1. Overall Industry Growth Trend
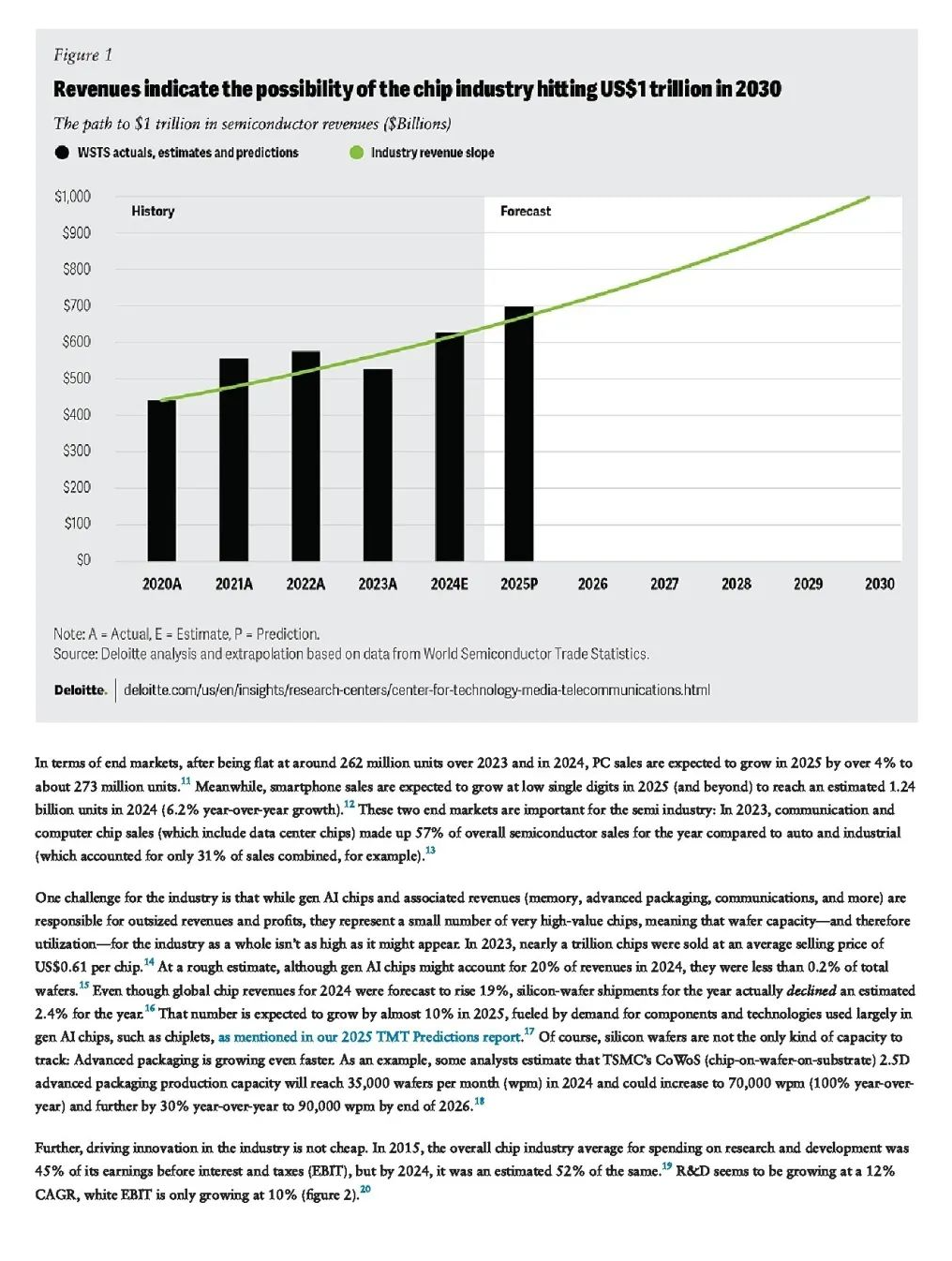
The global semiconductor industry is expected to reach a new sales high of $697 billion in 2025. Although demand in the personal computer (PC) and smartphone markets may remain moderate, artificial intelligence (AI) chips and data center construction have become the main driving forces. From 2025 to 2030, the industry is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.5%, with a common goal of achieving $1 trillion in chip sales by 2030, assuming the industry continues to grow at this rate, the industry’s scale will reach $2 trillion by 2040. The stock market is often a leading indicator of industry performance; as of mid-December 2024, the total market capitalization of the world’s top ten chip companies was $6.5 trillion, a 93% increase from $3.4 trillion in mid-December 2023, and a 235% increase from $1.9 trillion in mid-November 2022.
2. Technology Development Trends
(1) Advanced Packaging Technology
Advanced packaging technology will become an important development direction in the semiconductor industry in 2025, with its market size and application scope continuously expanding.
1. Market Size Growth
According to Yole’s disclosure, the global advanced packaging market reached $43.9 billion in 2023, a year-on-year increase of 19.62%. It is expected that the industry size will grow to $47.25 billion in 2024, and from 2023 to 2028, the semiconductor advanced packaging market is expected to grow by $22.79 billion, with a CAGR of 8.72%.
2. Types and Applications of Technology
• 2.5D and 3D Packaging: In 2.5D packaging, chips are placed side by side on a mediator layer, interconnected through micro bumps on the chips and wiring in the mediator layer, with interconnections between upper and lower layers achieved through silicon vias, and then soldered to traditional 2D packaging substrates, suitable for high-end server chipsets, etc. 3D packaging directly stacks multiple chips vertically, achieving electrical connections through silicon vias, further enhancing integration and communication efficiency. For example, NVIDIA’s high-end GPU chips use 2.5D packaging technology, connecting with high-speed memory chips to enhance graphics processing capabilities.
• System-in-Package (SiP): SiP integrates multiple chips with different functions into a single package, forming a complete system, suitable for wearable devices, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, etc. For example, smartwatches use SiP technology to integrate various functional chips, achieving multiple functionalities.
• Wafer-Level Packaging (WLP): WLP performs packaging testing at the wafer stage, with the packaged chip size being nearly the same as the bare chip, achieving minimal chip size. This packaging technology is commonly used in consumer electronics with strict size requirements, such as Bluetooth chips, RF chips, etc.
3. Technical Advantages
Advanced packaging technology can enhance chip performance, reduce costs, and minimize size. For example, flip-chip packaging eliminates the wire bonding process, shortens signal transmission paths, and improves electrical and thermal performance. Wafer-level packaging reduces packaging processes, lowering costs.
(2) AI Chip Technology
By 2025, the AI chip market value will exceed $150 billion, becoming an important force driving the growth of the semiconductor industry. AI chips include CPUs, GPUs, data center communication chips, memory, power chips, etc. As AI technology continues to develop, the performance and functionality requirements for AI chips are also increasing, prompting chip manufacturers to increase R&D investment and drive innovation and upgrades in AI chip technology.

3. Reshaping the Industry Ecosystem
The development of advanced packaging technology is reshaping the semiconductor industry ecosystem, having a profound impact on various links in the industry chain.
(1) Impact on the Design Phase
Advanced packaging technology is driving a shift in chip design towards system-level design. Chip designers need to expand from individual chips to entire systems, including integrating multiple bare chips into advanced packaging. For example, companies like Intel have integrated chips of different processes using advanced packaging technology to optimize performance and costs.
(2) Impact on the Manufacturing Phase
Advanced packaging technology imposes higher requirements on manufacturing processes, requiring high-precision equipment and process control. For example, the manufacturing of silicon vias in 3D packaging requires drilling tiny vias on extremely thin silicon wafers while ensuring the verticality and conductivity of the vias. Additionally, advanced packaging technology has also driven upgrades in packaging equipment, such as photolithography machines and etching equipment.
(3) Impact on the Industry Chain Structure
The development of advanced packaging technology is changing the value distribution in the semiconductor industry chain. The importance of the backend packaging phase is increasingly highlighted, becoming a key driver of innovation and system performance. For example, TSMC has integrated multiple chips using CoWoS advanced packaging technology, significantly improving integration and performance, dominating the high-end packaging market.
(4) Impact on Market Competition
Advanced packaging technology has become a new focus of competition among enterprises. International giants such as TSMC, Intel, and Samsung occupy important positions in the advanced packaging field, while domestic companies like JCET and Tongfu Microelectronics are also making breakthroughs. For example, JCET has made significant progress in 2.5D packaging technology, with yield rates improved to 98%, helping to reduce the cost of domestic GPUs by 30%.
4. Challenges Facing the Industry
(1) Geopolitical Tensions
Geopolitical tensions are intensifying, bringing many uncertainties to the semiconductor industry. Trade frictions and export control policies between countries may lead to disruptions or delays in the semiconductor supply chain, affecting companies’ production plans and market layouts. For example, the U.S. export control measures on semiconductors to China have restricted the export of certain advanced technologies, equipment, and products to China, hindering the development of China’s semiconductor industry.
(2) Supply Chain Disruption Risks
The semiconductor industry chain is long, involving multiple links and numerous suppliers; any problem in one link can lead to supply chain disruptions. Natural disasters, pandemics, equipment failures, and other factors can trigger supply chain disruption risks. For example, the outbreak of COVID-19 in 2020 impacted the global semiconductor industry chain, causing some chip manufacturing companies to halt operations, leading to chip supply shortages that affected the development of various industries such as automotive and electronics.
(3) Talent Shortage Issues
The semiconductor industry is technology-intensive, with a strong demand for specialized talent. However, the global semiconductor industry is currently facing a talent shortage, especially in high-end chip design, advanced manufacturing processes, and packaging testing. The talent shortage not only limits the pace of technological innovation and product development for companies but also affects the industry’s development potential. According to relevant institutions, the talent gap in the global semiconductor industry is expected to further widen in the coming years, and companies need to increase efforts in talent training and recruitment to meet the demands of industry development.
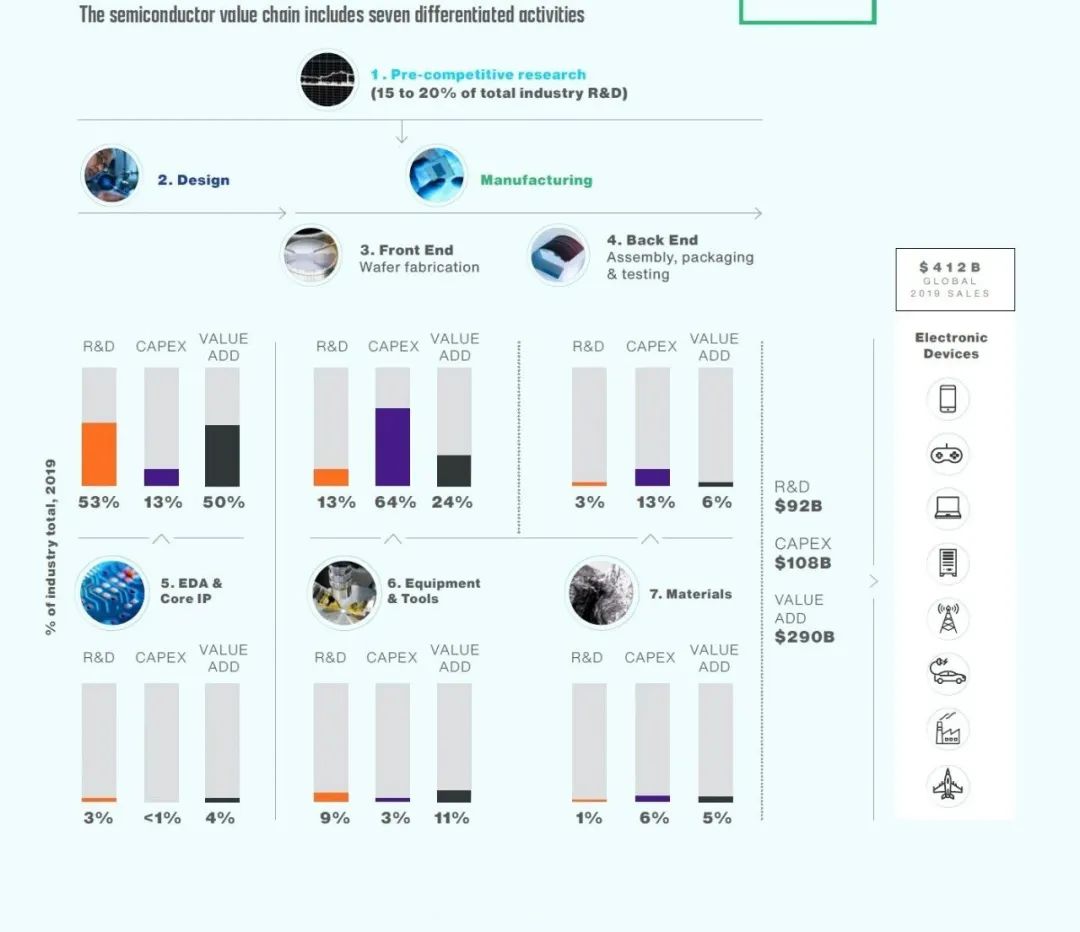
5. Response Strategies
(1) Strengthening R&D Innovation
Semiconductor companies need to continuously increase R&D investment, strengthen cooperation with universities and research institutions, conduct cutting-edge technology research and innovation, and enhance the core competitiveness of enterprises. For example, companies like Intel and Samsung invest heavily in R&D each year, continuously launching new chip architectures, manufacturing processes, and packaging technologies to maintain their leading position in the industry. Domestic companies should also emphasize R&D innovation, actively invest resources, and strive to narrow the gap with international advanced levels.
(2) Optimizing Supply Chain Layout
Companies should optimize their supply chain layout to enhance the stability and resilience of the supply chain. This can be achieved by establishing a diversified supplier system to reduce dependence on a single supplier; strengthening deep cooperation with suppliers to jointly respond to market changes and risks; and establishing a supply chain early warning mechanism to promptly identify and resolve potential issues. Additionally, companies can integrate upstream and downstream resources in the industry chain through investments and acquisitions to enhance the integration capabilities and synergy effects of the supply chain.
(3) Attracting and Cultivating Talent
Talent is key to the development of the semiconductor industry, and companies need to take various measures to attract and cultivate talent. On one hand, improve talent compensation, provide competitive salaries and benefits to attract outstanding talent to join the company; on the other hand, strengthen the construction of talent training systems through internal training, external learning, and practical exercises to enhance employees’ professional skills and overall quality. Furthermore, companies can collaborate with universities and vocational schools to carry out joint training projects to supply more high-quality professional talent to the industry.

6. Future Outlook
In 2025, the global semiconductor industry will welcome new development opportunities driven by emerging applications such as artificial intelligence and data center construction. However, the industry also faces challenges in geopolitics, supply chains, and talent. Companies need to actively respond to these challenges by strengthening R&D innovation, optimizing supply chain layouts, and attracting and cultivating talent to enhance their competitiveness and promote the sustainable and healthy development of the industry. At the same time, with continuous technological advancements and market changes, the semiconductor industry will continue to present new opportunities and challenges, requiring companies and practitioners to maintain keen market insight and innovative capabilities to adapt to future development needs.
(Source: STK World Chip Inventory Service. This article is produced by the Qingdao West Coast International Investment Promotion Center, reprinted for sharing and learning purposes only, not for commercial use. If there is any infringement, please contact for deletion.)
