#RenesasMicrocontroller #IntervalTimer #WatchTimer
The Interval Timer is known in Chinese as 间隔定时器, and its core function is to generate periodic events (usually interrupts) after precise, configurable time intervals. It is the cornerstone for implementing time references, periodic task scheduling, precise delays, timeout detection, and other functions in embedded systems.
The Interval Timer of Renesas microcontrollers is similar to the Watch Timer (监视定时器), generated by the same module, as shown in the block diagram below.
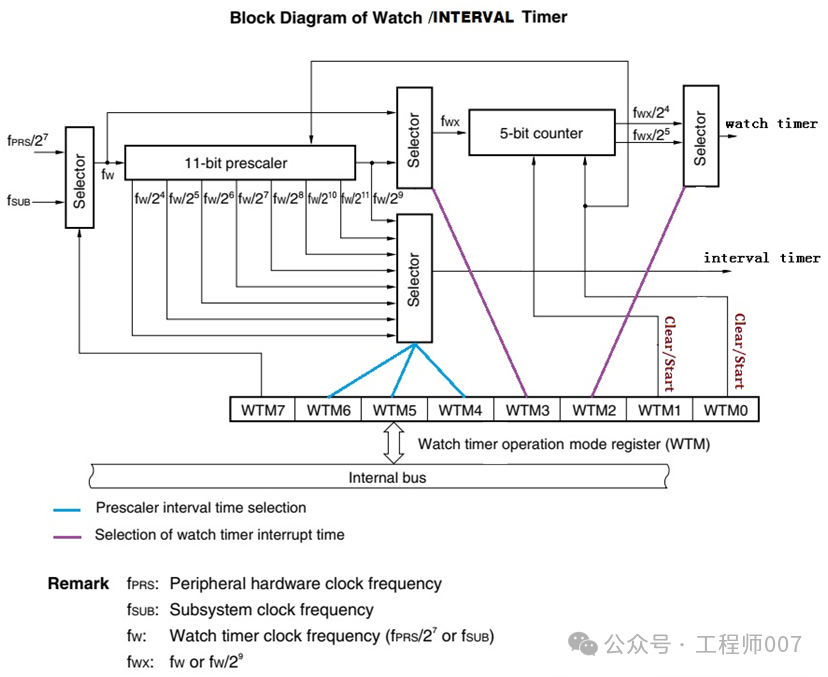
Here, attention should be paid to the working mode control register WTM,
The difference between the two is that the Interval Timer can generate a wider variety of time intervals. Compare the two tables below.
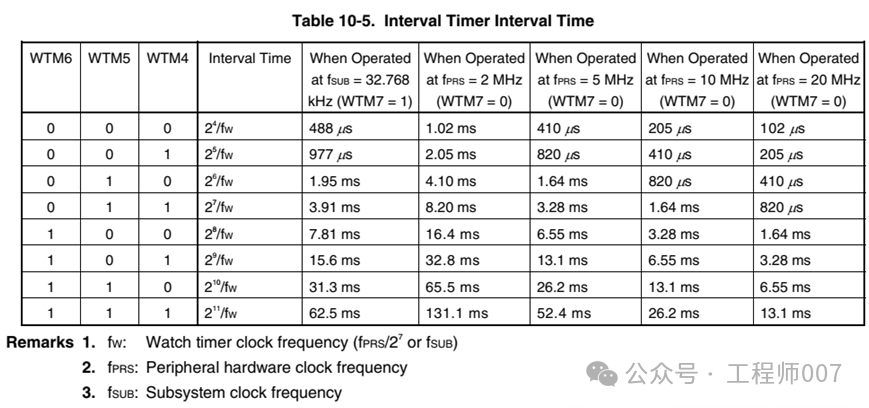
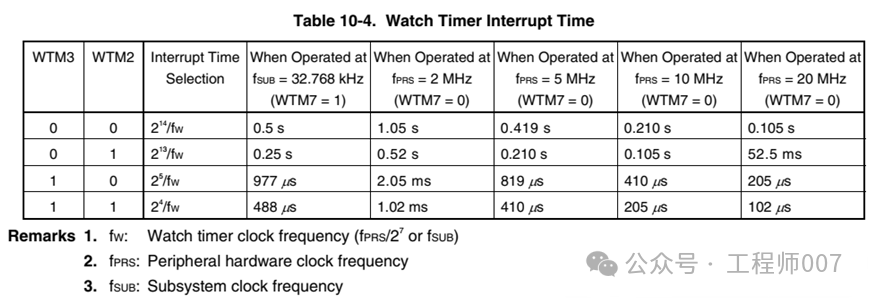
The Interval Timer and Watch Timer can work simultaneously. The differences are roughly as follows:
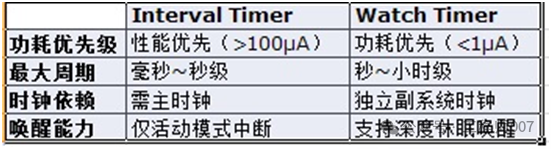
Requires minute-level periodic wake-up → Optional Watch Timer
Requires millisecond-level precise control → Optional Interval Timer
Why use the Interval Timer?
●Accuracy: Based on hardware clock, the accuracy is far superior to software delay loops (not affected by interrupt latency or instruction execution time variations).
●Low CPU Overhead: The CPU only needs to execute tasks when interrupts occur, allowing it to enter low-power modes (Sleep/Stop) or perform other tasks during wait periods, greatly improving CPU efficiency.
●Periodic Guarantee: The automatic reload mechanism ensures strict periodicity of events.
●Reliability: Hardware-implemented timing is less likely to be disrupted by software errors (unless the timer itself is misconfigured).
●Versatility: It serves as the foundation for implementing more complex timing functions (such as PWM, input capture) and is a core component for building real-time systems.
Typical Application Scenarios:
●Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) Heartbeat: Provides fixed time slices for the task scheduler (Tick).
●Periodic Task Scheduling: Executes sensor data collection, state machine scanning, control algorithm calculations, communication protocol processing, etc., at fixed intervals (e.g., 1ms, 10ms, 100ms).
●Precise Delays: Used in situations requiring precise timing (e.g., communication timing, peripheral initialization wait).
●Generate Simple Square Waves: Toggle the IO pin level in the interval timer interrupt.
●Trigger Other Peripherals: Regularly trigger ADC to start conversions, DMA transfers, etc.
Differences from Regular Timers/Counters:
●Regular Timers/Counters: More general-purpose, can be configured for various modes (counting external events, PWM, input capture, etc.). Using it as an interval timer is one of its functions.
●Interval Timer: Specifically refers to the configuration for periodic auto-reload (Auto Reload) mode, focusing on generating fixed time interval events. It emphasizes the “interval” and “automatic repetition”.
In summary, the Interval Timer of Renesas microcontrollers is a hardware-enhanced peripheral that utilizes internal counters, configurable clock sources, and automatic reload mechanisms to generate periodic interrupts or signals with extremely high precision and very low CPU overhead. It is the cornerstone for implementing time management, periodic task execution, precise delays, and timeout detection in embedded systems. Specific implementation details can be found in the relevant datasheet.