1. Introduction
In database clusters, network isolation is one of the common fault scenarios. For example, when a node cannot communicate with other nodes due to a network interruption, the cluster may trigger a master-slave switch, data synchronization interruption, or split-brain issues.
By actively injecting network isolation faults, we can verify the cluster’s high availability, data consistency, and fault recovery mechanisms. This article will take the Kingbase database master-slave cluster as an example to analyze how to simulate node network isolation using the tc and chaosblade tools, and observe the expected behavior of the cluster.
2. Expected Behavior in Network Isolation Scenarios
2.1 Experimental Environment
Cluster Architecture:
2-node KingbaseES master-slave cluster (1 master + 1 slave)
Network Isolation Target:
Simulate the master node (IP: 192.168.17.12) being unable to communicate with the slave node (192.168.17.13).
2.2 Expected Behavior
For a 2-node master-slave cluster, if the master and standby library experience network isolation, and the standby library promotes itself to master, after the network isolation fault recovery, the cluster will experience split-brain. Each database has corresponding solutions for this.
Here, I asked AI about the technical measures to prevent split-brain in 2-node clusters for Oracle, MySQL, and PostgreSQL.

Next, I consulted the response plan for the Kingbase database 2-node master-slave cluster.
1. Master Node Perspective:
If the master node is isolated, it will switch from synchronous to asynchronous mode due to not receiving ACK from the slave node.
2. Slave Node Perspective:
The slave node detects a timeout from the master node and checks whether the gateway of the master-slave network is reachable. If the gateway is unreachable, it indicates a network fault on its side, and it will stop the cluster switching component from running and will not promote itself to master. If the gateway is reachable, it will determine that the master library has a network fault and will execute the promotion operation.
3. Client Perspective:
Write requests may be temporarily blocked, and after the master completes the asynchronous state switch, it will return to normal.
3. Practical Testing of Network Isolation Faults
3.1 Method 1: Using Chaosblade (Chaos Engineering Experiment Tool)
Applicable Scenario:
Automated testing, precise control of the experimental lifecycle.
Steps
1. Install Chaosblade:
wget https://chaosblade.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/agent/github/1.7.1/chaosblade-1.7.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz tar -xvf chaosblade-1.7.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz cd chaosblade-1.7.1 2. Inject Network Isolation Experiment:
Check the cluster status before injection.

# Block all network traffic on the standby node's current network interface, recover after 120s ./blade create network loss --percent 100 --interface ens33 --timeout 120 3. Verify Experiment Status:
The master node cannot ping the standby node, and the cluster status shows abnormal.
ping 192.168.17.13 ./repmgr cluster show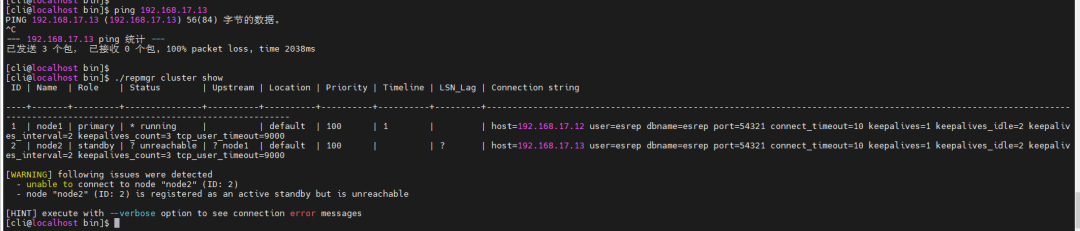
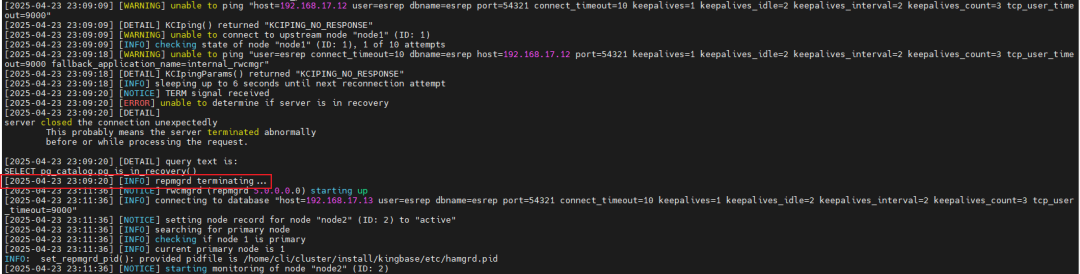
Check the standby cluster logs; after the standby node cannot ping the gateway, it stops the operation of the cluster component repmgrd.
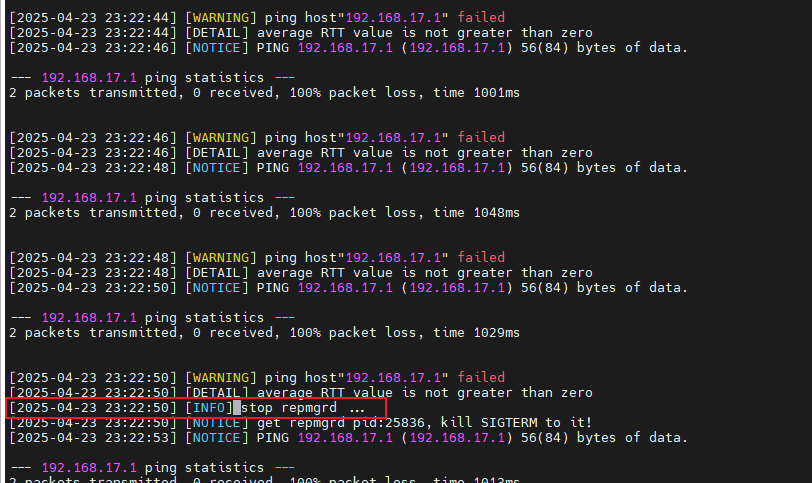
Due to the cluster component stopping, the promotion operation is interrupted.
4. Stop the Experiment:
Wait for 120s after the fault timeout.
After the standby network isolation fault recovers, the cluster automatically returns to normal.
3.2 Method 2: Using the tc Command (Temporary Traffic Block)
Applicable Scenario:
Quick testing, no need for persistent configuration, no external tools required.
Steps
1. Block traffic to the master node from the standby node, including the gateway, simulating a network interruption on the standby node:
# Confirm the master node's network interface name (e.g., ens33) ip addr show # Add queue rules tc qdisc add dev ens33 root handle 1: htb # Block traffic to master node 192.168.17.12 tc filter add dev ens33 protocol ip parent 1: prio 1 u32 match ip dst 192.168.17.12 flowid 1:1 action drop # Block traffic to gateway 192.168.17.1, note that executing this will cause the gateway to be unable to process traffic, which may lead to SSH connection drop tc filter add dev ens33 protocol ip parent 1: prio 1 u32 match ip dst 192.168.17.1 flowid 1:1 action drop 2. Verify Network Isolation:
# Try to ping the standby node from the master node ping 192.168.17.12 # Expected result: Request timeout # View tc rules tc -s filter show dev ens33 3. Restore Network:
tc qdisc del dev ens33 root The test results are consistent with those observed using Chaosblade.
3. Practical Conclusions
1. When the master library suddenly “loses contact” with the subordinate (standby library), it will not immediately fail; instead, it will switch to asynchronous mode and continue working while attempting to reconnect, avoiding sudden business interruptions.
2. When the standby library finds it cannot contact the master, it will not rush to promote itself; instead, it will check whether the gateway of the master-slave network is reachable. If the gateway is unreachable, it indicates a network fault on its side, and it will stop the cluster switching component from running and will not promote itself:
In summary, here are the performances of network isolation in three scenarios:
🟡 Master library is isolated (master library gateway unreachable)
→ Standby library detects: its network is normal, gateway is reachable
→ Conclusion: Master is truly offline → Standby safely promotes itself to master
🔵 Standby library is isolated (cannot connect to gateway)
→ Self-check reveals the network cable is unplugged → Remains idle and does not promote
⚫ Both master and standby are isolated (both cannot connect to the gateway)
→ Both nodes are offline → Standby resolutely does not claim the throne
Additional Note:
The Kingbase database cluster component also provides a running_under_failure_trusted_servers parameter to control whether the database can continue running after failing to ping the trusted gateway.
Set to on: If pinging the trusted gateway fails, the database is unaffected;
Set to off: If pinging the trusted gateway fails, the database will shut down.