For more content, please click on ABB Robot Practical Skills above to follow.
You can also click the official account below Classic Articles to browse more content.
For reprints, please leave a message in the background first, let’s support original content together and promote the use and development of robots.
This official account provides technical support for various ABB robot applications, simulations, and graduation projects. For details, please leave a message in the background.
1) On-site robots act as PROFIBUS slaves and communicate with PLC.
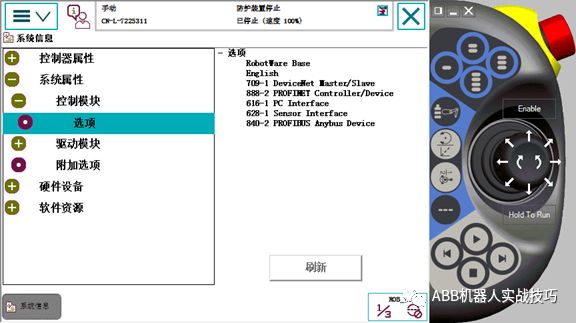
2) The robot needs to have the following option: 840-2PROFIBUS Anybus Device.
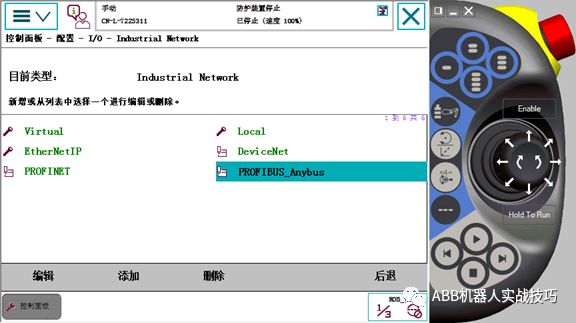
3) Teach pendant – control panel – configuration – IO – Industry Network – PROFIBUS ANYBUS.
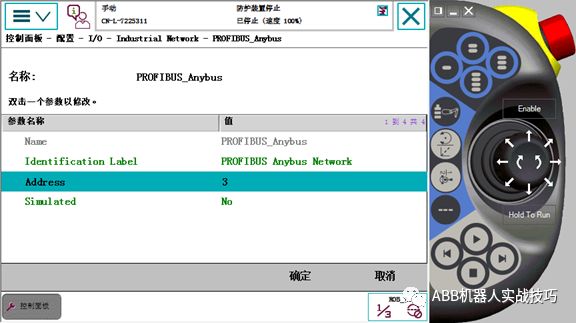
4) Modify the station number.
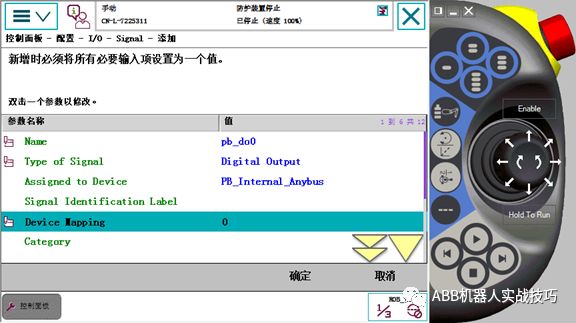
5) Signal: create a new signal, input Name, select type, choose the device as PB_Internal_anybus, and set mapping.
Click Read Original to learn about robot studio simulation and get the complete teaching video.
More Content
Voice control of ABB robots.
Mobile access to web control of robots.
Calculate distance between two points.
Cross Connection Viewer.
New I/O DSQC1030 configuration.
Two robots communicating via DEVICENET.
Defining TCP for four-axis robots.
Grouping input/output high and low byte issues.
Recalculate TCP after tool change.
Configuring servo welding gun for ABB robots.
Different calling methods for routine programs.
Configuring PROFINET master for ABB robots.
How to move after robot collision.
Teaching four points to complete stacking.
Setting to not prompt for angle path faults.
Introduction to ABB robot options.
Improving robot trajectory accuracy.
Configuring PROFINET master for ABB robots.Methods for multi-tasking with ABB robots.
SearchL command.
External PLC selecting robot program.
ABB robots batch quickly create IO signals.
One-click return to HOME program.
Trajectory speed color scale display and event display.
Batch modification of position data on the teach pendant.
View and set robot variables via web.
Secondary development: installing pcsdk and loading dll.
Introduction to spot welding commands and data.
Introduction to glue dispensing commands and data.
Modifying the upper and lower limits of each axis of the robot.
Explaining Wobjdata data.
Preventing robot pre-reading.
Real-time graphical display of robot speed on the teach pendant.
4 robots collaboration – Transformers.
Disabling and recovering interrupts.
Custom function to check HOME position.
Stop and stop moving commands.
Connection between conveyor tracking and vision.
Wiring for emergency stop and automatic stop.
Dual robots + guide rail coordinated bending.
[Original] Happy New Year YUMI Collaborative Programming.
[Original] Programming for dual robots and positioners.
[Original] Using ABB robot Pdisp trajectory offset.
[Original] Differences in ABB robot data storage types.
[Original] Creating stacking programs with ABB robots.
[Original] How to create dynamic gripper tools.
[Original] How to capture DI pulse signals during robot program execution.
[Original] How to create arrays with ABB robots.
[Original] Creating custom data types with ABB robots.
Long press to recognize the QR code and follow ABB Robot Practical Skills.
