

At that time, he uploaded a video on Bilibili, showcasing the process of using his homemade robotic arm to sew grapes remotely in a bathroom! The barrage of comments was lively.
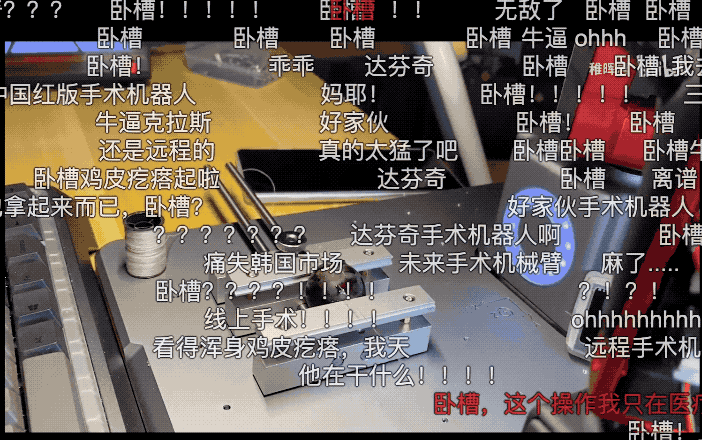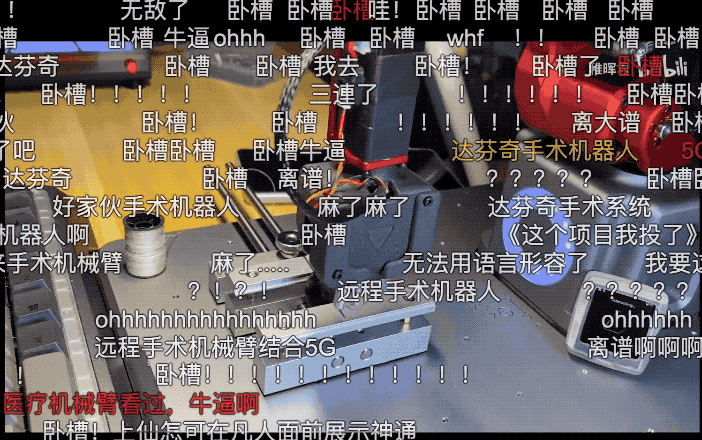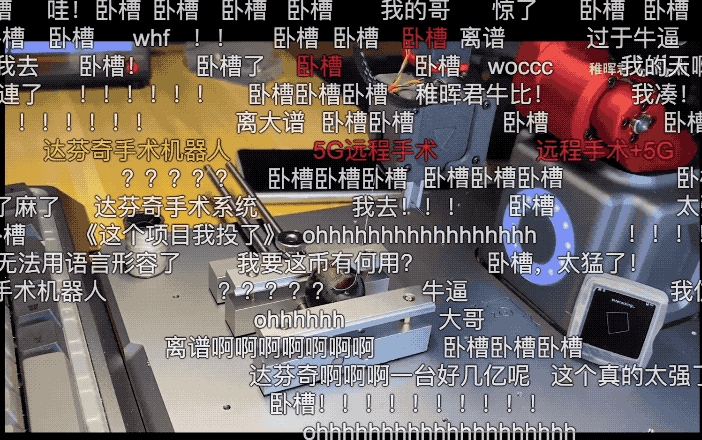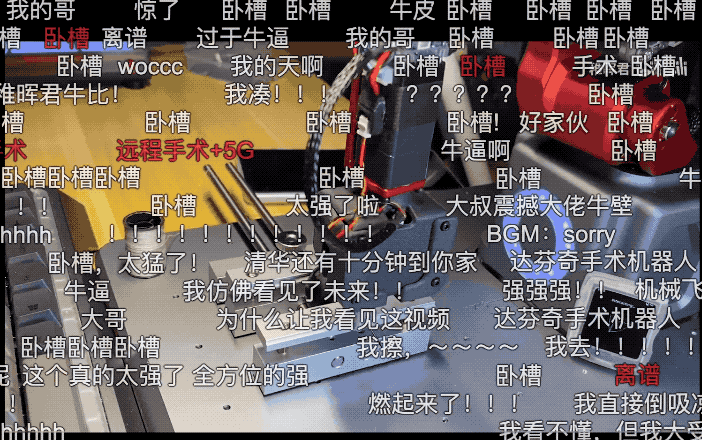

-
Clearer application scenarios: Compared to humanoid robots, robotic arms have clearer and broader application scenarios in industrial automation, logistics, and service industries, and they also have a price advantage. -
Mature technology system: The technology of robotic arms has developed over decades, forming a relatively mature technology system and industrial chain, which is more conducive to integrating embodied multimodal large models.
-
More competitive cost pricing: The R&D and manufacturing costs of humanoid robots are much higher than those of robotic arms, especially in achieving complex human movements and perception capabilities. The high costs result in a very long investment return cycle and profit cycle for humanoid robots. -
Greater policy support: From automobile manufacturing to electronic product assembly, robotic arms have become an indispensable part of industrial automation due to their high efficiency, precision, and reliability, with increasing policy support.

-
One is the generalization issue of constructing the “base model” of robotic arms and the motion control solutions in real scenarios.
-
Another is the current issue of integrating the popular “fusion of vision, language, and action” embodied multimodal large models.
-
Lastly, we focus on exploring how robotic manipulation can approach human capabilities.







