
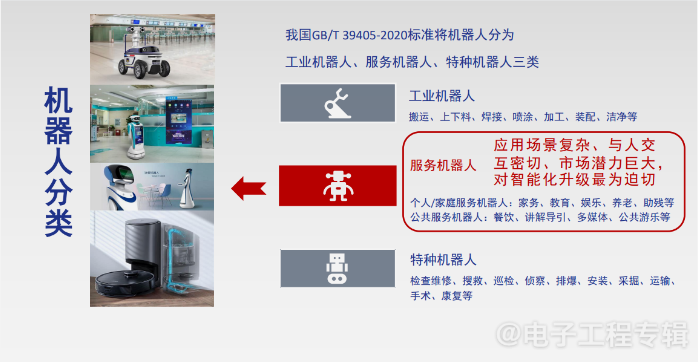
-
Industrial robots, whose main functions include handling, loading and unloading, welding, spraying, processing, assembling, and cleaning; -
Service robots, which are further divided into personal/family service robots and public service robots. The former mainly includes household chores, education, entertainment, elderly care, and assistance for the disabled, while the latter mainly includes dining, guiding, multimedia, and public entertainment; -
Special robots, whose main functions include inspection and maintenance, search and rescue, patrol, reconnaissance, bomb disposal, installation, mining, transportation, surgery, and rehabilitation.

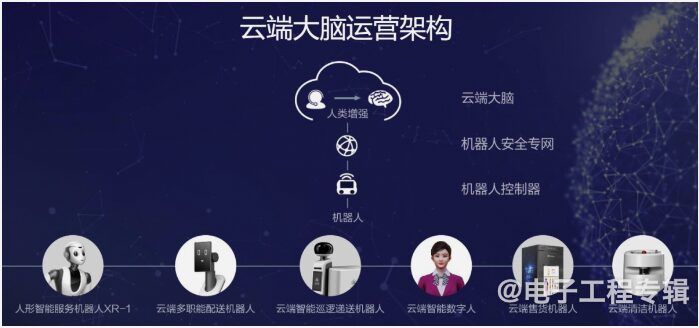


-
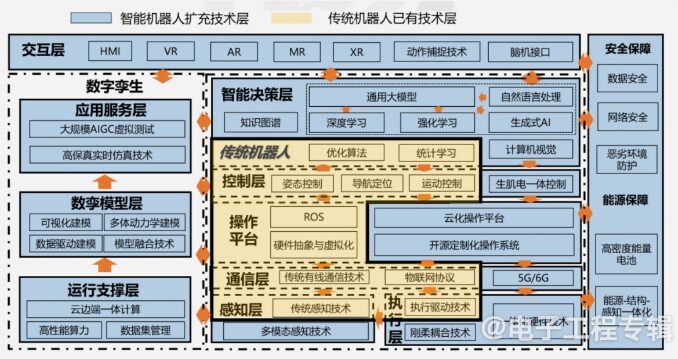
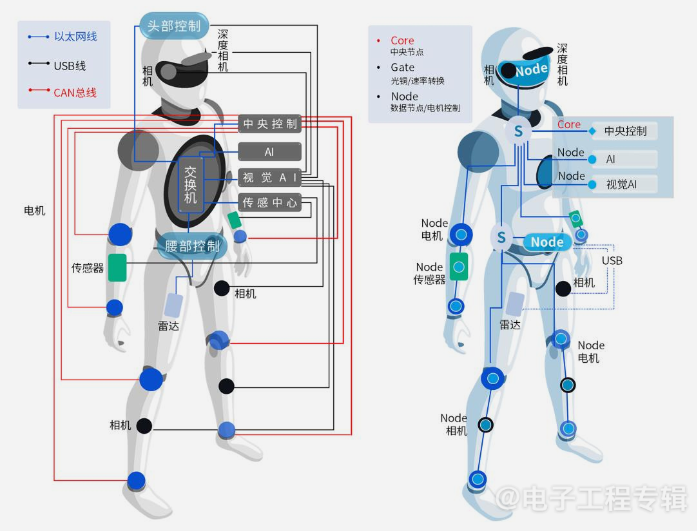
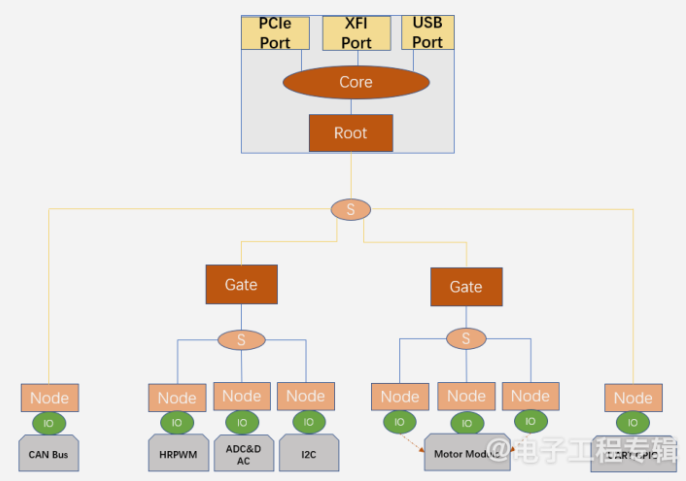
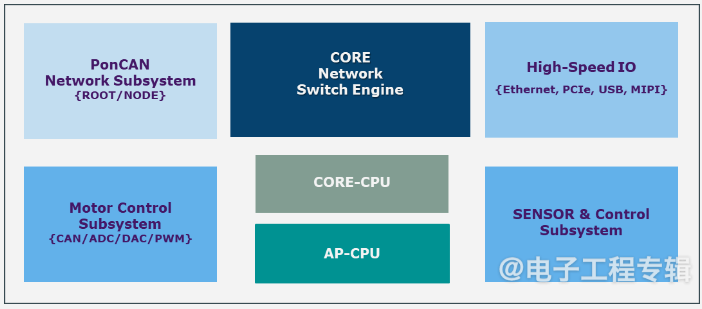
Super complex motor control: Robots have 30-50 or more joints. -
Super numerous sensor access: Robots need to connect to an increasing number of sensors. -
Delicate appearance design: Robots are developing towards more miniaturization, with limited space. -
Bandwidth delay: Upgrading Ethernet solutions to over 1G networks is a significant challenge, with high latency and packet loss rates. -
Communication standards: Multiple protocols coexist, causing a lack of uniformity.

-
Men Remain Boys Until Death: The First SMT Solder Paste Machine in the Hands of Older Men
-
Disassembling a 9.9 Yuan Shipping Charging Button Night Light
-
Sharing Several High-Quality Free Circuit Design Software
-
Disassembling a Handheld Thermometer: Cost-Cutting Operations Everywhere
-
Jumping Jobs in the U.S. Is Innocent; When Will Domestic Follow Suit?
