
Share interest, spread happiness,
increase knowledge, and leave beautiful.
Dear, this is the LearingYard Academy!
Today, the editor brings you “Yue Lan (138) – Intensive Reading of Journal Articles”
“Multi-criteria decision support
and uncertainty handling, propagation and
visualisation for emergency and
remediation management“ research object and keyword definition”.
Welcome to visit!
1. Content Summary (Summary of Content)
This issue will introduce the research object and keyword definitions of the intensively read replica paper “Crowd intelligence knowledge mining method based on co-word network – application in emergency decision-making” in terms of mind maps, intensively read content, and knowledge supplementation.
2. Mind Mapping (Mind Mapping)
3. Intensive Reading Content (Intensive reading content)
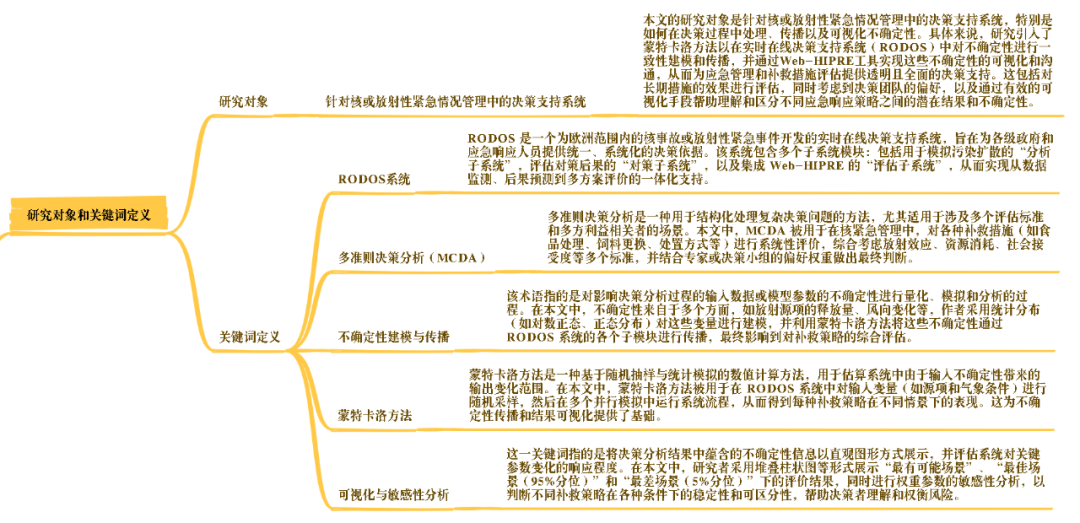
(1) Research Object –—Decision support systems in nuclear or radiological emergency management (Research object—Decision support systems in nuclear or radiological emergency management)
The research object of this paper is the decision support system in nuclear or radiological emergency management, especially how to handle, propagate and visualize uncertainty in the decision-making process. Specifically, the study introduces Monte Carlo methods to model and propagate uncertainties consistently in the real-time online decision support system (RODOS), and visualizes and communicates these uncertainties through the Web-HIPRE tool, so as to provide transparent and comprehensive decision support for emergency management and remedial measures evaluation. This includes the evaluation of the effects of long-term measures, taking into account the preferences of the decision-making team, and helping to understand and distinguish the potential results and uncertainties between different emergency response strategies through effective visualization.
(2) Keyword Definition (Keyword definition)
1. RODOS System (RODOS System)
RODOS is a real-time online decision support system developed for nuclear accidents or radiological emergencies in Europe, aiming to provide a unified and systematic basis for decision-making for governments at all levels and emergency responders. The system consists of multiple subsystem modules: including an “analysis subsystem” for simulating the spread of contamination, a “countermeasures subsystem” for evaluating the consequences of countermeasures, and an “evaluation subsystem” that integrates Web-HIPRE, thereby achieving integrated support from data monitoring, consequence prediction to multi-scenario evaluation.
2. Multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA)
Multi-criteria decision analysis is a method for structured processing of complex decision problems, especially for scenarios involving multiple evaluation criteria and multiple stakeholders. In this paper, MCDA is used to systematically evaluate various remedial measures (such as food treatment, feed replacement, disposal methods, etc.) in nuclear emergency management, taking into account multiple criteria such as radiation effects, resource consumption, and social acceptance, and combining the preference weights of experts or decision-making groups to make final judgments.
3. Uncertainty modeling and propagation (Uncertainty modeling and propagation)
This term refers to the process of quantifying, simulating, and analyzing the uncertainty of input data or model parameters that affect the decision-making analysis process. In this paper, the uncertainty comes from multiple aspects, such as the release of radioactive source items, wind direction changes, etc. The author uses statistical distributions (such as lognormal and normal distribution) to model these variables and uses the Monte Carlo method to propagate these uncertainties through the various submodules of the RODOS system, ultimately affecting the comprehensive evaluation of the remediation strategy.
4. Monte Carlo method (Monte Carlo method)
The Monte Carlo method is a numerical calculation method based on random sampling and statistical simulation, which is used to estimate the range of output variations caused by input uncertainty in the system. In this paper, the Monte Carlo method is used to randomly sample input variables (such as source terms and meteorological conditions) in the RODOS system, and then run the system process in multiple parallel simulations to obtain the performance of each remediation strategy under different scenarios. This provides a basis for uncertainty propagation and result visualization.
5. Visualization and sensitivity analysis (Visualization and sensitivity analysis)
This keyword refers to the use of intuitive graphical representations of the uncertainty information contained in the decision analysis results, and the evaluation of the system’s response to changes in key parameters. In this paper, the researchers used stacked bar charts and other forms to display the evaluation results under the “most likely scenario”, “best scenario (95% percentile)” and “worst scenario (5% percentile)”, and conducted sensitivity analysis of weight parameters to determine the stability and distinguishability of different remediation strategies under various conditions, helping decision makers understand and weigh risks.
4. Knowledge Supplement (Knowledge supplement)
Web-HIPRE (Hierarchical Preference Analysis) is a browser-based graphical decision support tool for dealing with decision problems with complex structures, multiple criteria, and diverse opinions of participants. It was born in the System Analysis Laboratory of the Helsinki University of Technology in Finland and was developed by Mustajoki, Hämäläinen and others. It aims to provide a structured, multi-dimensional decision modeling and evaluation platform for governments, research institutions, enterprises or crisis management departments.
The core function of Web-HIPRE is to decompose a complex decision-making problem with multiple objectives and multiple options through a “criteria hierarchy”, allowing users to analyze the relative importance and influence of each decision factor layer by layer, and finally comprehensively form clear decision recommendations or rankings.
Web-HIPRE is built on two classical multi-criteria decision-making theories:
1. MAVT (Multi-Attribute Value Theory)
Multi-attribute value theory focuses on establishing an independent value function for each criterion and deriving the comprehensive value of each option through linear weighted summation. In MAVT, the weight of each criterion and sub-criterion (reflecting its importance) is determined by the user’s assignment, which is suitable for scenarios with abundant quantitative data or where users can clearly express their preferences.
2. AHP (Analytic Hierarchy Process)
The analytic hierarchy process is a classic method proposed by Thomas Saaty, which emphasizes the relative importance of pairwise comparison criteria and options to derive consistent weight distribution results. It is suitable for using relative judgment to derive weights when user preferences are difficult to express in absolute numbers.
Web-HIPRE allows users to flexibly switch between MAVT and AHP modes to meet the needs of different decision-making styles and information backgrounds.
That’s all for today’s sharing.
If you have a unique idea about the article,
please leave us a message,
and let us meet tomorrow.
I wish you a nice day!

Copywriter |yyz
Typesetting |yyz
Review |hzy
Translation: Google Translate
References: Baidu Encyclopedia,Chat GPT
References: Jutta Geldermann, Valentin Bertsch, Otto Rentz. Multi-criteria decision support and uncertainty handling, propagation and visualisation for emergency and remediation management [J]. Operations Research, 2006, 1(1): 755-760.
This article is organized and published by LearningYard. If there is any infringement, please leave a message in the background!