Click↑↑Technical Training, follow and pinto subscribe for free long-term
190,000+Industrial control professionals follow this WeChat platform: technical sharing, learning exchange, industrial control videos
RS232 and RS485 are common interfaces in low-voltage applications. Many friends mention the differences between them, so today let’s learn about them together.
1. Physical Structure of Interfaces
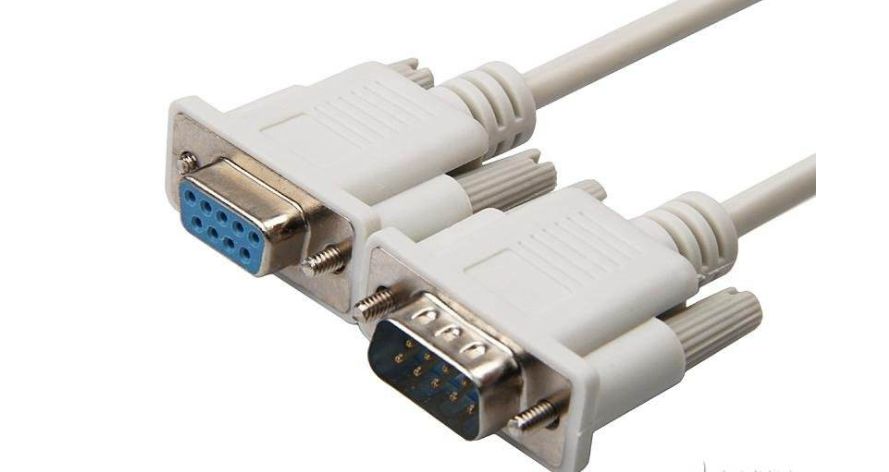
One of the computer communication interfaces, RS-232 typically appears in the form of 9 pins (DB-9) or 25 pins (DB-25). Generally, personal computers have two sets of RS-232 interfaces, referred to as COM1 and COM2.
The connector uses a DB-25 25-pin plug. Some devices connect to the PC using the RS-232 interface, which requires only three wires: “send data”, “receive data”, and “signal ground” as it does not use transmission control signals from the other party. Therefore, a DB-9 9-pin plug is used, and the transmission line is shielded twisted pair.
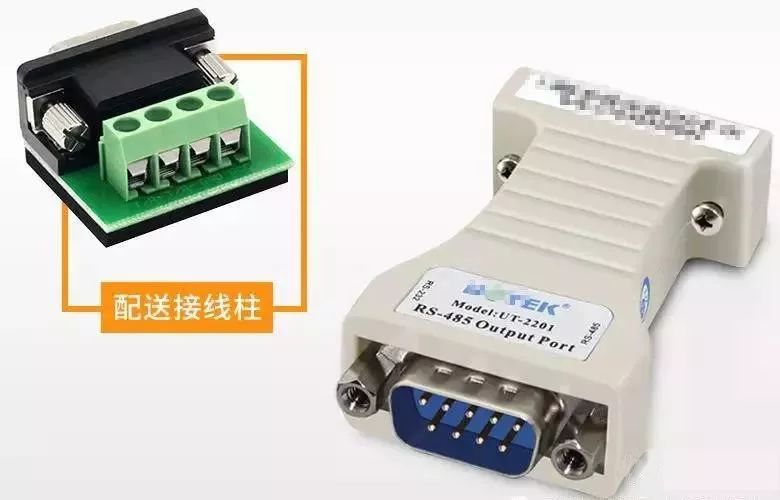
RS485 does not have a specific physical shape and is based on the actual engineering situation.
2. Electronic Characteristics of Interfaces
1. RS232:Transmits Voltage Level Signals
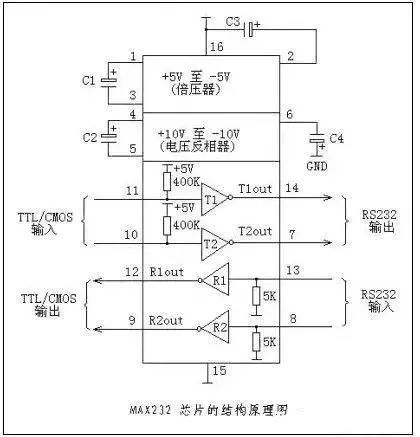
The signal voltage levels of the interface are relatively high (signal “1” is “-3V to -15V” and signal “0” is “3V to 15V”), which can easily damage the interface circuit’s chip. Also, since it is not compatible with TTL levels (0~”<0.8v”, 1~”>2.0V”), a level conversion circuit is required to connect to TTL circuits. Additionally, it has poor anti-interference capability.
2. RS485:Transmits Differential Signals
Logic “1” is represented by a voltage difference of + (2—6) V between the two lines; logic “0” is represented by a voltage difference of – (2—6) V. The signal voltage levels of the interface are lower than those of RS-232, making it less likely to damage the interface circuit’s chip, and this level is compatible with TTL levels, facilitating connections to TTL circuits.
3. Communication Distance
RS232 has a limited transmission distance, with a standard maximum transmission distance of 15 meters, and only supports point-to-point communication, with a maximum transmission rate of 20kB/s.
RS485 has a maximum wireless transmission distance of 1200 meters. The maximum transmission rate is 10Mbps, and only at a transmission rate of 100Kb/S can the maximum communication distance be achieved. Using impedance-matched, low-loss dedicated cables can achieve 1800 meters! Beyond 1200 meters, repeaters (up to 8) can be added, making the transmission distance nearly 10Km.
4. Support for Multi-Point Communication
RS232:RS232 interfaces only allow for the connection of 1 transceiver on the bus, so it cannot support multi-station transceiver capabilities and only supports point-to-point communication.
RS485:RS485 interfaces allow for the connection of up to 128 transceivers on the bus. This allows for multi-station communication capabilities, enabling users to easily establish a device network using a single RS485 interface.
5. Differences in Communication Lines
Can use three-core twisted pair, three-core shielded cable, etc.
Can use two-core twisted pair, two-core shielded cable, etc. In low-speed, short-distance, and interference-free situations, ordinary twisted pairs can be used; otherwise, for high-speed, long-line transmission, dedicated RS485 cables with impedance matching (generally 120Ω) must be used (STP-120Ω (for RS485 & CAN) one pair 18AWG), and in environments with severe interference, armored twisted shielded cables (ASTP-120Ω (for RS485 & CAN) one pair 18AWG) should be used.
Since the transmission distance of RS232 is only 15 meters, what is its purpose?
In fact, its application is very wide, as it can connect various devices, such as monitoring, upgrading or debugging other devices, etc. Its function is similar to that of USB; as USB ports become more common, more devices that convert USB to RS-232 or other interfaces will emerge.
Through the USB interface, more RS-232 devices can be connected, achieving higher transmission speeds and true plug-and-play, while solving the drawback of USB interfaces being unable to transmit over long distances (USB communication distance is within 5 meters).
Source: Internet, copyright belongs to the original author, infringement will be deleted.
Share good articles, just clickto view~
Click↓Read the originalFree learning electrical, PLC, and other electrical knowledge