To see the virtuous and aspire to be like them, to see the unvirtuous and reflect on oneself. —The Analects of Confucius, Chapter on Benevolence
The security industry is an important sector born from the modern society’s demand for safety. With continuous technological advancements, video surveillance technology has evolved from “seeing” to “seeing far,” “seeing clearly,” and finally to “understanding.” This evolution has propelled the industry from analog surveillance to digital surveillance, network high-definition surveillance, and ultimately into the era of intelligent surveillance. Each leap in technology is inseparable from the innovation of upstream core technologies.
In security monitoring systems, image sensors serve as core components, undertaking the critical task of converting optical signals into electrical signals, generating high-quality digital images or videos, and providing visual monitoring data for the system. The performance of these sensors directly affects the clarity, sensitivity, and intelligence level of the monitoring system, making them one of the core driving forces behind the industry’s development.
1. Introduction
SmartSens Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. (stock abbreviation: SmartSens, stock code: 688213) is a high-tech enterprise engaged in the research, design, and sales of CMOS image sensor chip products. Headquartered in the Minhang District of Shanghai, China, the company has established R&D centers in multiple cities and countries. Since its inception, SmartSens has focused on innovation and research in high-end imaging technology, gaining recognition and favor from numerous clients due to its performance advantages. As a company dedicated to providing CMOS image sensor products that cover multiple application scenarios and full performance requirements, SmartSens’s products have been applied in various fields, including security monitoring, machine vision, intelligent automotive electronics, and smartphones. SmartSens adheres to the vision of “using cutting-edge intelligent imaging technology to help people better see and understand the world,” with customer needs as the core driving force, continuously promoting the upgrade of cutting-edge imaging technology, expanding product application fields, and working with partners to advance the deep development of future intelligent imaging technology.
2. SC5336P Parameters
Resolution: 5 Megapixels
Pixel Array: 2888H x 1628V
Pixel Size: 2.0um x 2.0um
Maximum Image Transfer Rate: 2880H x 1620V @30fps 10bit
Optical Size: 1/2.7″
Output Interface: 8/10-bit 1/2 Lane MIPI
Output Format: RAW RGB
CRA: 15°
Sensitivity: 2806 mV/lux.s
Dynamic Range: Linear mode 75.4dB; HDR mode 85.69dB
Signal-to-Noise Ratio: 36.7 dB
Operating Temperature Range: -30°C~+85°C
Optimal Operating Temperature: -20°C~+60°C
Power Supply: Analog AVDD=2.8V, IO Voltage DOVDD=1.8V, Core Voltage DVDD 1.5V default external power supply.
Package Size: 35-pin CSP, 6.450mm x 4.226mm
ESD Level: HBM Classification 2, CDM Classification C3
3. Design References and Considerations
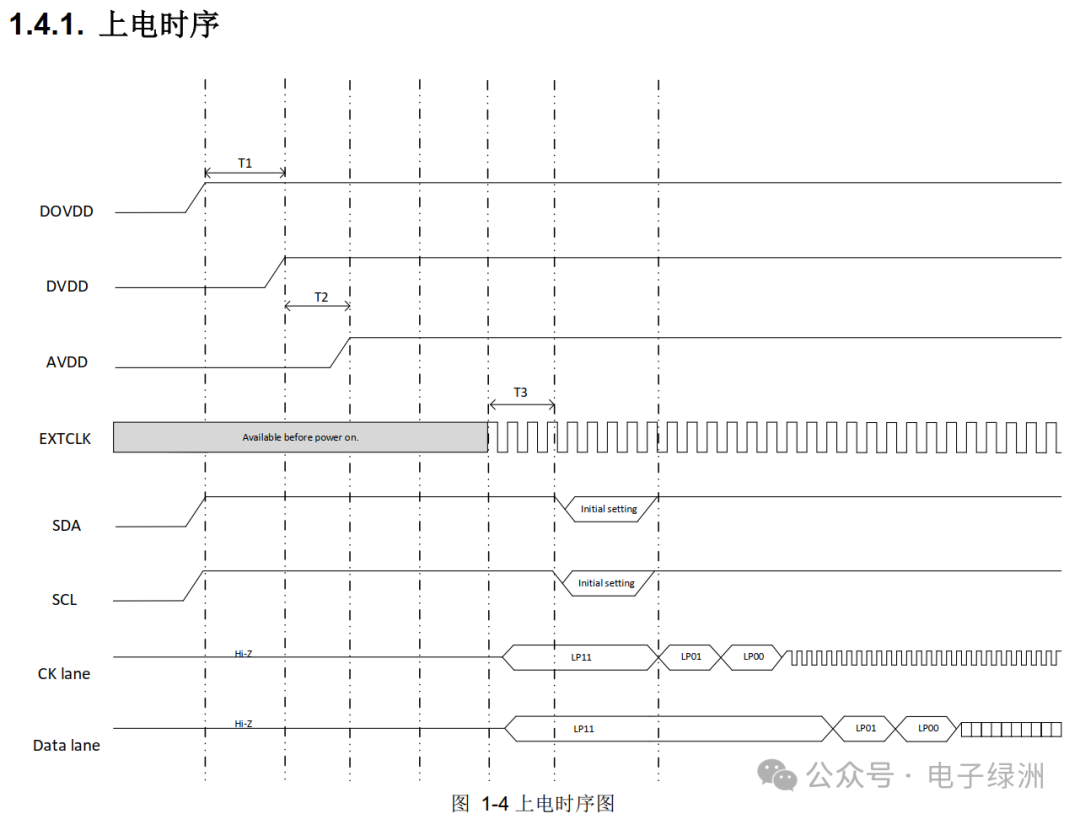
1. Power-Up Timing
1) T1≥0ms, T2≥0ms, T3≥4ms
2) DOVDD > DVDD > AVDD > MCLK (software controlled)
Hardware Design Considerations:
A. The timing design for power supplies of 1.8V, 1.5V, and 2.8V must be noted.
B. The core voltage DVDD of 1.5V cannot be omitted.
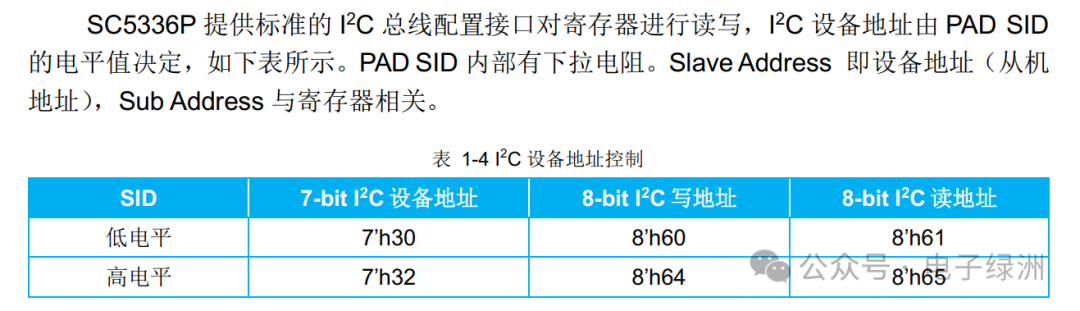
2. I2C Address
The SID pin is the configuration pin, with a built-in pull-down resistor, defaulting to low level, corresponding to Device ID 7’h30.
Hardware Design Considerations:
A. The I2C write address is the I2C device address shifted left by one bit, and the I2C read address is the I2C write address plus one.
B. In typical binocular designs, a single I2C bus is shared, with one sensor pulled low and the other pulled high.
3. MIPI Interface
Supports 1/2 lane data transmission, with each pixel supporting 8/10bit, and a transmission rate not exceeding 1.0Gbps.
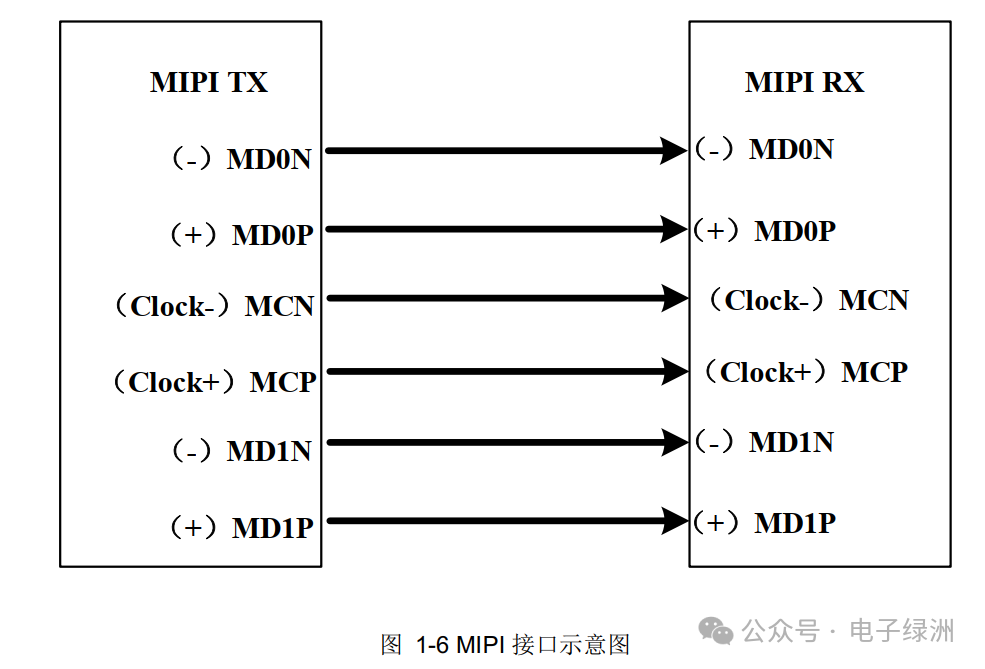
Hardware Design Considerations:
A. The length requirement for differential pairs is 10mil, and the spacing requirement for differential pairs is 100mil.
B. Avoid placing resistors in series or capacitors in parallel with differential pairs. In high-speed mode, the typical differential voltage is 200mV.
C. During layout, ensure that the three pairs of differential lines have complete reference ground and are not segmented. Avoid drilling holes, and if necessary, ensure there are return ground vias.
4. AEC/AGC
AEC/AGC are both adjusted based on brightness, with AEC adjusting exposure time and AGC adjusting gain, ultimately keeping the image brightness within a set threshold range.
AEC/AGC Control Strategy:
The SC5336P does not have AEC/AGC functionality; it needs to be implemented through the backend platform. In the entire AEC/AGC process, it is not an independent adjustment of the sensor’s exposure time or gain; the adjustment strategy is: prioritize exposure time, and when the exposure time reaches its maximum and cannot be further adjusted, then adjust gain. For example, in the case of an image being too dark, the adjustment sequence is: ① do not enable any gain until the exposure time reaches its limit; ② after the exposure time reaches its limit, start calling automatic gain control. It should be noted that enabling gain will directly lead to a multiple amplification of average noise; increasing exposure time will help improve the signal-to-noise ratio. Conversely, when the image is too bright, gain should be disabled first, and if the image is still too bright after all gain is disabled, then reduce the exposure time. Exposure time and gain form an interactive adjustment system that should be considered comprehensively during debugging.
Hardware Design Considerations:
A. During long-term reliability testing, the software can set the AGC gain to maximum, as hardware issues may become more apparent.
For example, if the analog voltage of 2.8V has significant ripple, it may cause stripes; excessive temperature may lead to severe thermal noise.
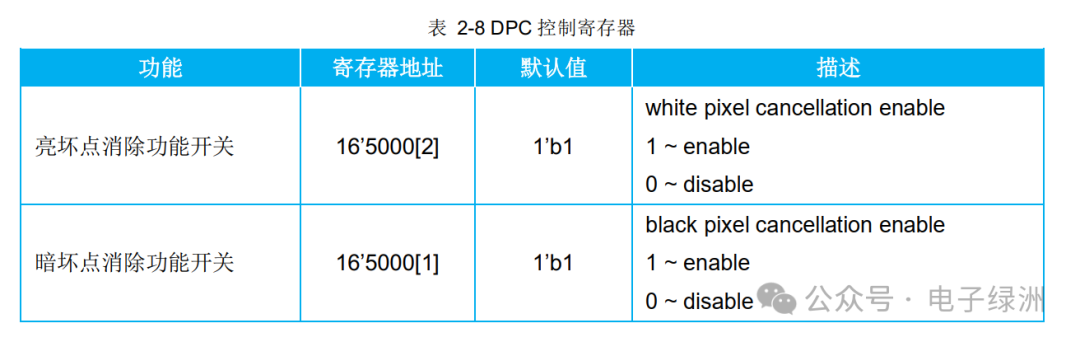
5. DPC Function
DPC: Defect Pixel Correction.
The principle of defect pixel judgment is that the current pixel value is greater (or less) than the values of surrounding pixels of the same color, and the difference exceeds a set threshold.
The SC5336P classifies defect pixels into bright defect pixels (white pixels) and dark defect pixels (black pixels) based on this principle.
Hardware Design Considerations:
A. When introducing a new sensor, strictly control the number of defect pixels, for example, 30 (Light mode), 30 (Dark mode).
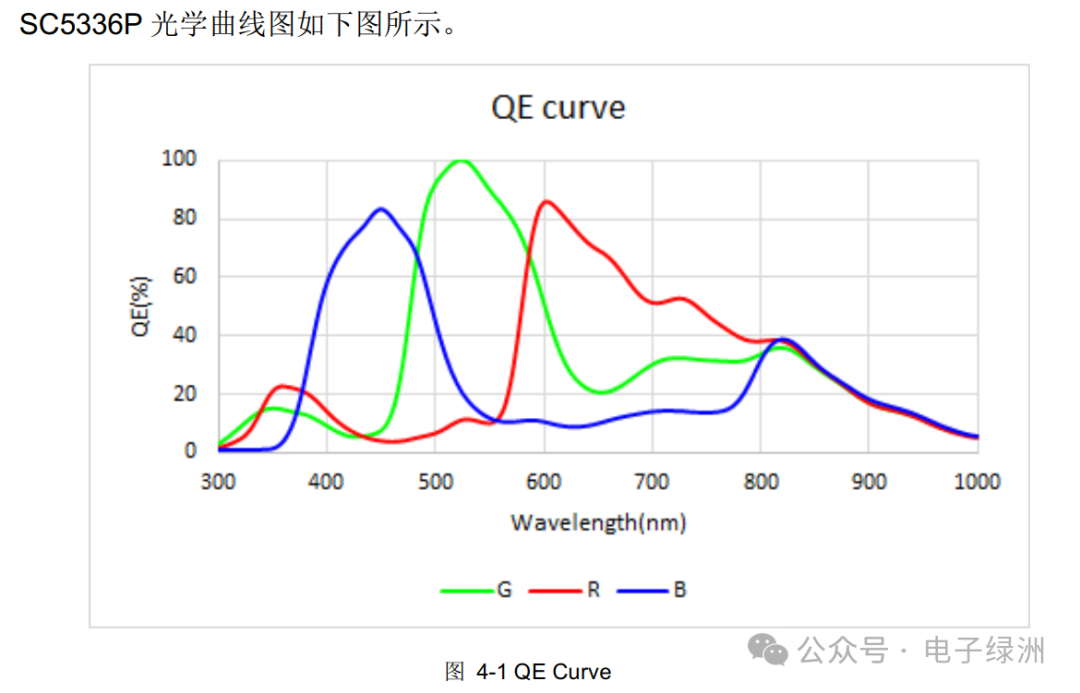
6. QE Curve
The Quantum Efficiency (QE) curve describes the response capability of an image sensor (such as CMOS or CCD sensors) to photons at different wavelengths. It indicates the sensor’s ability to convert incident photons into electrons, typically expressed as a percentage or the number of electrons generated per photon (e-/photon).
Hardware Design Considerations:
A. Conduct actual tests of images under low and high illumination.
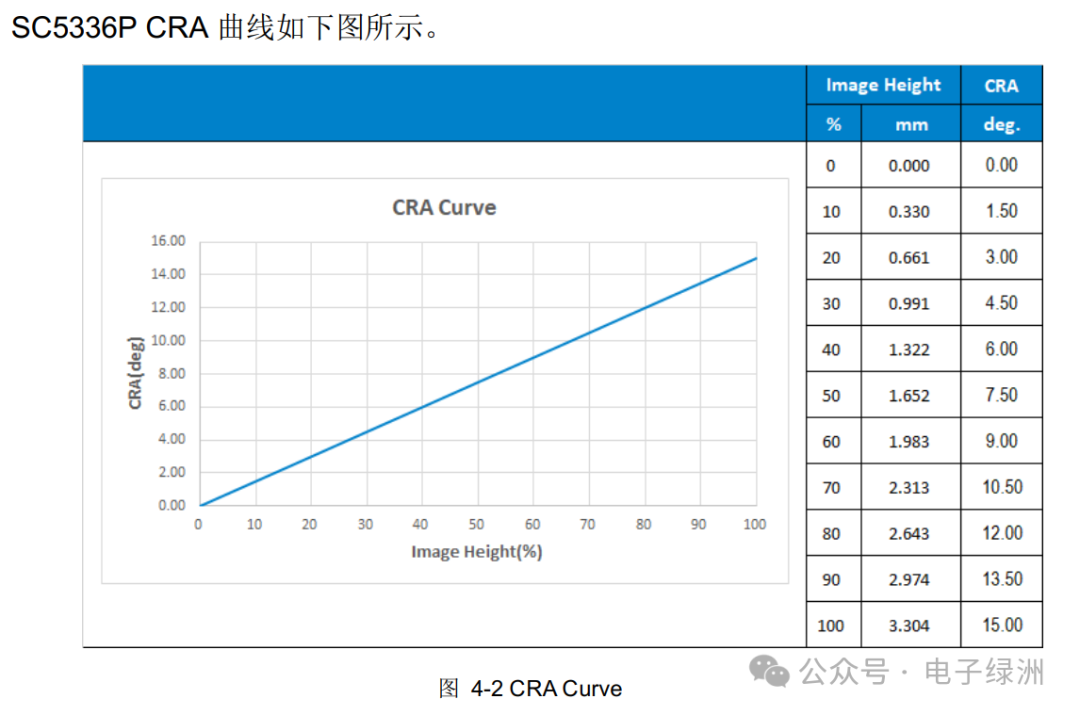
7. Chief Ray Angle (CRA)
The CRA of the SC5336P is a maximum of 15°.
Hardware Design Considerations:
1. The CRA of the lens must match the CRA of the sensor; otherwise, the image will exhibit uneven illumination and dark corners.
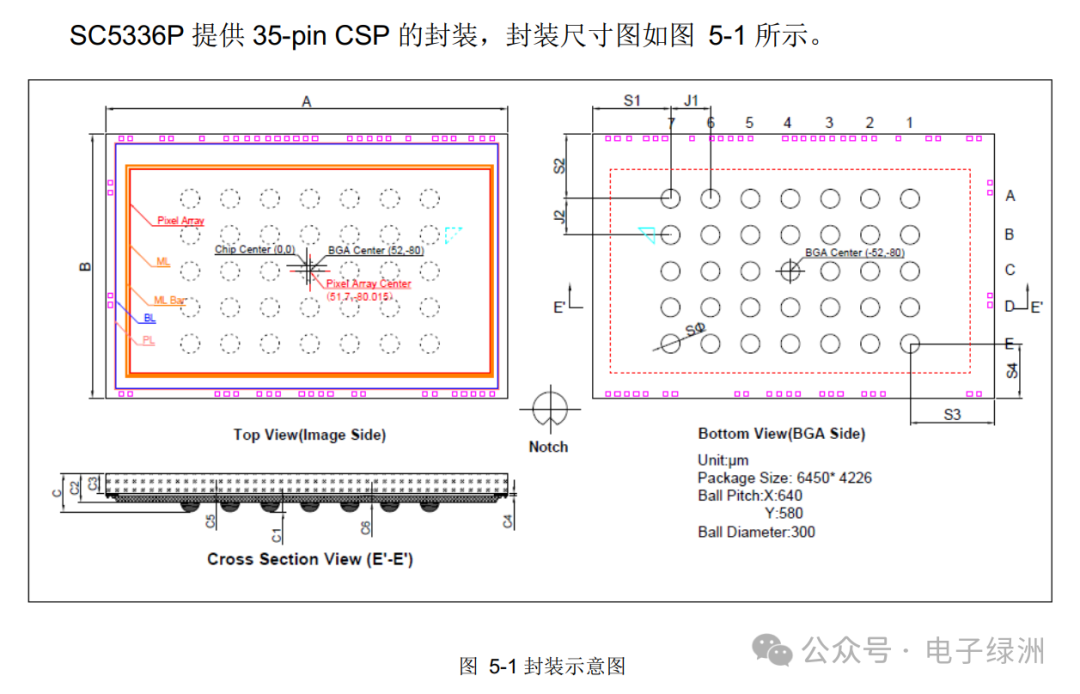
8. Packaging
The SC5336P package: 35-pin CSP
Hardware Design Considerations:
A. The Array Center is the optical center and must align with the center of the lens.
B. The pins of SC2336P/SC3336P/SC4336P/SC401AI/SC5336P are Pin to Pin. (However, the voltage of DVDD may be internally or externally supplied).
The physical dimensions of different sensors also vary; when designing the forbidden layout area, consider a margin of 2mm.
4. Conclusion
1. The analog voltage of 2.8V can use a high PSRR LDO (PSRR: power supply rejection rate), to avoid potential image ripple.
2. SmartSens sensors are all “foot A1”; the imaging direction is opposite to the A1 pin. In contrast, GalaxyCore’s sensor has the A1 pin in the positive direction.
3. The front and back of the SmartSens sensor have some boxes that can be used to identify the SmartSens sensor model or the A1 pin.
4. At high and low temperatures, some parameters may be affected; attention should be paid to examples of high and low-temperature testing applications.
——END——
In the jungle society, tears are never believed; no amount of complaints will help, and no one will pity you.
Recommended Reading
【Teardown Series】Ezviz CB2-4G 4G Unlimited Flow 3 Million Ultra-Clear Large Capacity Lithium Battery Indoor Smart Monitoring Home Camera AOV All-Day Recording
ISP DPC Defect Pixel Correction Technology in Image Processing
【Sensor Series】Security Camera Monitoring CMOS Image Sensor – SmartSens SC4336P
【Teardown Series】Ezviz’s Jingxiaodou Dual-Camera 10 Million Camera Monitoring D220
The Difference Between Good Die and Inked Die: A Comprehensive Analysis from Wafer to Finished Product
Like, Share, and RevisitThank you for your “three consecutive supports”Limited-time free QR code to join the group, exchange more technical and industry information
