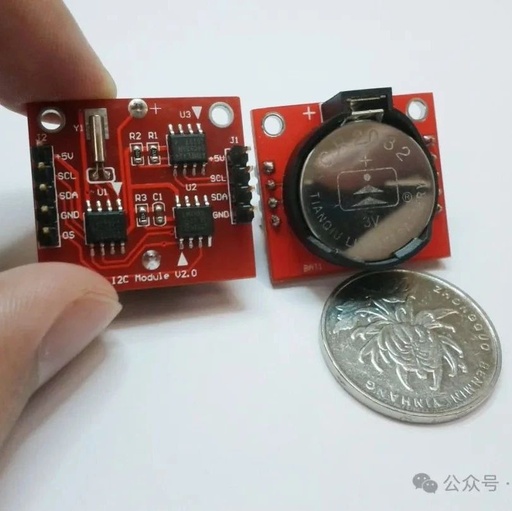
Principles, Differences, and Connections of the Three Major Embedded Protocols: UART, SPI, and I²C
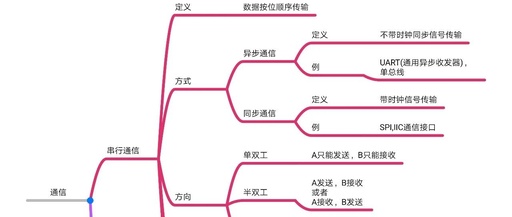
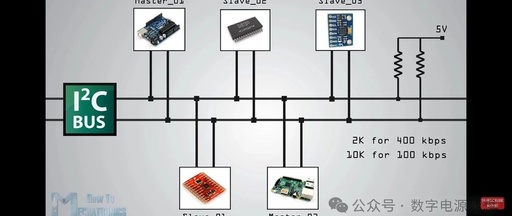
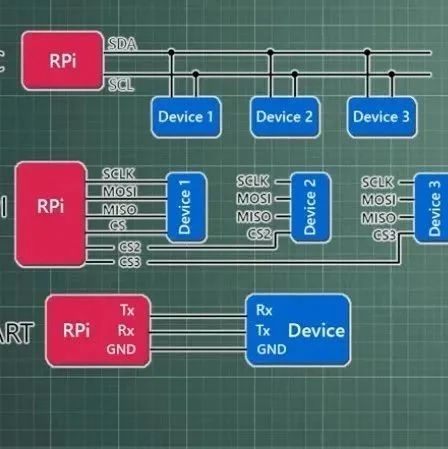
1. UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) The host and slave must connect at least three wires: RX, TX, and GND. TX is used for sending data, while RX is for receiving data (the transmission and reception are not on the same line, hence it is full-duplex). Basic Characteristics: Asynchronous Communication: No shared clock signal, relies on … Read more