Introduction
Linux is a type of Unix operating system, designed and developed by Linus Torvalds while studying at the University of Helsinki in 1991. Today, the Linux family has nearly 140 different versions that all use the Linux kernel.
Advantages of Linux Operating System
Free and Open Source: Open source code
Security: No need for antivirus software, no need to block adware and Trojans
Stability: Linux systems can run without failure for years
Multithreading, Multi-user: Support for multiple users and parallel operations
High Compatibility: Supports most biological software
LOGIN TO LINUX SYSTEM
Method 1
Log in to the Linux environment on your personal computer
Once the Linux server is established, we can log in to the server from a PC using commands or tools.
Method 2
Log in to the Linux server from Windows
1) Use software: putty
2) Download link:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1aOKwMZvQGIqQ2xn25MlNBg Extract code: rspi
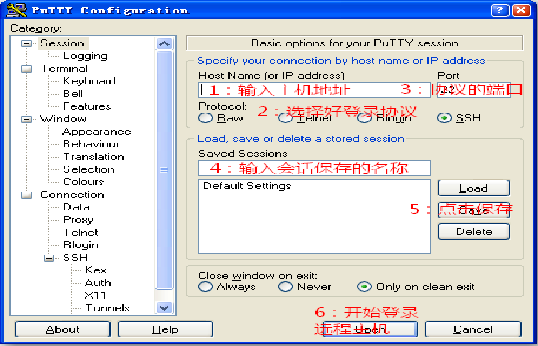
Image credit: Teacher Ju Jia
3) Log out: exit
Common Directory and File Operation Commands
01
Basic Concepts
Directory: Equivalent to a folder in Windows
File: Equivalent to a document or application in Windows
Path: The storage address of files or directories composed of various levels of directories
02
View Command Help Document
man [command_name]
$man pwd
1. A typical man manual includes the following sections:
NAME: The name of the command.
SYNOPSIS: A brief description of how to use the command.
DESCRIPTION: Detailed description of the command’s usage, including the functions of various parameter options.
SEE ALSO: Lists other related manual page entries that may be useful.
AUTHOR, COPYRIGHT: Information about the author and copyright.
2. Exit man command: q
help [built-in_command]
$help pwd
Used to view help for built-in Linux commands
Help outputs all built-in commands
03
Directory Operation Commands
Display current path: pwd
$pwd
/share/home/teacher
Change path: cd [directory]
Two methods to enter the basic folder:
1. Absolute path
$cd /share/home/teacher/Linux/basic
2. Relative path
$cd ./Linux/basic
Two ways to represent paths
1. Absolute path:
Starts from the root directory “/”, separated by “/” for each level of directories
/share/home/teacher/Linux
2. Relative path:
The position of the target directory relative to the current directory
. represents the current directory, (“./” is often omitted);
.. represents the parent directory;
~ represents the user’s home directory.
Enter the parent directory:
cd ..
Return to the previous directory before switching:
For example: $help pwd
Enter the personal home directory:
cd ~
cd
Display the contents of a specified directory in tree form: tree [directory]
tree displays the files and subdirectories in the current directory (default)
tree dir displays the files and subdirectories in the dir directory
$tree
.
|– asia
|– china
|– example
|– file1
|– file2
|– score.txt
`– world
3 directories, 4 files
Create directory: mkdir [directory]
mkdir dir0 creates dir0 directory in the current directory
mkdir -p dir0/sub1/sub2 recursively creates directories
Delete directory: rm –r [directory]
rm -r dir0 deletes directory dir0
04
Directory and File Operation Commands
List files or subdirectories: ls [directory]
ls displays information in the current path
ls -l displays detailed information in long format
ls -t displays information in chronological order
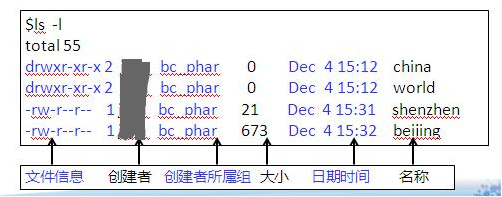
Image credit: Teacher Ju Jia
Copy files or directories: cp
cp file temp creates a copy of file as temp
cp file ./dir1 copies file to dir1 directory
cp -r ./dir1 ./dir2 copies directory dir1 to dir2 directory
Delete files or directories: rm
rm temp deletes file temp
rm -r ./dir2 deletes directory dir2 and its contents
Change file or directory name: mv
mv file1 file2 renames file1 to file2
mv ./dir ./DIR if the target folder ./DIR does not exist, renames dir to DIR
Move files or directories: mv
mv file ./dir file1 moves to dir
mv ./dir1 ./dir2 if the target folder ./dir2 exists, moves dir1 into dir2
05
File Operation Commands
View file content:
1. Display all: cat [file]
2. Display page by page: more [file] (Enter moves one line; Space moves one page, q to exit)
3. Scroll display: less [file] (Use up and down keys to navigate; q to exit view; can also view content in directory)
View part of a file:
1. Display first N lines (default 10 lines): head [-N] [file]
2. Display last N lines (default 10 lines): tail [-N] [file]
Display the number of lines in a file: wc -l [file]
$wc -l score.txt
7 score.txt
Display specified columns or fields in a file: cut [file]
cut -f1,3-5 refGene displays the 1st column and the 3rd to 5th columns in the file (default tab-separated)
$cut -f1,3-5 refGene
chr1 mRNA 1179157 1199097
chr1 mRNA 1207439 1217272
……
sort [file]: Sort the contents of the file in alphabetical order and output
1
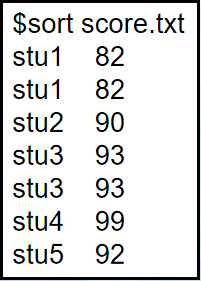
2
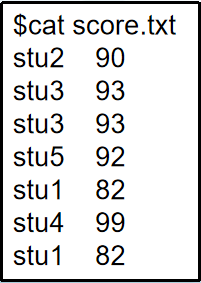
uniq [file]: Compare adjacent lines and display non-repeating lines
1
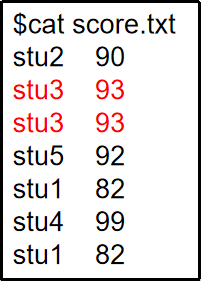
2
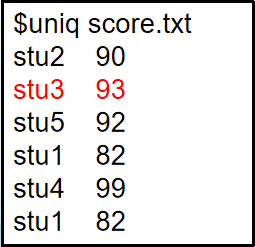
Note: The uniq command only removes adjacent duplicate lines; non-adjacent lines are not filtered.
uniq is often used with the sort command
$sort score.txt |uniq >score_uniq.txt
$cat score_uniq.txt
stu1 82
stu2 90
stu3 93
stu4 99
stu5 92
Common Operators
1. “|” Pipe operator
2. “>” Output redirection operator
3. “>>” Append operator
File Compression Backup: tar
1. Compress: tar zcf china.tar.gz china
2. Decompress: tar zxf china.tar.gz

Image credit: Teacher Ju Jia
06
Other Common Commands
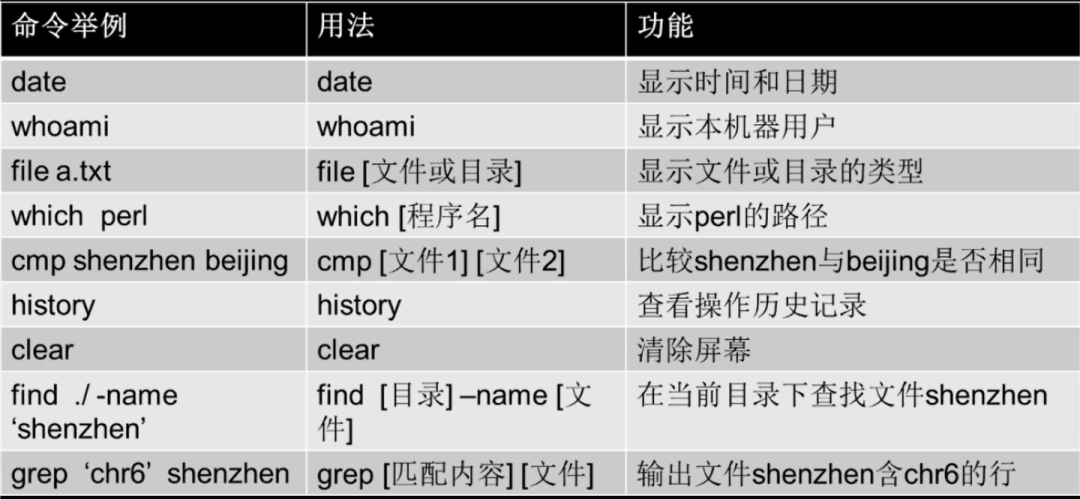
Image credit: Teacher Ju Jia
07
Precautions for Beginners During Operation
No such file or directory: Path or file name error, the computer cannot find it
Permission denied: Path or file name is correct, but operating in an inappropriate path, permission is not allowed
Command not found: Check for correct spelling; whether it is uppercase; whether there is a space between commands and between command and file name
Using the vi Editor
01
Basic Concepts
vi editor: The most famous editor under Linux, and a tool that we must master when learning Linux
Usage:
vi <filename_EXISTING>
or
vi <filename_NEW>
Edit a file or create a new file
02
Two Working Modes of Vi
1. Command mode: In this mode, you can save, exit, cut, paste, and perform other operations on the file. Any characters entered are treated as commands
2. Input mode: Used to input and edit files, the user’s typing will be displayed on the screen, written as text to the user’s file
Start vi: vi [filename]
For example: vi test.txt
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
“test.txt” [new file] 0,0-1 All
Edit File
Press the 【i】 key to edit the file
You can use the keyboard’s up and down arrows to move the cursor
1 A
2 B
3 C
~
~
~
~
~
— INSERT –1,3All
Save and Exit vi
Press the 【Esc】 key, then type “:wq” or “:q!”, and press 【Enter】
1 A
2 B
3 C
4 D
~
~
~
:wq
:wq Save and Exit
:q! Exit without saving
Common Commands
Need to be used in command mode, press 【Esc】 and then type the command
/CG search ‘CG’
:1,3 m 6 move the lines 1-3 to line 7
:1,3 co 6 copy the lines 1-3 to line 7
:1,3 d delete lines 1-3
:u Undo last change
:w Save the file but keep it open
Conclusion
01
Review of Common Commands
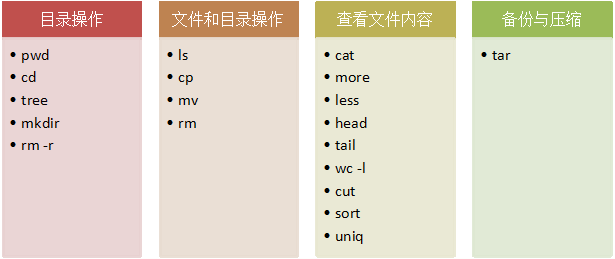
Image credit: Teacher Ju Jia
02
Using the Vi Editor
vi editor is the most commonly used text editor under Linux
vi editor has two working modes: input mode and command mode
As a bioinformatics worker, it is essential to master the above content!

Training Recommendations
1. Free Course | Linux Basics
2. Bioinformatics Training | Professional Skills Training for Genomic Data Analysis
Contact Us
Consultation Phone: 0755-36352045
Consultation Time: Monday to Friday 9:00-18:00
Consultation Email: [email protected]

Long press to follow our official account
▼

Follow our official account, reply with keywords to check:
Bioinformatics Certification┊Genetic Counseling Certification┊Joint Training Enrollment┊Certification┊
Offline Courses┊Online Courses┊ Micro Course Microbial Genomics┊Genomics┊SCI Writing┊RNA-Seq┊
R Plotting┊Gene Location Annotation┊Bioinformatics Introduction Tumor┊Single Gene Disease┊Precision Medicine┊Non-invasive Prenatal┊

BGI Genomics Academy
WeChat ID : bgicollege
Your best helper for gene technology learning!