The common method for calculating the electrostatic potential of molecules is using Gaussian software, but what many do not know is that VASP can also be used. The specific method is as follows:
(1) Optimize the molecular structure;
(2) Perform static calculations: Add parameters to the INCAR file to generate CHGCAR and LOCPOT (LCHARG = .T. and LVHAR = .TRUE.)
(3) Convert the formats of CHGCAR and LOCPOT to cube format: there are two methods, one is through VASPKIT>329 and 429 or their respective cube format files; the other is through Multiwfn (download link: http://sobereva.com/multiwfn/download.html) for format conversion. Drag CHGCAR into the Multiwfn command line and press enter to prompt for unit conversion, input ‘y’, select function 13’s command 0, and follow the prompts to input the save path to generate the .cub file, which is saved by default in the directory where Multiwfn.exe is located. Reopen Multiwfn.exe, drag LOCPOT into the Multiwfn command line and press enter, here it is converted to electrostatic potential (during this format conversion, you can choose not to convert units based on your needs, as the color distinction is more obvious after conversion). This results in CHGCAR.cub and LOCPOT.cub.
(4) Use VMD for visualization: Open VMD, and the following three windows will be displayed
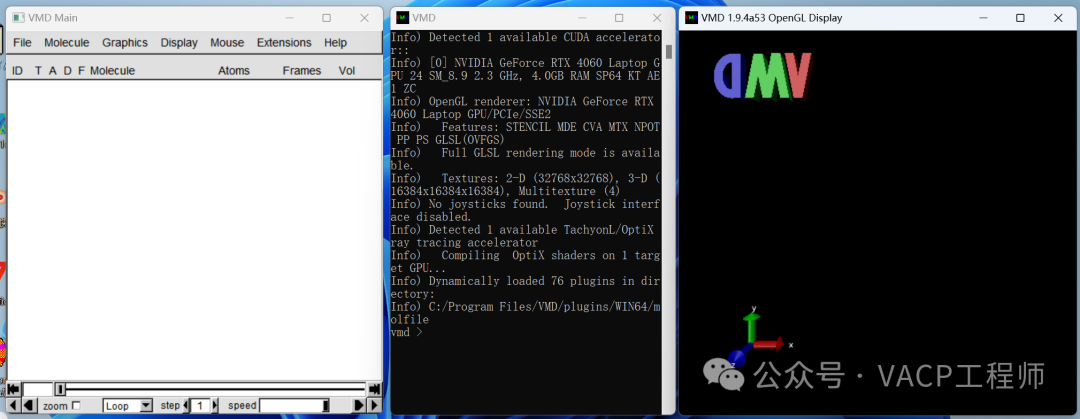
Drag CHGCAR.cub into window 3, and make the following settings in window 1:
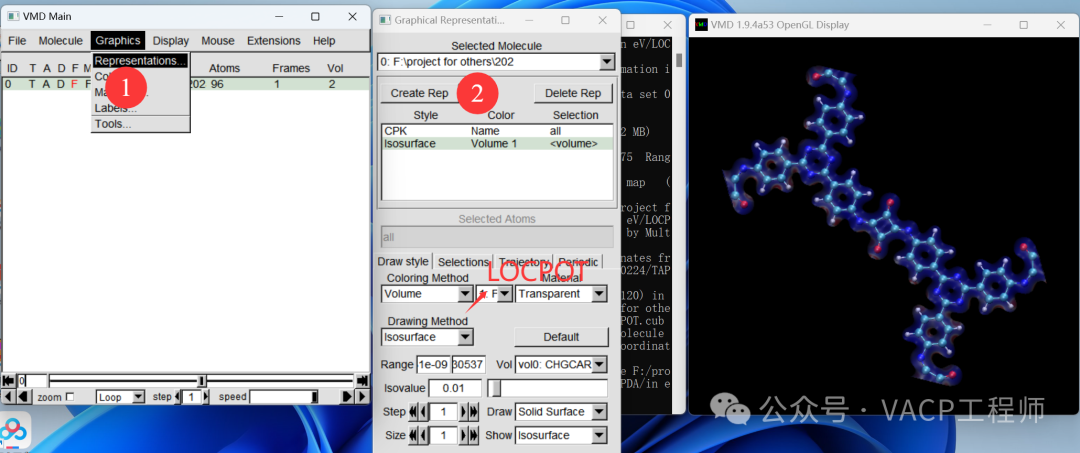
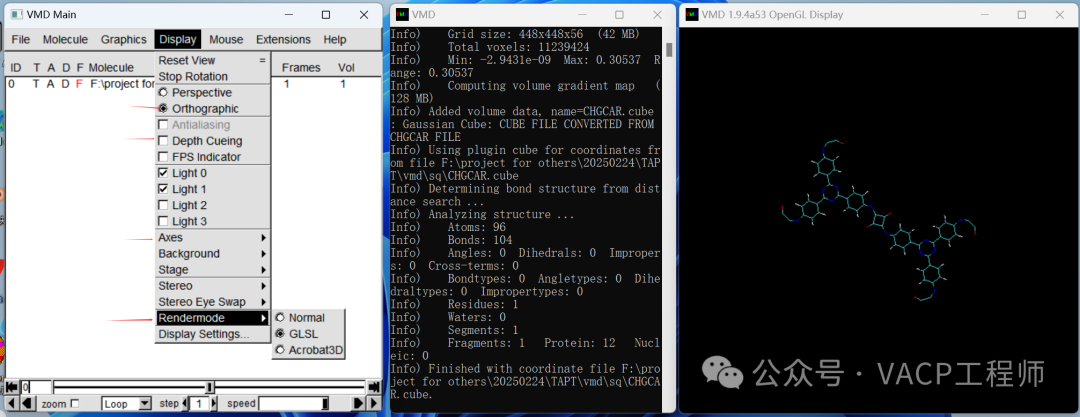 Then right-click on the items that appear in window 1, select Load Data into Molecule, click Browse, choose LOCPOT.cub, and click Load to import it, then close the window. Note that VMD does not support Chinese paths.
Then right-click on the items that appear in window 1, select Load Data into Molecule, click Browse, choose LOCPOT.cub, and click Load to import it, then close the window. Note that VMD does not support Chinese paths.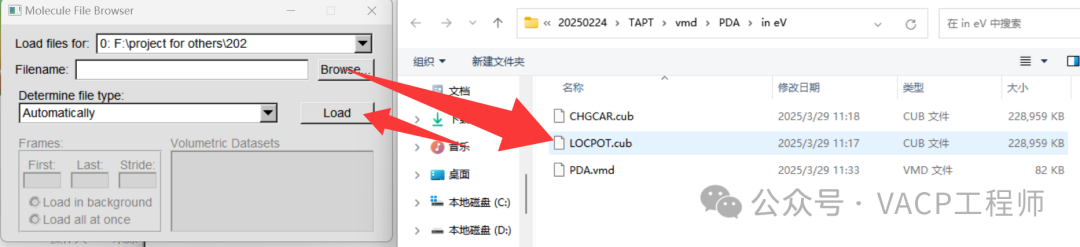 Display structure
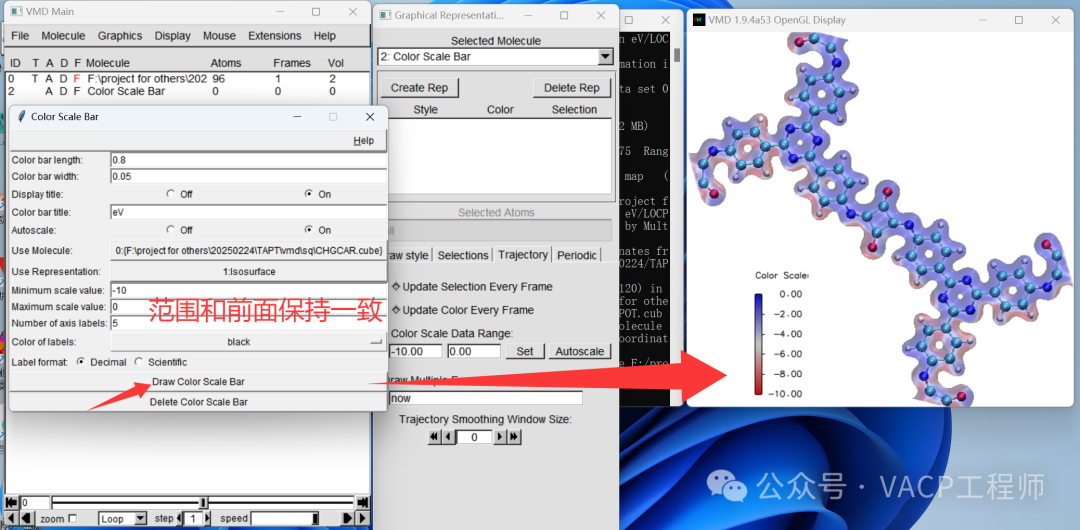
Display structure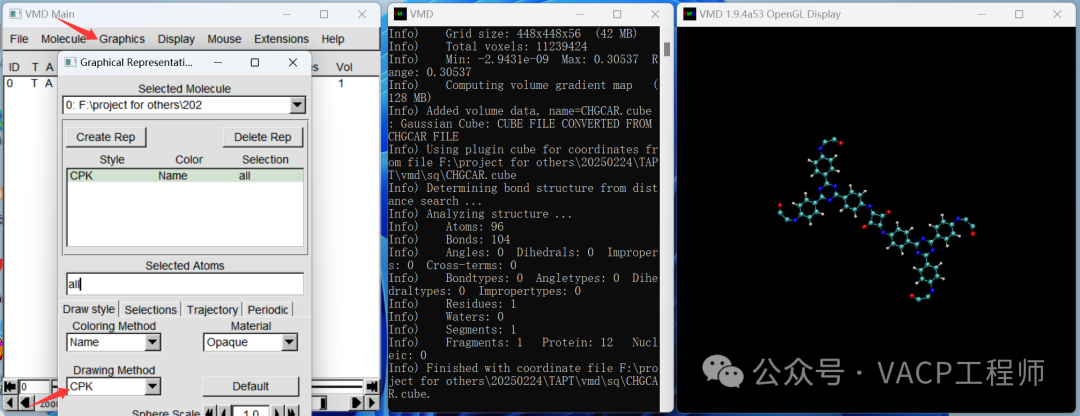 The color of the atoms can be adjusted, as shown below:
The color of the atoms can be adjusted, as shown below: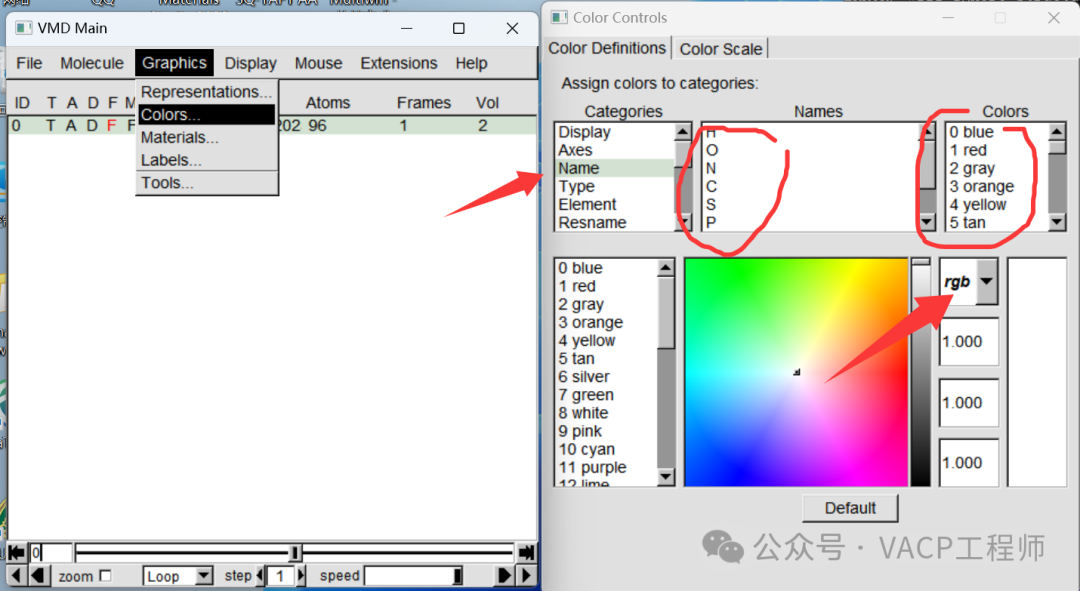
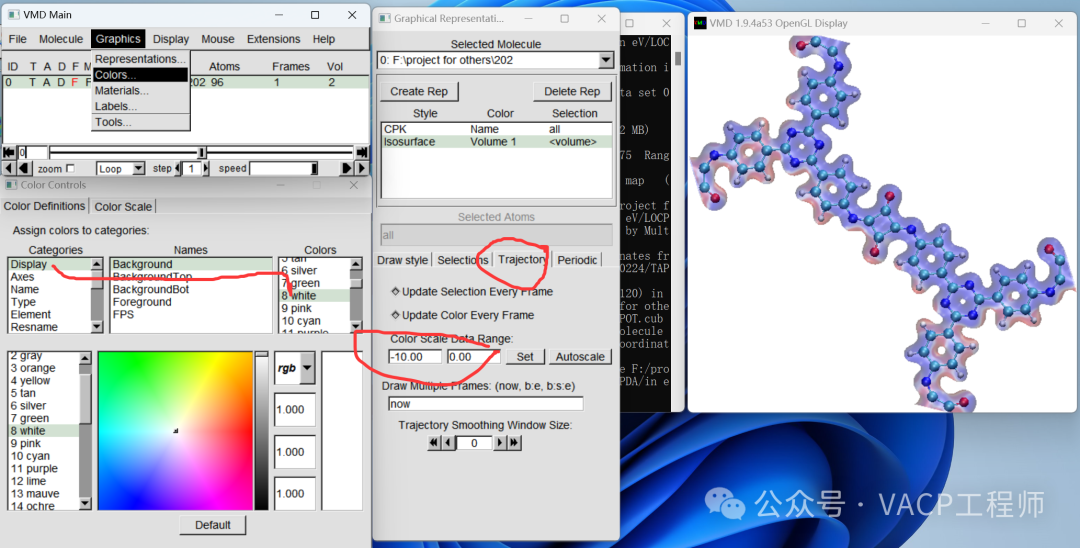
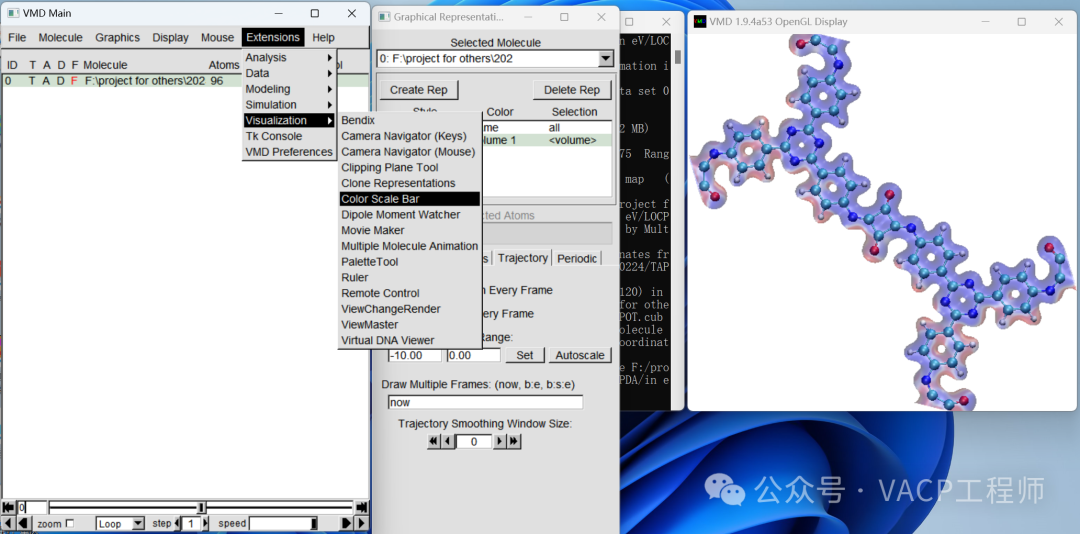
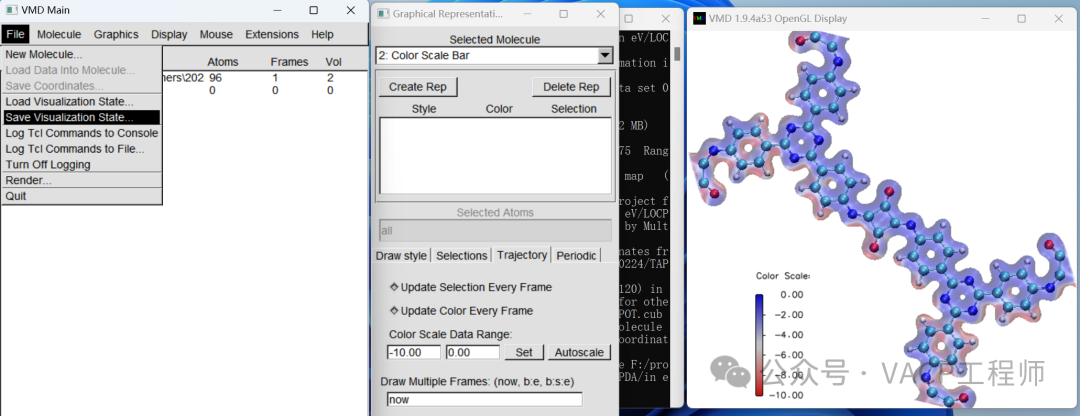 To facilitate future modifications, you can save the view as a .vmd file using File-Save Visualization State. Note: it should be in the same path as the original file.
To facilitate future modifications, you can save the view as a .vmd file using File-Save Visualization State. Note: it should be in the same path as the original file.