In the current field of industrial automation, EtherCAT (Ethernet for Control Automation Technology) has been widely used as a high-performance, real-time industrial Ethernet communication protocol. With its efficient data transmission capabilities, precise synchronization performance, and flexible topology, it has become an indispensable part of many automation systems. As the basic unit in the EtherCAT network, the performance and cost of EtherCAT slaves directly affect the competitiveness and application range of the entire system. There are various EtherCAT slave solutions available on the market, each with its unique characteristics and applicable scenarios. Below, we will detail several major EtherCAT slave solutions.

1. Traditional Beckhoff ET1100 Chip Solution
Beckhoff, as the founder and main promoter of EtherCAT technology, has its ET1100 series chips as a benchmark in EtherCAT slave solutions. This type of solution typically includes a master control chip, an ESC (EtherCAT Slave Controller), and a PHY (Physical Layer). The master control chip is responsible for processing application logic, the ESC handles the EtherCAT communication protocol, and the PHY is responsible for the physical layer signal transmission.
The advantage of this solution lies in its stability and reliability, which have been validated over a long period in the market, and it supports various complex EtherCAT functionalities. However, its drawbacks are also evident, namely the high cost. The need for separate ESC and PHY chips, along with potentially additional peripheral circuits, makes it difficult to reduce the overall hardware cost. In the increasingly competitive environment of the domestic general product market, this high-cost solution is becoming less adaptable to market demands.
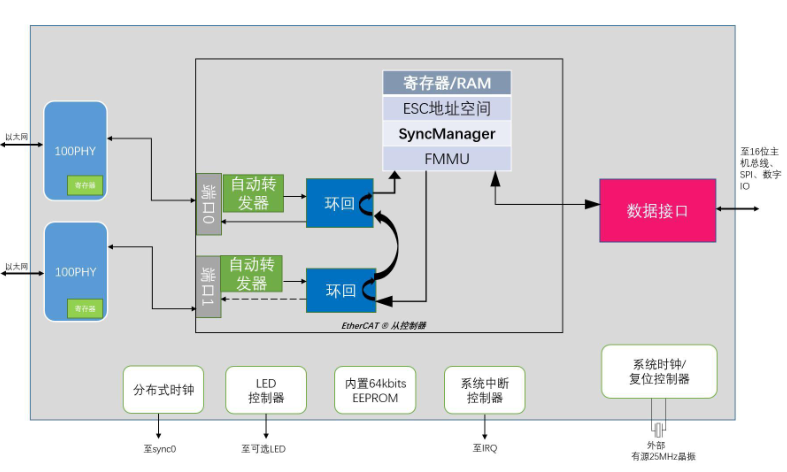
2. ESC Solutions Integrated with PHY
To reduce costs, some manufacturers have begun to introduce ESC solutions integrated with PHY, such as LAN925 and AX58100. These solutions combine the ESC and PHY into one, reducing the number of hardware components and thus lowering costs. Additionally, the integration of PHY also enhances the performance and stability of signal transmission.

The advantages of this solution include relatively low costs and improved signal transmission performance and stability due to the integration of PHY. However, the flexibility of this solution may be somewhat affected, as it does not allow for the free selection of different PHY chips to meet specific application needs like traditional solutions. Furthermore, the high integration of ESC and PHY raises higher requirements for manufacturers’ R&D capabilities and production processes.
3. Master Control Integrated ESC Solutions
With the development of microelectronics technology, some manufacturers have begun to offer master control integrated ESC solutions, such as Renesas’ n2l series and certain products from Infineon. These solutions integrate ESC functionality into the master control chip, making the entire system more compact and efficient. Since the master control chip handles both application logic and the EtherCAT communication protocol, this solution has a clear performance advantage.
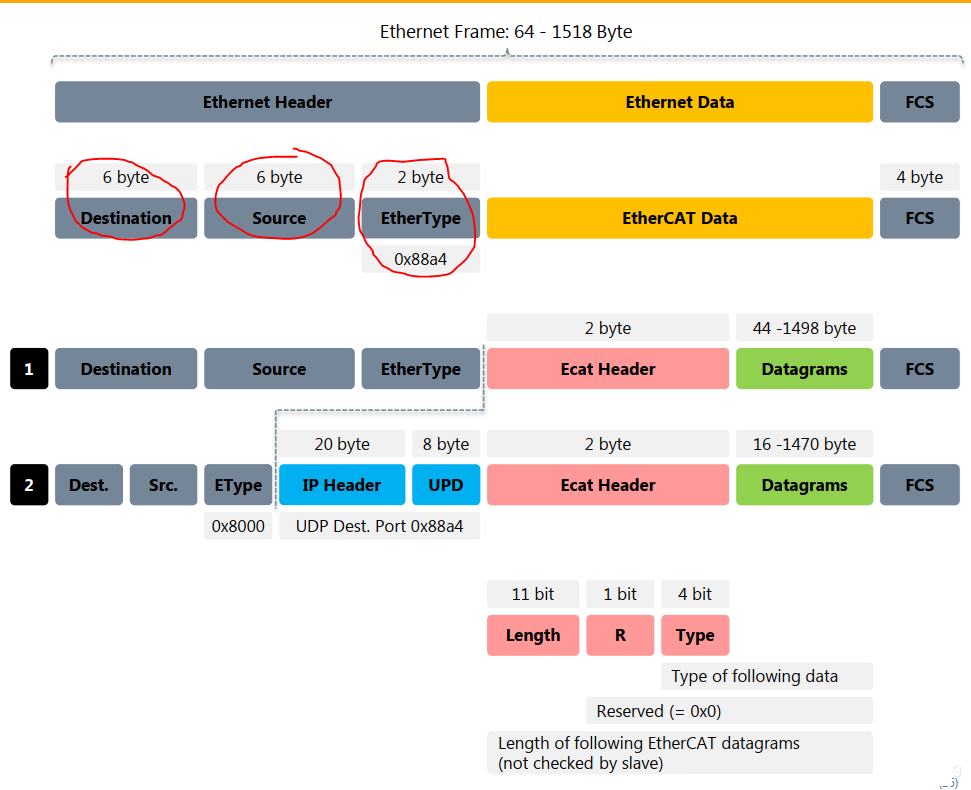
The advantages of this solution include low cost, high integration, and superior performance. By integrating ESC functionality into the master control chip, the number and complexity of hardware components are reduced, thereby lowering costs. Additionally, since the master control chip simultaneously processes application logic and the EtherCAT communication protocol, the overall system’s response speed is faster and efficiency is higher. However, this solution requires high R&D capabilities and production processes for the master control chip, and the integration of ESC functionality into the master control chip may impact the chip’s versatility.

4. FPGA Integrated IP Core or Direct Implementation of EtherCAT Solutions
In addition to the aforementioned solutions, there is a more specialized EtherCAT slave solution, which involves integrating EtherCAT IP cores into an FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) or directly using FPGA to implement EtherCAT functionality. This solution offers extremely high flexibility and customizability, allowing the EtherCAT slave’s functionality and performance to be tailored to specific application needs.
However, the R&D costs for this solution are relatively high, requiring strong FPGA development capabilities and experience. Additionally, due to the limited hardware resources and performance of FPGAs, there may be certain limitations when handling complex EtherCAT functionalities. Furthermore, directly using FPGA to implement EtherCAT functionality demands a high level of expertise and experience from the R&D personnel, and it may require a longer development cycle and higher R&D costs.
Currently, there are various EtherCAT slave solutions available on the market, each with its unique characteristics and applicable scenarios. When selecting a specific solution, it is essential to consider actual application needs, cost budgets, R&D capabilities, and other factors comprehensively. With the continuous advancement of technology and the ongoing development of the market, it is believed that more excellent EtherCAT slave solutions will emerge in the future, injecting new vitality into the development of the industrial automation field.