In today’s rapidly evolving software development landscape, ensuring high quality and reliability of code is a core objective for every development team. Static testing, as an efficient quality assurance method, is gradually becoming an indispensable part of the development process. It analyzes the syntax, structure, processes, and interfaces of source code without executing the program, helping developers identify and correct potential issues in the early stages, significantly reducing later repair costs and enhancing the overall quality of the software.
Steps for Implementing Static Testing
1. Preparation: Laying the Foundation for Testing
Before starting static testing, thorough preparation is key to ensuring a smooth testing process. First, it is essential to clarify the objectives and scope of the testing, determining the code areas, functional points, and key targets that static testing needs to cover. This step helps the team focus on critical areas and avoid resource wastage. Next, a detailed testing plan should be developed based on the objectives and scope, including task assignments, personnel distribution, and timelines. Additionally, selecting appropriate tools is an important part of the preparation work. Choosing code review tools or static code analysis tools based on requirements can ensure the efficiency and accuracy of the testing work. Finally, setting up an environment suitable for static testing, including hardware, software, and network configurations, provides assurance for the smooth conduct of testing.
2. Implementing Testing: In-Depth Code Review
Once the preparation work is complete, the implementation phase of static testing can begin. Code review is one of the core tasks in this phase. By manually or using automated tools to inspect the code line by line, developers can identify defects, errors, or non-compliance with standards. Furthermore, using static code analysis tools to scan the code can further uncover potential defects, security vulnerabilities, and quality issues. This process not only helps developers identify risks early but also provides a basis for subsequent code optimization. Additionally, recording, classifying, and tracking identified defects to ensure each issue is properly addressed is an important part of defect management. Maintaining close communication with developers, testers, and others can help collaboratively identify and resolve issues that arise during testing, enhancing the overall efficiency of the team.
3. Result Analysis and Reporting: Summary and Feedback
The final stage of static testing is analyzing and summarizing the test results. Statistically analyzing the test results, including defect types, quantities, and distributions, helps the team understand the current state of code quality and provides a basis for future improvements. Writing a test report is an important task in this phase, detailing the test objectives, scope, processes, results, and improvement suggestions. The test report serves as a crucial basis for team communication and decision-making, as well as providing management with a clear summary of the testing. Additionally, it can verify the defects fixed by developers, ensuring that issues are thoroughly resolved, which is a key aspect of testing effectiveness. Finally, feedback on the test results should be provided to relevant personnel, and the static testing process should be optimized based on the results to help the team continuously improve testing effectiveness and enhance software quality.
PC-lint Plus: A Powerful Assistant for C/C++ Development
Among numerous static testing tools, PC-lint Plus (hereinafter referred to as PCLP) stands out with its powerful features and wide range of applications. PCLP is a static code analysis tool specifically designed for C and C++ development, widely used in software development. It deeply analyzes source code to identify potential defects, security vulnerabilities, and non-compliance with coding standards, helping developers recognize and fix these issues in the early stages, thereby enhancing the quality and reliability of the software.
The highlights of PCLP’s features are as follows:
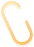
-
Comprehensive static analysis with high customization, capable of deeply scanning C and C++ source code to detect various issues such as logical errors, memory leaks, and unused variables.
-
Supports various industry standards, such as MISRA C/C++, AUTOSAR and CERT C, ensuring code compliance with strict industrial requirements.
-
Supports C++11, C++14, and C++17 standards, ensuring compatibility with modern development environments.
-
Multi-platform support: supports Windows, Linux and macOS among various operating systems.
-
Supports various development environments, including but not limited to Visual Studio Code, Code Composer Studio and IAR compilers.
-
Widely used in software development companies, individual developers, and educational institutions, particularly suitable for industries with high code quality requirements, such as automotive, avionics, and medical devices.
This article will also introduce how to call PCLP for static code analysis through the built-in plugin of VectorCAST. This method is applicable to VectorCAST 2022 SP5 and later versions, with the 2024 SP6 version being used in this article.
Configuring and Adding the MISRA C 2012 Rule Library
1) Open the rules.lnt file in the Windows directory of the PCLP configuration package and modify the absolute path of au-misra3.lnt to point to the local PCLP installation directory’s au-misra3.lnt.
If needed for testing, other rule libraries can also be added to the tool, and the method for adding them is to include the absolute path of the library in the rules.lnt file.
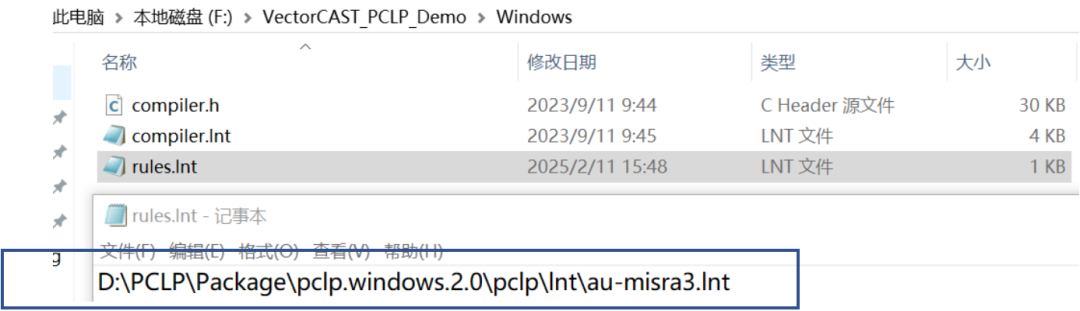
2) Open VectorCAST, select Help->Example Environments to build a C language sample environment.
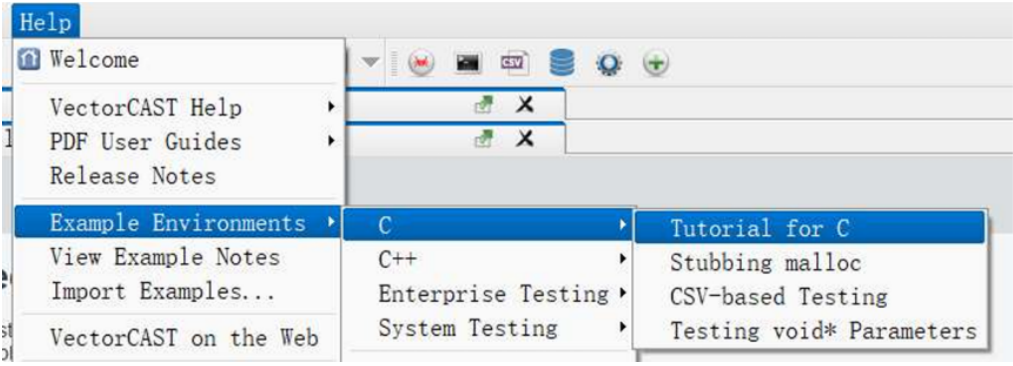
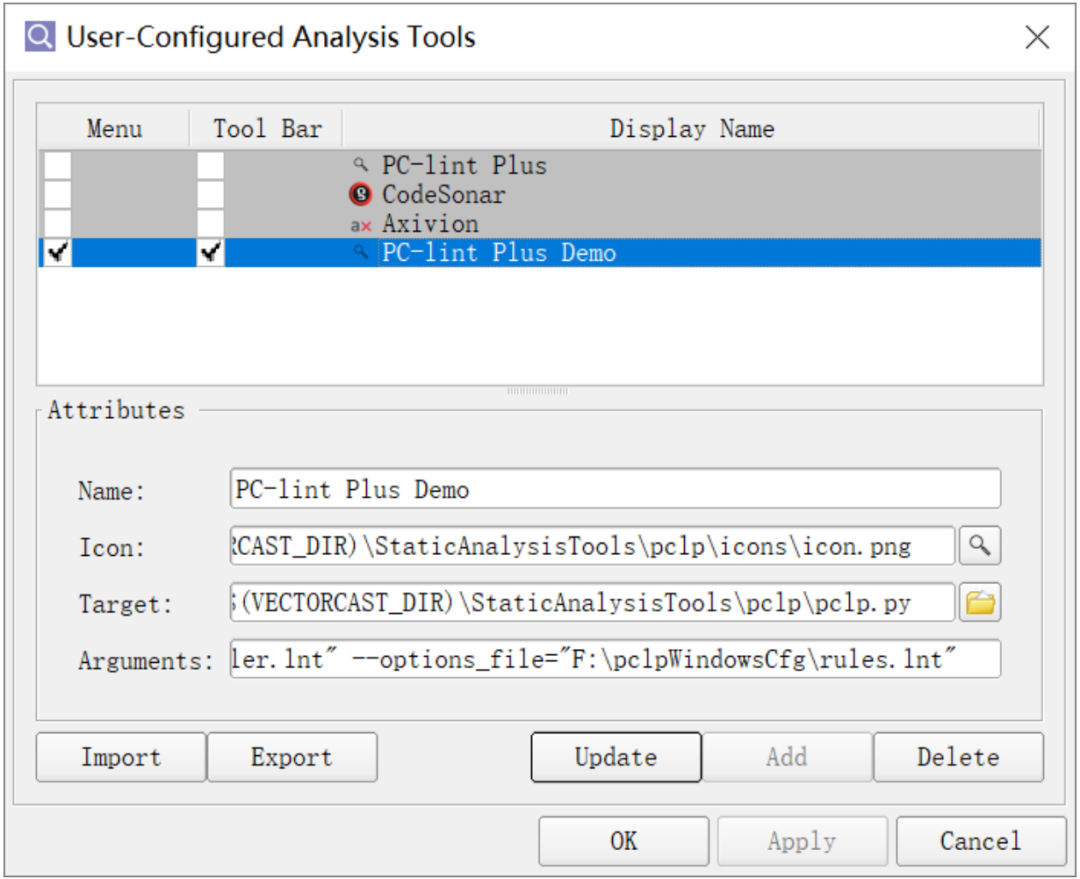
3) After successful construction, select Static Analysis->Edit Analysis Tools from the menu bar.

4) Select the PC-Lint Plus icon:
a) Customize the plugin name in the Name field below;
b) In the Arguments field below, write parameters based on this example.
–PCLP_CMD=”PATH\pclp64.exe”
–compiler_options_file=”PATH\compiler.lnt”
–options_file=”PATH\rules.lnt”
Then click the Add button.
Here, the –PCLP_CMD in Arguments points to the local PCLP software’s pclp64.exe path, –compiler_options_file points to the path of compiler.lnt in the configuration package, and –options_file points to the path of rules.lnt in the configuration package.
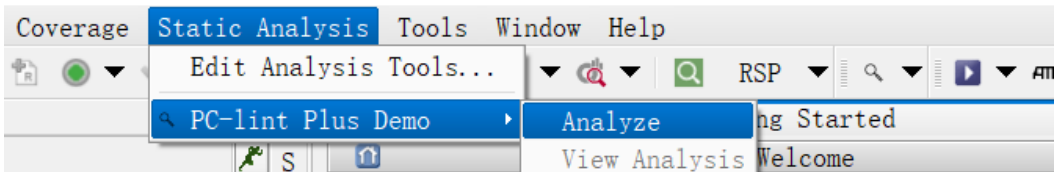
5) After saving the options, follow the instructions in the image below to perform static analysis and view risk alerts in the VectorCAST interface.
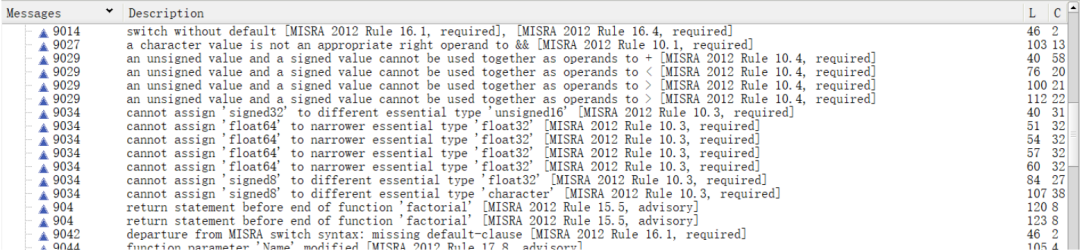
These results indicate that there are risks described in the rule library within the code. By modifying the code to eliminate risks, the risk alerts in the report can be reduced.
Once the PC-lint Plus testing environment is configured, it can be used to test other code.
Thus, the PC-lint Plus testing environment is set up, and now the journey of code testing can begin.
Conclusion
Through static testing, development teams can identify those “invisible flaws” in the code early on, and with powerful tools like PC-lint Plus, resolve these issues one by one. Throughout the process, not only is the quality of the code improved, but the reliability of the software is also ensured, allowing development teams to face complex project requirements and tight delivery timelines with greater confidence.
END
Dongxin Chuangzhi has been deeply engaged in various fields such as electronic and electrical architecture development, in-vehicle bus communication and diagnostic testing, vehicle control system XIL simulation testing platforms, control system and vehicle function testing services, embedded software development and integration services, etc., committed to providing customers with safe and reliable R&D tools and “localized, rapid, customized, and productized” solutions. Dongxin Chuangzhi not only maintains a leading position in traditional automotive electronics fields, such as CAN/LIN/Ethernet development and testing, control system function testing, vehicle function validation testing, control system HIL simulation platforms, AUTOSAR software development and services, but also continuously invests in R&D for emerging technologies, such as ADAS intelligent driving simulation, HMI testing and validation, SOA architecture development, V2X testing and validation, OTA testing and validation, information security and functional safety, achieving gratifying results. Dongxin Chuangzhi has several experienced technical service teams that are “daring to challenge, eager to progress, good at fighting, and loyal to customers,” integrating global high-quality resources with many partners to provide customers with “efficient, high-quality, and high-value” products and services.
Previous Recommendations:
MISRA C and MISRA C++: Guardians of Automotive Software Safety