Linux commands are used to manage the Linux system. In the Linux system, everything from the CPU, memory, disk drives, keyboard, mouse, to users is treated as files, and the commands for managing the Linux system are core to its normal operation.
Online Query and Help Commands (2)
man: View command help, a dictionary of commands; there is also info, which is more complex but not commonly used.
help: View help for built-in Linux commands, such as the cd command.
File and Directory Operation Commands (18)
ls: Short for list, it lists the contents of a directory along with their attribute information.
cd: Short for change directory, it switches from the current working directory to the specified working directory.
cp: Short for copy, its function is to copy files or directories.
find: Means to search, used to find directories and files within them.
mkdir: Short for make directories, its function is to create directories.
mv: Short for move, its function is to move or rename files.
pwd: Short for print working directory, its function is to display the absolute path of the current working directory.
rename: Used to rename files.
rm: Short for remove, its function is to delete one or more files or directories.
rmdir: Short for remove empty directories, its function is to delete empty directories.
touch: Creates a new empty file or changes the timestamp attribute of an existing file.
tree: Displays the contents of a directory in a tree structure.
basename: Displays the file or directory name.
dirname: Displays the file or directory path.
chattr: Changes the extended attributes of a file.
lsattr: Views the extended attributes of files.
file: Displays the type of a file.
md5sum: Calculates and verifies the MD5 value of files.
View File and Content Processing Commands (21)
cat: Short for concatenate, it is used to connect multiple files and print them to the screen or redirect to a specified file.
tactac: The reverse spelling of cat, thus the command functions to display file content in reverse.
more: Displays file content page by page.
less: Displays file content page by page, opposite to the more command.
head: Displays the head of the file content.
tail: Displays the tail of the file content.
cut: Splits each line of a file by a specified delimiter and outputs it.
split: Splits a file into different small segments.
paste: Merges file content by line.
sort: Sorts the text content of a file.
uniq: Removes duplicate lines.
wc: Counts the number of lines, words, or bytes in a file.
iconv: Converts the encoding format of a file.
dos2unix: Converts DOS format files to UNIX format.
diff: Short for difference, compares the differences between files, commonly used for text files.
vimdiff: Command-line visualization tool for comparing files, often used for text files.
rev: Outputs file content in reverse.
grep/egrep: Filters strings, commonly referred to as the “three musketeers”.
join: Merges two files based on matching fields.
tr: Replaces or deletes characters.
vi/vim: Command-line text editor.
File Compression and Decompression Commands (4)
tar: Packs and compresses files.
Information Display Commands (11)
uname: Command that displays operating system-related information.
hostname: Displays or sets the current system’s hostname.
dmesg: Displays boot information, used for diagnosing system failures.
uptime: Displays system uptime and load.
stat: Displays the status of a file or filesystem.
du: Calculates disk space usage.
df: Reports the usage of filesystem disk space.
top: Displays real-time system resource usage.
free: Views system memory.
date: Displays and sets the system time.
cal: Views calendar and other time information.
File Search Commands (4)
which: Finds binary commands, searching according to the environment variable PATH.
find: Traverses the disk to find files or directories.
whereis: Finds binary commands, searching according to the environment variable PATH.
locate: Searches for commands from the database (/var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db), using updatedb to update the database.
User Management Commands (10)
usermod: Modifies the properties of an existing user in the system.
groupadd: Adds a user group.
passwd: Modifies user password.
chage: Modifies the expiration date of user passwords.
id: Views the user’s uid, gid, and the groups they belong to.
su: Switches user identity.
visudo: Command for editing the /etc/sudoers file.
sudo: Executes commands as another user (default is root) that are allowed in the sudoers file.
Basic Network Operation Commands (11)
telnet: Uses the TELNET protocol for remote login.
ssh: Uses the SSH encryption protocol for remote login.
scp: Short for secure copy, used to copy files between different hosts.
wget: Command-line tool for downloading files.
ping: Tests network connectivity between hosts.
route: Displays and sets the routing table of the Linux system.
ifconfig: Command to view, configure, enable, or disable network interfaces.
ifup: Starts the network card.
ifdown: Shuts down the network card.
netstat: Views network status.
ss: Views network status.
Advanced Network Operation Commands (9)
nmap: Network scanning command.
lsof: Short for list open files, lists the files that have been opened in the system.
mail: Sends and receives emails.
mutt: Email management command.
nslookup: Interactive command for querying Internet DNS servers.
dig: Finds the DNS resolution process.
host: Command for querying DNS.
traceroute: Traces the routing status of data transmission.
tcpdump: Command-line packet capture tool.
Disk and Filesystem Commands (16)
mount: Mounts a filesystem.
umount: Unmounts a filesystem.
fsck: Checks and repairs the Linux filesystem.
dd: Converts or copies files.
dumpe2fs: Exports ext2/ext3/ext4 filesystem information.
fdisk: Disk partition command, suitable for partitions below 2TB.
parted: Disk partition command, with no disk size limit, commonly used for partitions below 2TB.
mkfs: Formats and creates a Linux filesystem.
partprobe: Updates the kernel’s hard disk partition table information.
e2fsck: Checks ext2/ext3/ext4 type filesystems.
mkswap: Creates a Linux swap partition.
swapon: Enables the swap partition.
swapoff: Disables the swap partition.
sync: Writes data from the memory buffer to the disk.
resize2fs: Adjusts the size of ext2/ext3/ext4 filesystems.
System Permissions and User Authorization Commands (4)
chmod: Changes file or directory permissions.
chown: Changes the owner and group of a file or directory.
chgrp: Changes the user group of a file.
umask: Displays or sets the permission mask.
View System User Login Information Commands (7)
whoami: Displays the current effective user name, equivalent to executing id -un command.
who: Displays information about users currently logged into the system.
w: Displays a list of users logged into the system and the commands they are executing.
last: Displays users who logged into the system.
lastlog: Displays the last login information for all users in the system.
users: Displays a list of all users currently logged into the system.
finger: Searches for and displays user information.
Built-in Commands and Others (19)
echo: Prints variables or directly outputs specified strings.
printf: Formats the output to standard output.
rpm: Command for managing rpm packages.
yum: Command for automating the management of rpm packages.
watch: Periodically executes a given command and displays the output in full screen.
alias: Sets a system alias.
unalias: Cancels a system alias.
date: Views or sets the system time.
clear: Clears the screen, referred to as clearing the screen.
history: Views the history of executed commands.
eject: Ejects the optical drive.
time: Calculates the execution time of commands.
nc: A powerful network tool.
xargs: Converts standard input into command line arguments.
exec: Calls and executes commands.
export: Sets or displays environment variables.
unset: Deletes variables or functions.
type: Used to determine whether another command is a built-in command.
bc: Command-line scientific calculator.
System Management and Performance Monitoring Commands (9)
chkconfig: Manages Linux system startup items.
vmstat: Virtual memory statistics.
mpstat: Displays status statistics for each available CPU.
iostat: Statistics for system I/O.
sar: Collects comprehensive performance data for the system, including CPU, run queue, disk I/O, paging (swap area), memory, CPU interrupts, and network.
ipcs: Reports the status of inter-process communication facilities in Linux, including messages, shared memory, and semaphore information.
ipcrm: Used to delete one or more message queues, semaphore sets, or shared memory identifiers.
strace: Used for diagnosing and debugging Linux user space tracking. We use it to monitor the interaction between user space processes and the kernel, such as system calls, signal transmission, and process state changes.
ltrace: Command that tracks library function calls of a process and shows which library functions are called.
Shutdown/Restart/Logout and View System Information Commands (6)
shutdown: Shuts down the system.
halt: Shuts down the system.
poweroff: Turns off the power.
logout: Exits the current logged-in shell.
exit: Exits the current logged-in shell.
Ctrl+d: Shortcut key to exit the current logged-in shell.
Process Management Related Commands (15)
bg: Moves a command paused in the background to continue executing (runs in the background).
fg: Brings a command from the background to the foreground to continue running.
jobs: Views how many commands are currently running in the background.
kill: Terminates a process.
killall: Terminates processes by name.
pkill: Terminates processes by name.
crontab: Command for scheduled tasks.
ps: Displays a snapshot of processes.
pstree: Displays processes in a tree format.
nice/renice: Adjusts the priority of program execution.
nohup: Runs a specified command while ignoring hangup signals.
pgrep: Finds processes matching conditions.
runlevel: Views the current run level of the system.
init: Switches run levels.
service: Starts, stops, restarts, and shuts down system services, and can also display the current status of all system services.
IC Job Course Limited Time Benefits
To help more college students continue to improve and progress in their job search, mastering relevant professional skills and IC project experience, E Course Network has launched limited-time benefits including 6 Major Chip Design Employment Classes, IC Design Learning Card, and IC Backend Basic Training Course! If you want to enter the industry or improve, hurry up and scan the code to enjoy the latest discount!
Benefit One:
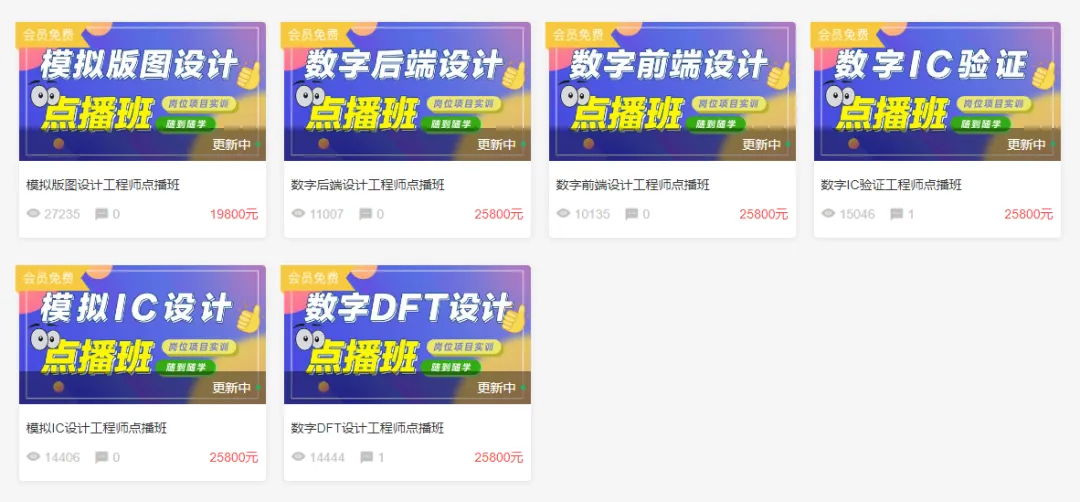
6 Major Chip Design Employment Classes and Qingying Course Discount of 1000 Yuan
E Course Network employment class courses are job-oriented, starting from basic Linux and gvim content with over 100 class hours, covering professional skills explanation for various positions, and the use of IC design EDA tools, highly practical and close to actual recruitment needs.
At the same time, each course is equipped with 2-3 IC design commercial projects that have been verified through tape-out, allowing students to practice running through the complete project process on the accompanying VNC server, enhancing engineering practice skills and mastering real and effective project experience.
Finally, E Course Network employment classes provide resume modification, mock interviews, internal recommendations from companies, and other employment services to help students increase resume submission opportunities, improve interview pass rates, and solve the last mile problem of employment, securing satisfactory offers.
From now on, registering for E Course Network employment classes and Qingying Course can enjoy a discount of 1000 yuan. After the event ends, the original price will be restored immediately. Interested students can scan the code to consult E Course Network teachers.
Scan the code to consult the course
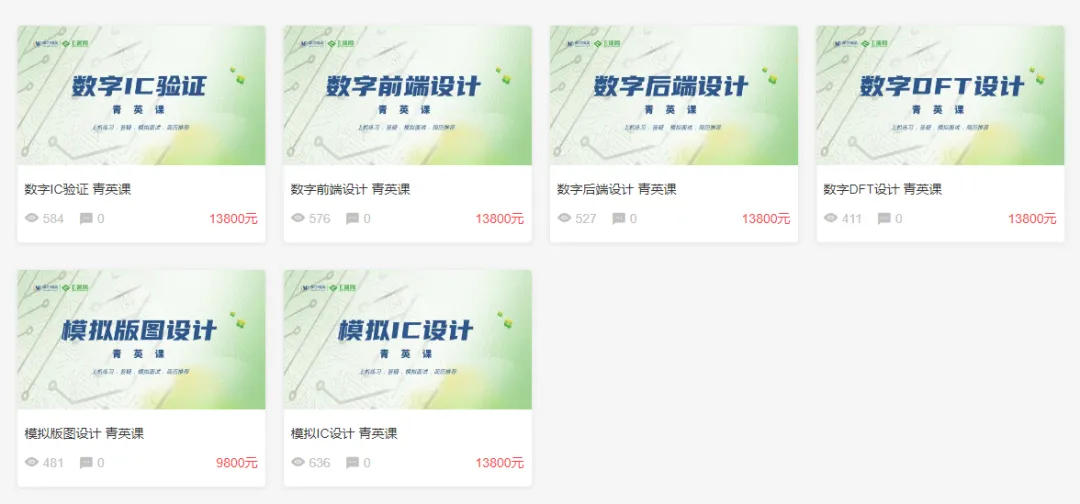
399 Yuan IC Design Learning Card with 1 Month Server Bonus
The IC Learning Card includes all basic courses in six major directions of chip design, totaling 21 courses, over 500 class hours! Less than 1 yuan per class hour!
All 21 courses are oriented towards the needs of IC design companies, establishing 6 major directions: design, verification, backend, DFT, analog design, and layout! There is also a general introductory course for the entire chip design process!
Course content is continuously optimized: PPT courseware, experimental manuals, and homework exercises! Students who need it can also use a VNC account for server practice, unlocking theoretical learning + practical environment data at once!
IC Learning Card is priced at 999 yuan on the E Course Network official website. During the event, the limited-time discount price is only 399 yuan, and you can also get 1 month of VNC account worth 2000 yuan, unlocking theoretical learning + practical environment data at once!
After this event ends, the price will return to 999 yuan immediately, and the VNC account will revert to 2000 yuan/month!
With the learning card, not only can you quickly master the fundamental knowledge of chip design, but you can also determine if you are suitable for a job in chip design. Each course can be completed in a few days, greatly improving learning efficiency! Interested students, hurry to consult and place orders!

Scan the code to consult the course
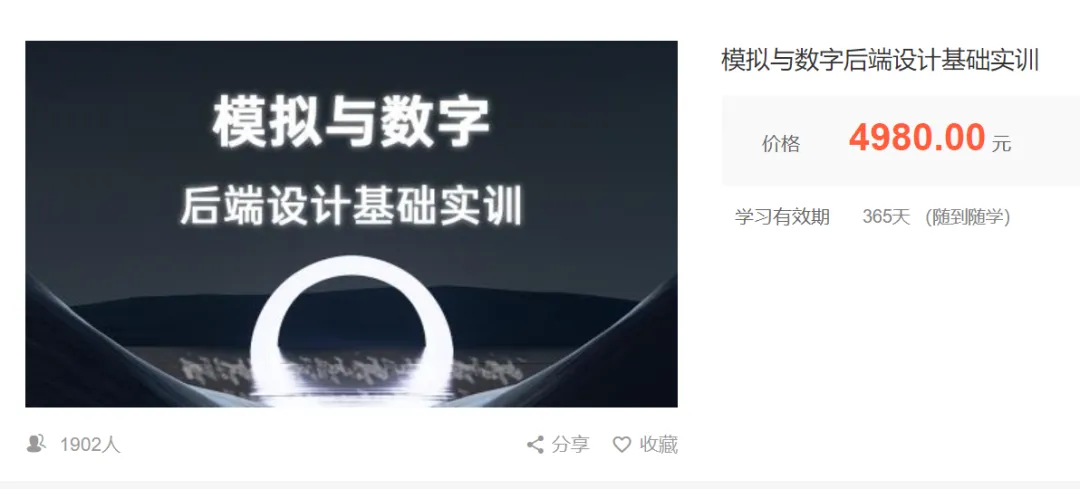
Digital Backend + Analog Layout Training Course Limited Time60% Off
The latest training course from E Course Network “Basic Training in Analog and Digital Backend Design”, covers the basic knowledge of digital backend design and analog layout design for two major positions, helping IC newcomers aiming for chip backend work to solidify their foundation and prepare adequately for job hunting.
This course has a total of 58 class hours and is equipped with 4 ALU experimental class hours at the end of the course, helping students practice in the lab, consolidating relevant skills and enhancing their resumes.
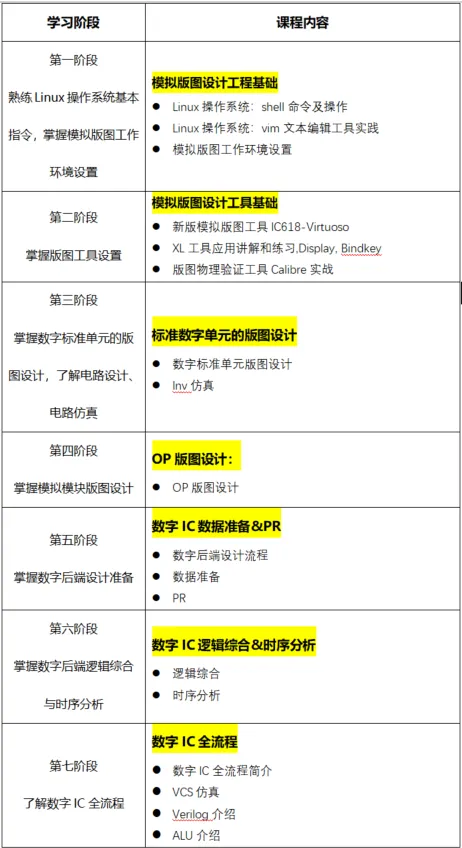
For detailed course content settings, please check the course outline below:
From now on, registering for this event course (a total of 58 class hours) can enjoy a 60% discount, with the discounted price being only 2980 yuan, and you can also get an additional 2 months of server access,completing the learning loop of theory and practice!
Students who want to master the professional skills of digital backend and analog layout and practice in the lab, hurry to scan the code for consultation, don’t miss this wave of discounts!
Scan the code to consult the course
E Course Network (www.eecourse.com) is a professional integrated circuit education platform under Moore Elite, dedicated to cultivating high-quality professionals in the semiconductor industry. The platform is oriented towards the job needs of integrated circuit companies, providing a training platform that fits the corporate environment, quickly training students to meet corporate needs.
E Course Network has a mature training platform, a complete curriculum system, and strong teaching resources, planning a high-quality course system of 168 courses in China’s semiconductor industry, covering the entire integrated circuit industry chain, and has 4 offline training bases. To date, a total of 15,367 people have been deeply trained, directly supplying 4,476 professional talents to the industry. It has established deep cooperative relationships with 143 universities and has held 240 corporate-specific IC training sessions.
 Source:www.cnblogs.com/chenliangchaoshuai/p/11827383.html,Author: Chen Liang, Thank you!
Source:www.cnblogs.com/chenliangchaoshuai/p/11827383.html,Author: Chen Liang, Thank you!







