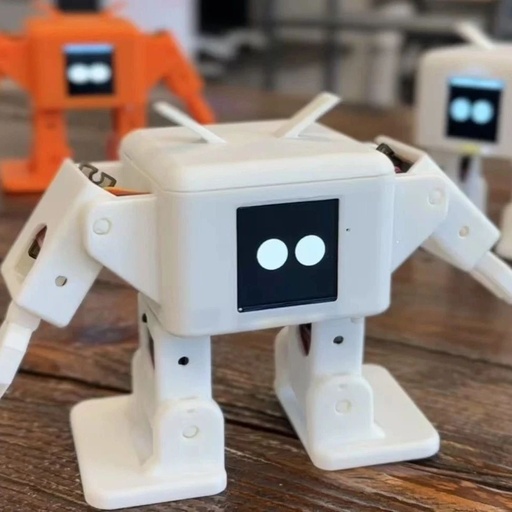
Chengbu: A Youth Team Develops an AI Desktop Humanoid Robot
Recently, the Development and Reform Bureau of Chengbu Miao Autonomous County revealed that the young entrepreneur Xiao Qiaowei has developed an AI desktop humanoid robot through his company, Flash Cat Technology Co., Ltd. This robot has attracted widespread attention from technology enthusiasts and developers worldwide since its launch. The AI desktop humanoid robot developed by … Read more