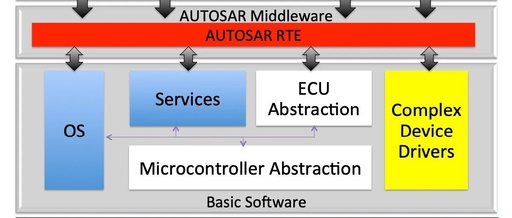
Understanding the Compilation Process of GCC
The compilation process of GCC mainly includes four stages: preprocessing, compilation, assembly, and linking. During this process, three tools are used: cc1, as, and collect2. Among them, cc1 is the compiler corresponding to the first and second stages, used to compile the source file hello.c into hello.s; as is the assembler corresponding to the third … Read more