Engineering program’s laboratory is located in the Engineering Training Center of Beijing Institute of Technology, Zhuhai College, which is a provincial-level experimental teaching demonstration center with a training area of 6,800 square meters and a total investment of over 30 million yuan. The robot training base includes a robot disassembly room, robot programming room, robot training area, robot research room, and intelligent manufacturing system platform, covering an area of 700 square meters and investing over 10 million yuan, which helps promote students’ absorption of theoretical knowledge;


Excellent faculty team: A multi-dimensional student guidance team with a sense of responsibility.

Diversified talent cultivation model: Cultivating high-level composite application-oriented professionals who are physically and mentally healthy, have a sound personality, solid theoretical foundation, high engineering literacy, and innovative ability, capable of adapting to technological development and changes in social demand;
Engineering education talent cultivation model: Focusing on engineering training and technological innovation education to promote the cultivation of application-oriented innovative talents. It integrates various measures such as practical teaching in class, project-based training, and practical case studies to enhance students’ professional skills and practical abilities to meet social needs;
Robotics competition promotion model: Internal competitions, provincial competitions, and national competitions are conducted in a gradient manner, with professional teachers guiding, senior students motivating junior students, and various associations promoting, enhancing hands-on practical abilities and providing strong support for students’ further innovation; student research associations accompany, such as the “Dongyang Team,” “Robot Association,” and “Tianyou Team,” with student teams winning over 175 awards in various national, provincial, and municipal competitions such as the “Mechanical Innovation Design Competition,” “National Educational Robot Competition,” and “National Electronic Design Competition,” allowing students to publish papers, apply for patents, and participate in college student innovation training projects.





Related competitions for the Robotics Engineering program include but are not limited to:
1) National College Student Robot Competition ROBOCON
2) National College Student Robot Competition RoboMaster
3) National College Student Robot Competition Robotac
4) China “Internet+” College Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Competition
5) “Challenge Cup” National College Student Extracurricular Academic Science and Technology Works Competition
6) “Challenge Cup” National College Student Entrepreneurship Plan Competition
7) National College Student Mechanical Innovation Design Competition
8) “Siemens Cup” China Intelligent Manufacturing Challenge
9) National College Student Engineering Training Comprehensive Ability Competition
10) Various provincial and municipal robot competitions in South China, etc.
School-enterprise cooperation talent cultivation model: Collaborating with large enterprises such as ABB, Zhuhai Gree, Kingsoft, Bojie Electronics, ZTE Intelligent, Weisi Port Robot Technology, and Haifeng Robot to provide students with quality practice and learning platforms, internship, and employment opportunities.



2. Core Courses
Circuit and Motor, Analog and Digital Electronics, Fundamentals of Mechanical Design, Microcontroller Principles and Interface Technology, Fundamentals of Control Engineering, Engineering Testing Technology, PLC Principles and Applications, CNC Technology, Industrial Robots, Robot Operating Systems, Machine Vision Technology, Internet of Things Technology, Robot Innovative Design, Inverter Technology, Intelligent Toy Design, Principles and Applications of Embedded Systems.
4
Graduate Work Showcase
Project Name: Remote Multi-Terrain Detection Robot
Guiding Teacher: Yin Xinyan
Designers: 2018 Class Robotics Engineering Major Gu Binbin, Yang Qingdi
Project Introduction: The robot detects the forward view through a camera, and based on user needs, it can switch different weights using the yolov5 deep learning algorithm to recognize and detect any object, sending the detected objects to the user remotely via the network. It can track faces using the OpenCV algorithm combined with PID control, and can also capture camera information and send it to the user’s email. Structurally, it uses an omnidirectional wheel mechanism and a rocker mechanism, allowing for complex movements such as “crab-like movement,” “single-wheel lifting,” and “rotation in place,” providing excellent obstacle-crossing performance.

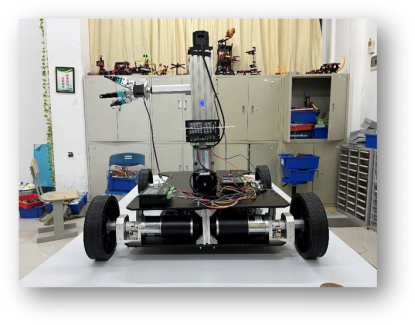
Project Name: Fully Steerable Self-Decision-Making Motion Platform
Guiding Teacher: Cao Shaoyong
Designers: 2018 Class Robotics Engineering Major Chen Jingwei, Ju Zhiyi
Project Introduction: The fully steerable self-decision-making motion platform features vector positioning, omnidirectional movement, load-carrying capabilities, transport functions, emergency stop functions, buzzer alarm functions, and upper computer and Bluetooth control functions. The mobile platform mainly obtains vector position information through vector pose sensors to achieve vector positioning. The circuit control system of the mobile platform is highly integrated, with programmable output power, ensuring high safety. This mobile platform is divided into a drive system and an application system, facilitating secondary development, and can achieve different functions by carrying different execution units, serving various fields such as industry, agriculture, services, aerospace, hazardous locations, and special industries based on demand.
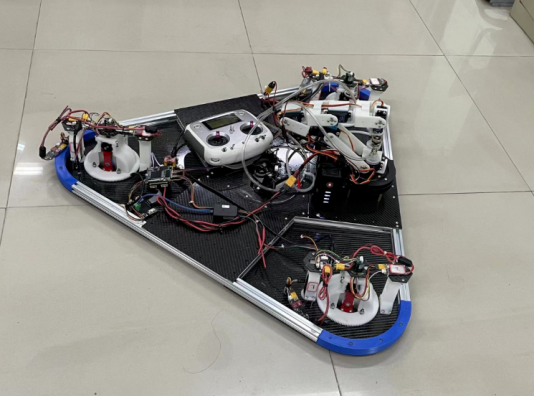
Project: Chess Game Robot
Guiding Teacher: Han Huanqing
Author Information: 2018 Class Robotics Engineering Major Chen Siqi, Ma Yuhui
Project Introduction: Players only need to operate two buttons for global chess play, using visual recognition to monitor the positions of all chess pieces, then calculating the next move using a game algorithm, and communicating the corresponding data to the controller via serial communication to control the robotic arm to move to the corresponding position, achieving the goal of chess play.
Then, the game algorithm calculates the next move and communicates the corresponding data to the controller, controlling

Project Name: Dragon Fruit Picking Robot
Guiding Teacher: Cao Shaoyong
Project Information: 2018 Class Robotics Engineering Xie Jiaxi, Huang Junxin, Zhang Yanggang
Project Introduction: The dragon fruit picking robot is remotely controlled to drive to the working position, activating a dual-camera to take pictures of the dragon fruit. After image algorithm processing, it obtains the depth map of the target object, allowing the user to click on the target object in the depth map. The Raspberry Pi then sends the target object’s depth information to the control system, which controls the robotic arm and gripper to pick the dragon fruit, completing the picking task.
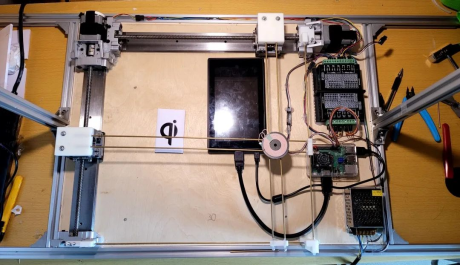
Project Name: Visual Recognition Wireless Charging Table
Guiding Teacher: Huang Shiqing
Project Authors: 2018 Class Robotics Engineering Li You, Liang Chaoyou, Zou Chengxi
Project Introduction: This project achieves the function of automatically wirelessly charging devices present on the table. When a device is placed on the table, the camera recognizes the device’s position information, and the motor slide rail automatically moves the charging coil inside the table under the device for charging. When multiple devices are present, it charges them according to their priority.
Project Name: Swarm Drone Based on ROS System
Guiding Teacher: Mo Weiqiang
Author Information: 2018 Class Robotics Engineering Lin Zhuangwei, Cai Kexin
Project Introduction: Three drones equipped with optical flow, laser modules, and other sensors assist in stable flight. Through ROS nodes, multiple drones can perform formation flying. The drones can identify their positions in the system indoors without GPS signals using UWB external positioning technology, completing mutual avoidance and ensuring safe formation flying.

Project Name: Underwater Detection Robot
Guiding Teacher: Liu Na
Author Information: 2018 Class Robotics Engineering Shen Jian, Wu Jiaxin
Project Introduction: The underwater detection robot is mainly designed for underwater pipeline inspection, developing visual processing algorithms for underwater detection, combined with path planning functions. It adopts a hybrid drive architecture combining a bionic tail fin and brushless thrusters, enabling flexible operations in various water environments, relying on the autonomous and remote detection modes of the underwater detection robot to achieve stable underwater operations.

Project Name: Water Environment Monitoring Unmanned Boat
Guiding Teacher: Yin Xinyan
Project Information: 2018 Class Robotics Engineering Lu Jiatang, Li Guansheng, Peng Yihui
Project Introduction: An unmanned boat for monitoring water environments in rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, conducting long-term real-time and comprehensive monitoring of water environments. This unmanned boat is self-powered, using wireless communication and cloud computing to transmit information to the upper computer onshore. The upper computer displays the water quality information, video information, obstacle information, and position and posture information collected by the lower computer system on the unmanned boat, analyzing the collected information to generate corresponding control commands sent back to the unmanned boat. The unmanned boat is also designed with a mobile APP for remote control for daily manual operations.

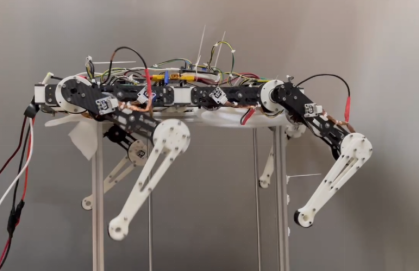
Project Name: A Quadruped Walking Robot
Guiding Teacher: Liu Na
Project Information: 2018 Class Robotics Engineering Qin Zihang, Zhu Baiquan, Zheng Qiuyu
Project Introduction: This design is a cost-effective, structurally stable, and high-performance eight-degree-of-freedom serial quadruped robot, using a 5008 brushless motor to achieve joint movement through belt transmission reduction. The brushless motor is controlled using a sensor-based FOC algorithm, with a self-designed FOC driver. It is equipped with an RGBD camera for positioning and mapping, ultimately achieving jogging, walking, positioning, and mapping of the quadruped robot.
Project Name: Intelligent Load-Following Robot
Guiding Teacher: Liu Na
Project Information: 2018 Class Robotics Engineering Wu Yuwen, Wu Guorui, Shi Zehong
Project Introduction: The intelligent load-following robot is mainly designed for autonomous intelligent transportation of goods in the warehousing and logistics industry. The intelligent load robot will adopt a mecanum wheel structure to achieve an omnidirectional wheeled chassis, combined with a suspension system to enable the robot to adapt to various obstacle avoidance capabilities in the warehousing and logistics environment; it will use a ball screw and guide rail structure to achieve lifting functions; and a synchronous wheel synchronous belt mechanism to achieve horizontal movement of the end-effector structure. The end-effector structure will use a dual-cylinder gripping method to grasp turnover boxes within specified size ranges. This research design can adapt to the logistics and warehousing industry’s transportation of goods, with additional object label recognition and person-following visual recognition functions, creating an autonomous moving logistics robot.
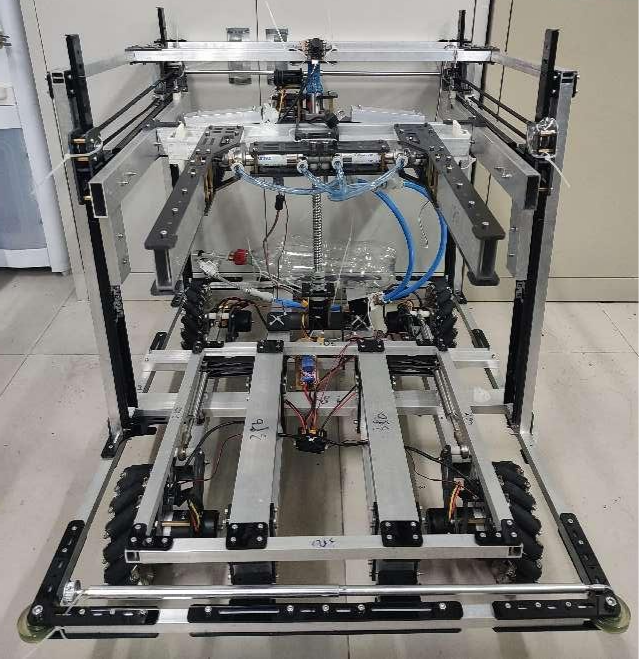
Project Name: Design of an Automatic Detection and Sorting Servo System for Workpieces Based on Vision
Author Information: 2018 Class Robotics Engineering Li Shengyan, Chen Wen, Jiang Hongpei
Guiding Teacher: Cao Yanling
Project Introduction: This project aims to design a system capable of quickly and efficiently detecting defects (scratches, dirt, and broken edges) in mobile phone screens, categorizing products based on defects through an automated machine vision detection and sorting system.

Project Name: New Energy Watchdog Robot
Guiding Teacher: Chen Ting
Designers: Yao Shengteng, Qu Zhaoyang, Dai Wei
Main Features: Face recognition, line following, light chasing, solar charging.
Project Introduction: Powered by solar energy, it uses a light-chasing system to keep the solar panel perpendicular to sunlight, maximizing solar energy absorption. It has a face recognition function, sending an email to the homeowner if a stranger is detected. It also features an automatic line-following function, allowing it to automatically move to a designated monitoring area.
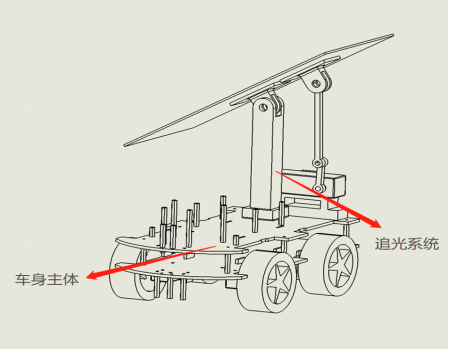
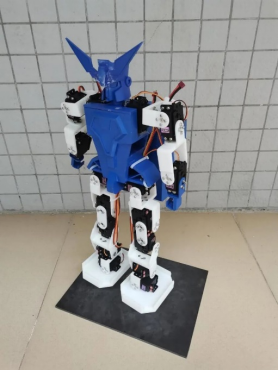
Project Name: Synchronous Machine System Based on Embedded Systems
Guiding Teachers: Mo Weiqiang, Huang Baoshan
Designers: Yang Zhuxin, Hong Peishan, Gao Zhichong
Main Features: Human-machine synchronization; machine vision; human posture recognition; humanoid robot.
Project Introduction: This is a synchronous machine system based on embedded systems, designed with a humanoid structure, with dual arms having 6 degrees of freedom and dual legs having 10 degrees of freedom, effectively achieving humanoid movements. This design can capture 3D images using a Kinect camera and use OpenNI to recognize human skeletal points, converting coordinates into angles using spatial vector methods, and transmitting the angles of human skeletons to the lower computer via socket communication. The microcontroller serves as the lower computer, adjusting PWM square waves to control servos, replicating human actions in the robot.
Project Name: Intelligent Service Robot for High-Speed Railway Stations Based on ROS System
Guiding Teachers: Lu Guiping, Pang Siqin
Designers: Huang Yingbo, Chen Fanrong, Chen Jianxin
Main Features: Autonomous navigation, voice interaction, luggage handling.
Project Introduction: China has formed several large high-speed railway stations with numerous train waiting areas, transporting many train schedules daily. Passengers searching for corresponding train schedules and waiting areas may have to walk long distances, consuming considerable time, especially if they carry a lot of luggage, making the process even more cumbersome.
This article addresses this issue by designing an intelligent service robot with transportation, navigation, and voice recognition functions. The robot can recognize passengers’ voice information regarding waiting areas and guide them to the corresponding waiting area, saving time in finding the waiting area while helping passengers carry their luggage, reducing their travel burden.
The intelligent service robot uses data collection from laser radar, IMU, and encoders, combined with mapping algorithms and Dijkstra’s global path planning algorithm to achieve navigation and positioning. It recognizes passengers’ waiting area information through a microphone array, guiding them to the corresponding waiting area.

Project Name: A Multi-Purpose Underwater Propulsion Backpack
Guiding Teacher: Cao Shaoyong
Designers: Huang Zhipeng, Liao Yingying, Tu Huaxin
Main Features: Backpack design, streamlined design, wide applicability.
Project Introduction: The underwater propulsion backpack’s shell adopts a streamlined design, allowing the backpack to perform optimally underwater. The backpack uses both wired and wireless control, enabling it to be worn by the user or remotely controlled for rescue, surveying, and other fields. The design of the underwater propulsion backpack also addresses the issue of hand injuries commonly associated with traditional handheld underwater propellers.
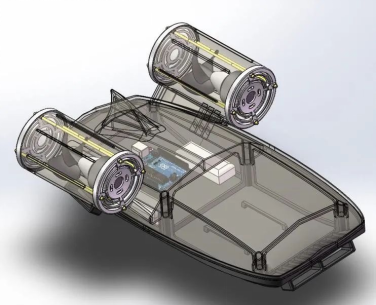

5
Graduate Destinations
Past Graduate Employment Directions
1. Manufacturing: Intelligent equipment, automation, industrial robots, electrical and electronic industries, electrical appliance industry, etc.;
2. Service Industry: Service robots, robot education, special robots, artificial intelligence, etc.;
3. Others: Higher education institutions, research institutes, government agencies, etc.
Further Study Representatives
1. Guo Masadi, 2017 Class Robotics Engineering 3, Guangdong University of Technology, Master’s Degree in Control Engineering
2. Ma Yuhui, 2018 Class Robotics Engineering 2, University of Hong Kong, Master’s Degree in Mechanical Engineering
3. He Xinyang, 2018 Class Robotics Engineering 1, Macau University of Science and Technology, Master’s Degree in Mechanical Engineering
Employment Representatives
1. Jiang Hongpei, 2018 Class Robotics Engineering 2, Shenzhen DJI Baidong Technology Co., Ltd.
2. Ruan Ruli, 2018 Class Robotics Engineering 3, BYD Company Limited
3. You Siyu, 2018 Class Robotics Engineering 3, iFlytek Co., Ltd.
4. Ye Jiesi, 2017 Class Robotics Engineering 3, Weisi Port Robot Technology Co., Ltd.
5. Chen Gan, 2017 Class Robotics Engineering 1, Zhuhai Xuanji Technology Co., Ltd.
Click to Follow the College’s Official WeChat Account

Source: New Media Center of the School of Industrial Automation
Layout : Yao DongkaiInitial Review :You LixueRe-examination : Ling BoxiongFinal Review : Zhang Zhiwan
Copyright COPYRIGHT
@ New Media Center of the School of Industrial Automation, Beijing Institute of Technology Zhuhai
Please indicate the author and source if reprinting
