In the field environment of Profibus, the systems we use are diverse, and the devices we are interfered with are varied, so the sources of interference are also peculiar. Many failures caused by interference are more difficult to troubleshoot than other failures. Before eliminating interference faults, we need to understand the types of interference.
To summarize: the types of interference are as follows:
-
Power Interference
Often, due to interference introduced by the power supply, there are many cases of PLC control system failures or even shutdowns, as the control system is generally powered directly by the power grid. Since the power grid usually has a wide coverage, with numerous devices within the network, especially when the operating environment and load of the power grid change, such as large switch operations, frequent startup and shutdown of large equipment, and harmonics caused by AC and DC drive devices, all of which can directly affect the power grid, and transmit through the power grid to the incoming end of the enterprise’s power equipment, leading to a significant decline in power quality. In severe cases, it can even cause damage to the electrical equipment, so isolation devices or purification devices are generally installed at the incoming power supply of the enterprise’s automation equipment, but the effectiveness varies greatly due to differences in device performance.
-
2. Signal Interference
During the onsite wiring construction in the metallurgy industry, there are often high-voltage and high-current lines very close to signal lines and communication lines, with frequent startup and shutdown of high-load electrical equipment. This situation is likely to cause rapid changes in the magnetic field around the signal and communication lines, thus interfering with the transmission of line signals. The interference introduced into the system can cause instability in analog signals, abnormal operation of digital signals, interruption of communication data, and in severe cases, can lead to communication interruptions, site loss, or even system paralysis due to instability of various signals, and can even cause irreparable damage to system hardware.
-
3. Load Interference
In the control systems of the petroleum industry, there are often many loads with energy storage characteristics, and without signal isolation devices or surge absorbers, when the control contacts switch, it can generate back electromotive forces that are several times or even tens of times higher than the power supply voltage, which can have a significant impact on related equipment in the system.
-
Ground Interference
The PLC control panel has a potential difference with the ground, and a standardized and well-functioning grounding system can reduce interference currents caused by this potential difference. Interference mixed into signal lines and communication cables can be introduced to the ground via grounding wires, thereby reducing the impact of interference. Unqualified ground wires and non-standard grounding methods are often significant causes of ground interference.
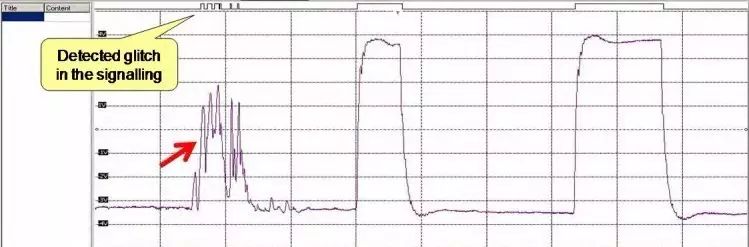
On project sites, various types of interference should be comprehensively resolved based on the actual situation. First, proper cable wiring and shielding work must be done, and shielding must be done between control cables and various signal lines. Control cables should be placed separately, and the Profibus-DP twisted pair should avoid being laid in the same route as other signal lines, control cables, and high-voltage power cables to minimize interference sources. During wiring, the shielding layer must be properly connected, leaving an appropriate length of the shielding layer to avoid contact with the inner wires.
Secondly, good grounding is an important measure to prevent interference in field buses. “Ground” is generally selected as the reference point of zero potential, and grounding establishes a path between two contact nodes, connecting the electrical equipment to the “ground”. The main purpose of grounding is to protect people and equipment safety and to reduce electromagnetic interference, etc. Attention to securing communication interfaces is also very important. Besides grounding, the impact of other equipment power and cables on communication signals is also significant. Where conditions permit, devices and power supplies with good isolation performance should be selected to isolate wiring as much as possible. Additionally, for interference on analog signals, a large number of analog signal isolators (also known as signal transmitters) should be used to resist interference. Signal isolators provide three-way isolation and signal conditioning for various analog signals, greatly reducing signal interference. Due to their strong anti-interference capability, installing signal isolators has become a common method in automated control systems, and their field applications are very widespread.
5.Conclusion
Profibus has become a very important field bus standard due to its many advantages, and the widespread application of the Profibus bus network has led to various network faults during installation, debugging, and field operation. Some faults are very complex and difficult to troubleshoot. Appropriate diagnostic methods and tools should be selected based on the characteristics of the faults for analysis and diagnosis, quickly locating and addressing faults to shorten debugging time or reduce downtime, thereby increasing factory efficiency. Through this research analysis, it is hoped to provide reference and assistance to the industrial automation field using Profibus.