eMMC has four commands:
-
BC: Broadcast command, no return value;
-
BCR: Broadcast command, requires a return value;
-
AC: Point-to-point addressing command, no data transfer on the DAT line;
-
ADTC: Point-to-point addressing command, data is transferred on the DAT line.
All commands and return values are completed on the CMD line.
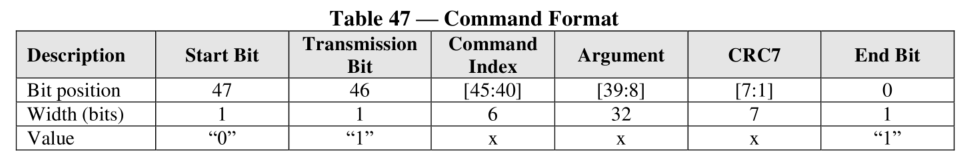
All commands are 48 bits in length, with a transfer time of 0.9 ms at a 52 MHz clock. The format is as shown in the table below:
The commands of eMMC are divided into different classes. Each class supports a range of device functions.
Class 0 is mandatory for all eMMCs, while other classes may be mandatory for specific device types or optional. By using different classes, different configurations can be utilized. The command classes supported by eMMC are stored as parameters in the Device Specific Data (CSD) register.
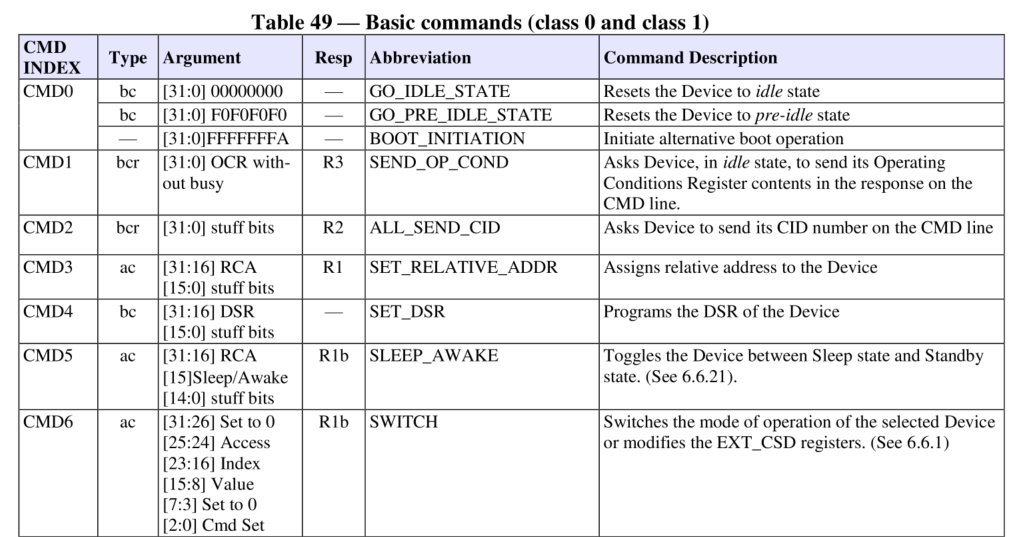
Below is a description of the commonly used CMD0/CMD1/CMD6.
All command return values are sent via CMD, and the length of the return value depends on the command type. There are a total of 5 types of return values.
R1: Common return value type, format as follows: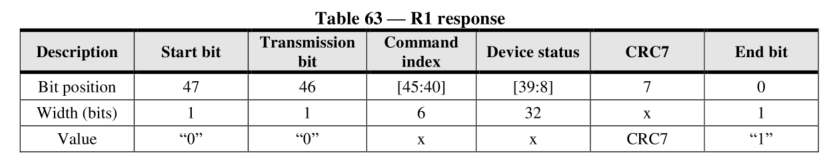 R1b: Similar to R1, but with an optional busy signal transmitted on DAT0.
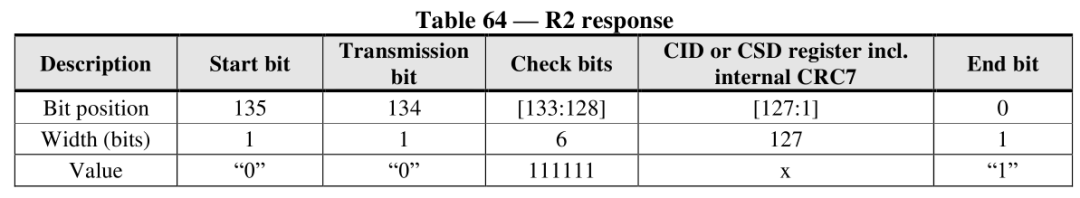
R2: CID, CSD register specific, CMD2 and CMD10 return CID register values, CMD9 returns CSD register values.
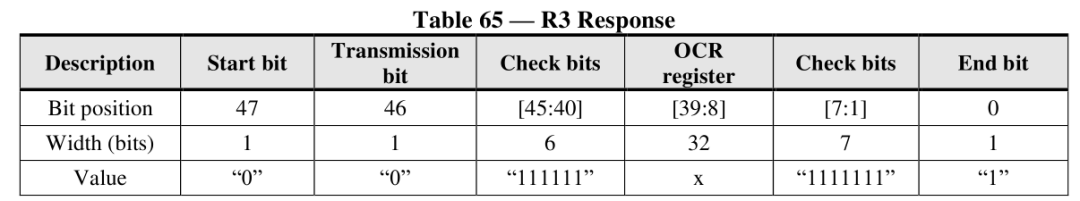
R3: OCR register specific, return value of CMD1 command.
R4: Fast IO, includes the RCA for addressing the device.
R1b: Similar to R1, but with an optional busy signal transmitted on DAT0.
R2: CID, CSD register specific, CMD2 and CMD10 return CID register values, CMD9 returns CSD register values.
R3: OCR register specific, return value of CMD1 command.
R4: Fast IO, includes the RCA for addressing the device.



👇 Click to read the original text and sign up for the event.