Recently, I have been organizing IP assets and need to check the IP occupancy status.There are many methods to determine whether an IP has been assigned, and the simplest way is to ping the target host to see if there is a response. The fping tool can provide batch ping functionality, and it needs to be installed first:
apt-get install fping The command to ping a subnet is:
The command to ping a subnet is:
fping -g 192.168.10.0/24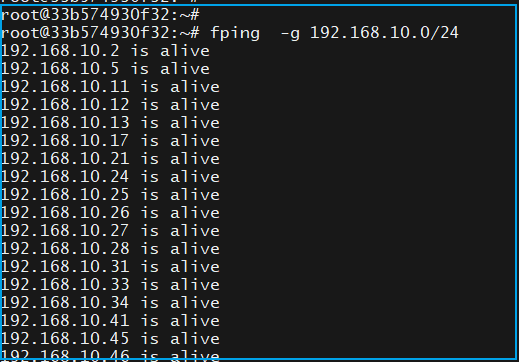 The output at the end of the command will provide the addresses that are not reachable:
The output at the end of the command will provide the addresses that are not reachable: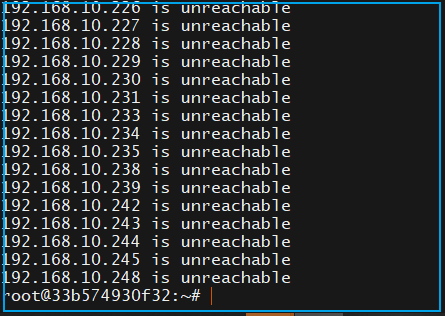 The results of the ping command do not prove that these IPs are not occupied, as firewalls can block pings.The command to prevent a host from pinging itself in Linux is:
The results of the ping command do not prove that these IPs are not occupied, as firewalls can block pings.The command to prevent a host from pinging itself in Linux is:
iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -j DROPAt this point, ICMP packets are unreachable, and the other party cannot determine if the host is online through ping. Instead, arping can be used to check if the other party is online.The arping command does not use ICMP packets but rather ARP broadcast messages.ARP broadcast messages are broadcasted within the same subnet, and if the other party is online, it will be forced to respond. Regardless of whether the other party wants to or not, if you call out to them, they will respond like Sun Wukong answering the Golden Horned and Silver Horned Kings with “I am here!”The arping command also needs to be installed in advance:
apt-get install arpingTo test if you can arping the other address while ICMP packets are disabled: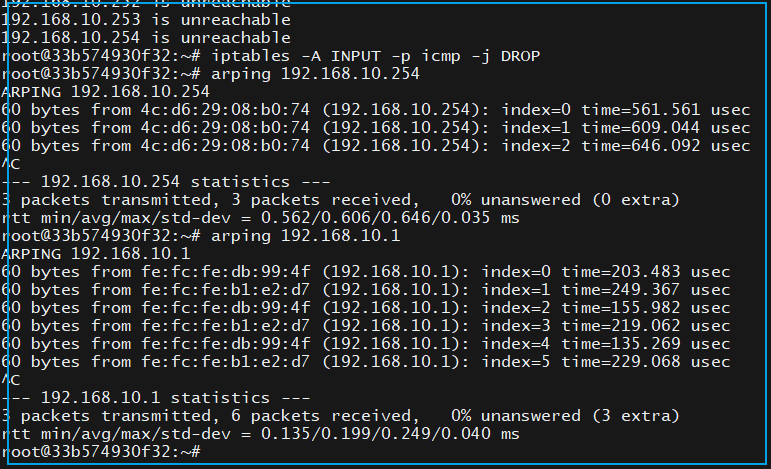 Among them, the ping or fping commands can cross subnets, while arping cannot.Using tcpdump, you can detect the “greetings” from the switch, as all packets are handed over to the switch for addressing.The switch addresses using the MAC address table. Therefore, the switch has the MAC addresses of all IPs.If the IP in the packet is not registered in the switch, the switch needs to “learn”. The learning process involves broadcasting ARP requests everywhere. By listening to the network card with tcpdump, we can know who is online.
Among them, the ping or fping commands can cross subnets, while arping cannot.Using tcpdump, you can detect the “greetings” from the switch, as all packets are handed over to the switch for addressing.The switch addresses using the MAC address table. Therefore, the switch has the MAC addresses of all IPs.If the IP in the packet is not registered in the switch, the switch needs to “learn”. The learning process involves broadcasting ARP requests everywhere. By listening to the network card with tcpdump, we can know who is online.
tcpdump -nq -i eth0 arp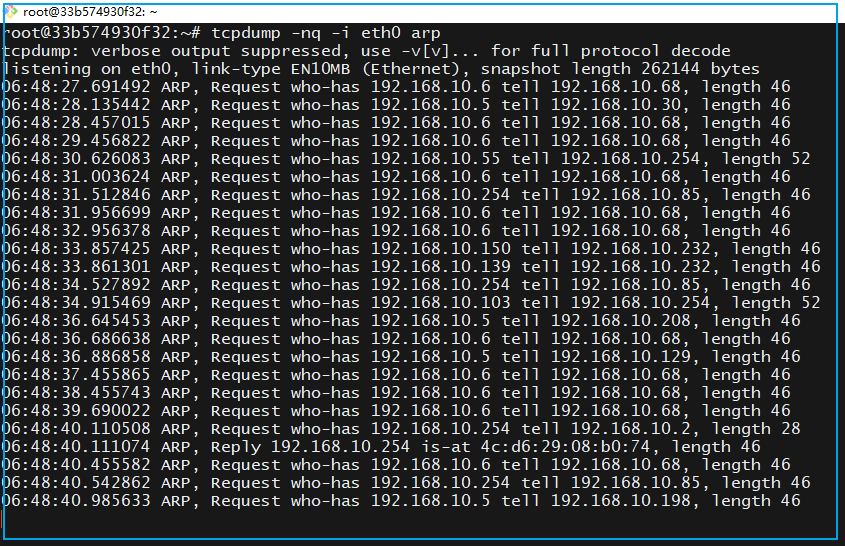 The above command means to listen to ARP packets on the eth0 network card.The following segment who-has IP tell 192.168.10.254
The above command means to listen to ARP packets on the eth0 network card.The following segment who-has IP tell 192.168.10.254
Request who-has 192.168.10.96 tell 192.168.10.254192.168.10.254 is the gateway, which is on the switch, meaning the switch is asking, who has the MAC address for 192.168.10.96?There are many requests for 192.168.10.6, indicating that many hosts need to communicate with it. However, it is clear that this IP is no longer in use, leading to continuous ARP requests directed at this IP within the VLAN.By listening to ARP packets, we can draw two conclusions:
- IPs that have not responded are free IPs.
- There are still data requests between these IPs (software configuration needs to be checked).
Listening to packets can only assist in judgment and cannot actively identify which IPs are free. Our goal in pinging the other party is to determine whether the IP is occupied or online.The most direct method is to log into the switch and check the ARP table.For example, on a Huawei switch, a command to check if an IP is online is:
display arp | include 192.168.10.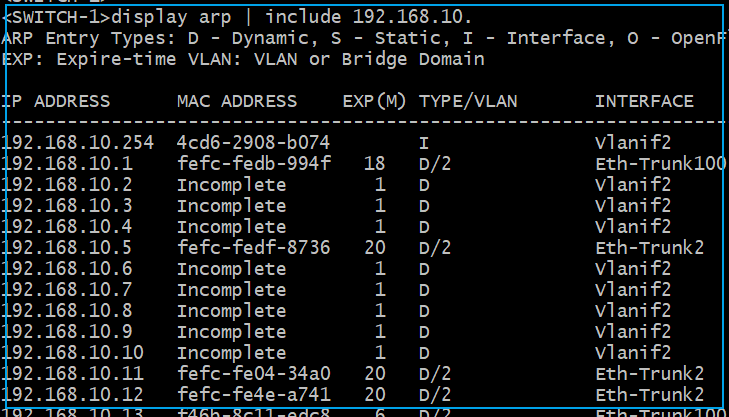 IPs marked as Incomplete are offline; if they have been offline for a long time, it indicates that the IP is free. Of course, only administrators have access to the switch. If you do not want to alert the administrator, you can discreetly use client tools for judgment.End of article.
IPs marked as Incomplete are offline; if they have been offline for a long time, it indicates that the IP is free. Of course, only administrators have access to the switch. If you do not want to alert the administrator, you can discreetly use client tools for judgment.End of article.