
3D Printing Technology: Reshaping the Precision and Personalization of Dental Care
In recent years, with the deep integration of digital technology and the medical field, the dental industry has undergone a silent revolution. In this transformation, digital 3D printers have quickly become a hot technology in the global dental field due to their efficiency, precision, and personalization. From custom dental crowns to invisible aligners, from implant guides to complete dentures, 3D printing is rapidly disrupting traditional dental treatment models, paving a new path from “standardized production” to “precision medicine”.
1. From “Hand-Carved” to “One-Click Printing”: How Technology is Redefining Dental Norms?
Traditional dental restorations rely on technicians to manually create models, which is time-consuming and prone to errors, requiring patients to make multiple trips to the clinic. The advent of digital 3D printers has completely digitized this process: by obtaining 3D data of the patient’s teeth through oral scanning, AI software automatically optimizes the design, and the printer can produce high-precision models within hours. For example, the invisible aligner brand Invisalign has reduced the production cycle of aligners from several weeks to just a few days using 3D printing technology, while achieving complete personalization for each set of aligners.Even more remarkable is the breakthrough in 3D printing materials, which has continuously expanded clinical application scenarios. Light-curing resins, biocompatible ceramics, and even temporary bone substitute materials can now cover the entire chain from temporary restorations to permanent implants. The Varseo series printers from the German company BEGO can directly print permanent crowns and bridges that meet EU CE certification, with strength and aesthetic effects comparable to traditional casting processes.
2. Efficiency Revolution: The “Digital Symbiosis” of Clinics and Laboratories
For dental clinics, 3D printers are not just tools but core assets that enhance competitiveness. A survey in the United States showed that clinics equipped with desktop 3D printers improved their restoration order processing efficiency by over 60%, with patient retention rates increasing by 35%. Some dental institutions in first-tier cities in China have begun to experiment with the “chairside instant printing” model: while patients are getting fillings, doctors design and print inlays on-site, achieving “one visit, immediate restoration”.
3. Personalized Medicine: From “One Tooth for Thousands” to “One Plan for One Person”
The true value of 3D printing technology lies in its unprecedented potential for personalizing medical solutions. In the field of dental implants, 3D-printed surgical guides that combine CBCT imaging and dynamic occlusion analysis can control the accuracy of implant placement to within 0.1 millimeters, significantly reducing surgical risks. In orthodontic treatment, the AI-driven design system developed by the South African company Dentologix can predict the correction path based on the patient’s maxillofacial development trends and simultaneously generate compatible 3D-printed attachments.
More cutting-edge applications have extended into the field of tissue engineering. A team from Harvard University successfully used biological 3D printing technology to cultivate live dental pulp tissue containing vascular networks on scaffold materials, laying the foundation for future “regenerative teeth”. Although this technology has not yet been commercialized, it indicates the potential shift in dental restoration from “replacement” to “regeneration”.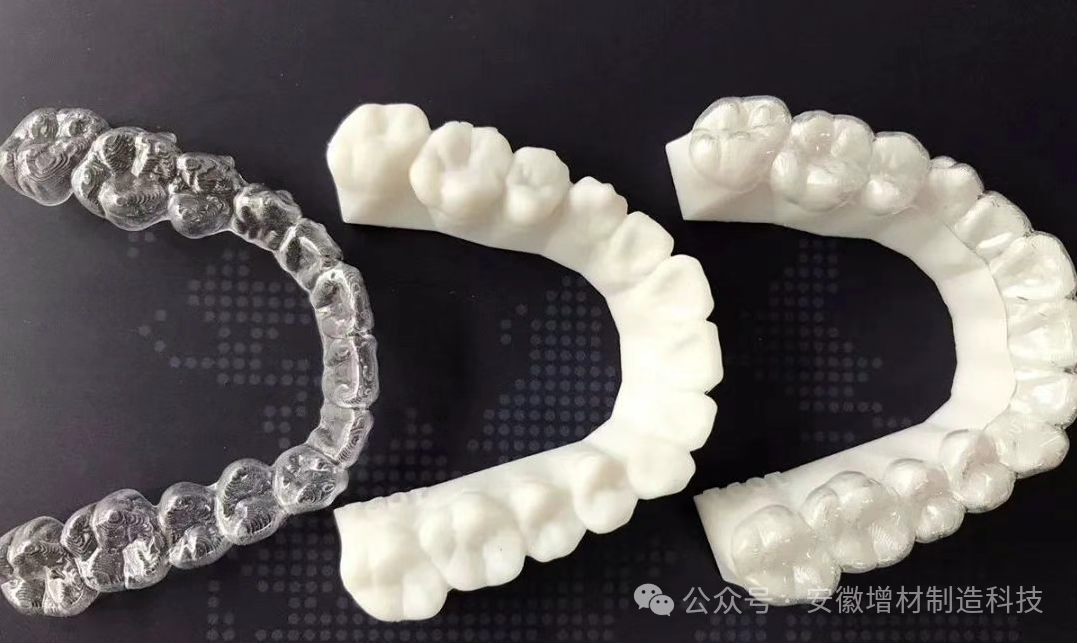
Conclusion: The “Critical Point” of Digital Dentistry Has Arrived
According to market research firm SmarTech Analysis, the global dental 3D printing market is expected to exceed $10 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate of 21.3%. Behind this data is the acceleration of technology from the laboratory to the clinic, as well as a profound transformation of the medical paradigm from experience-driven to data-driven.In the future, with the integration of 5G telemedicine, AI generative design, and multi-material mixed printing technologies, dental 3D printers may evolve into “oral health smart terminals”—capable of not only manufacturing teeth but also monitoring the oral microenvironment in real-time and warning of disease risks. When technological breakthroughs resonate with clinical needs, this digital revolution will ultimately reshape the technological logic behind every smile.