RS-232, RS-422, and RS-485 are all serial data interface standards. RS-232 is the most widely used serial interface for PC communication. RS-232 is defined as a single-ended standard that increases communication distance in low-speed serial communication. RS-232 uses an unbalanced transmission method, known as single-ended communication, while the RJ45 interface is typically used for data transmission, with the most common application being network card interfaces.
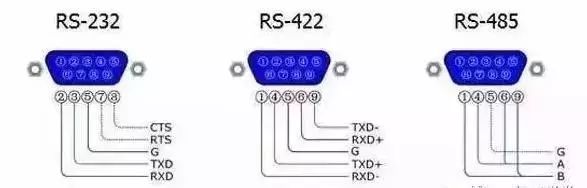
RS-232 is designed for point-to-point communication (i.e., using only one pair of sending and receiving devices), with a driver load of 3-7kΩ. Therefore, RS-232 is suitable for communication between local devices. The RS-422 and RS-485 serial interface standards differ from RS-232 in that data signals use differential transmission, also known as balanced transmission, employing a pair of twisted pairs. In early PC communications, RS-422 had a maximum transmission distance of 4000 feet and a maximum transmission rate of 10Mb/s.
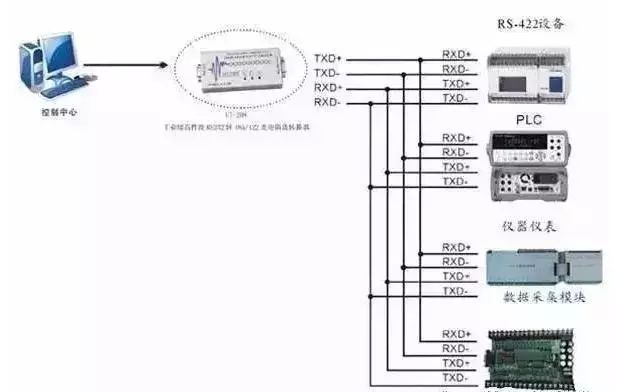
Like RS-422, RS-485 has a maximum transmission distance of approximately 1219 meters and a maximum transmission rate of 10Mb/s. The length of the balanced twisted pair is inversely proportional to the transmission rate; the specified maximum cable length can only be used at rates below 100kb/s. The highest rate transmission can only be achieved over very short distances. Generally, the maximum transmission rate over a 100-meter long twisted pair is only 1Mb/s. These asynchronous serial communication interfaces are used in computer measurement and control systems. RS232C is the serial bus standard formally established by the American Electronic Industries Association and is currently the most commonly used serial interface standard for data communication between computers and between computers and peripherals. The RS232C serial interface bus is applicable for communication distances not exceeding 15 meters, with a maximum transmission rate of 20kB/s.
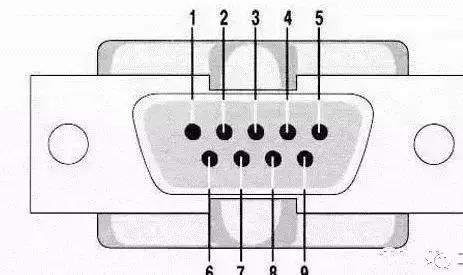
A complete RS-232C interface has 22 wires using a standard 25-pin plug. RS-232C uses logic levels where logic “1” is -5V to -15V, and logic “0” is +5V to +15V.
Disadvantages: Slow data transmission speed, short communication distance, unspecified calibrated connectors, and susceptibility to crosstalk between signals at the interface.
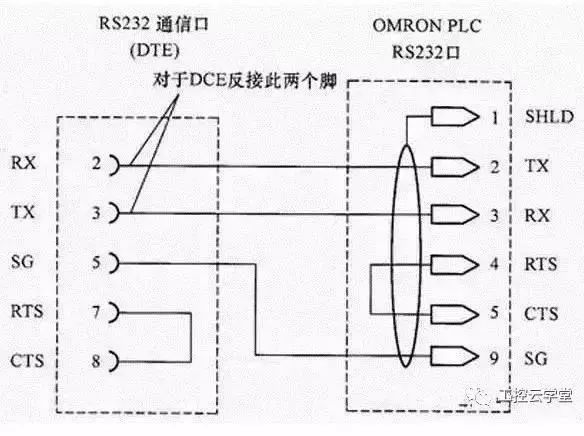
1. RS-232
Is a serial physical interface standard established by the American Electronic Industry Association (EIA). RS stands for