Author: Zhao Xiaofei
IoT Think Tank Original
Please indicate the source and origin when reprinting
Introduction
By the end of February this year, the number of NB-IoT connections in China has exceeded 100 million. According to Huawei’s predictions, by the end of this year, the number of NB-IoT connections may double. Of course, such a large-scale connection itself will not generate too high economic benefits; connection is not the goal. The goal is to improve quality, increase efficiency, and achieve high-quality development in various industries after the connection. Achieving this goal is where NB-IoT plays its role in new infrastructure.

On the afternoon of April 15, the 5G NB-IoT ‘Billion’ Journey Industry Summit was successfully held. Liu Yulin, Deputy Director of the Information and Communication Development Department of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, mentioned in his speech that the country’s emphasis on new infrastructure has brought significant development opportunities for emerging industries such as 5G and the Internet of Things. In the future, we need to accelerate the formation of a development pattern where technologies such as NB-IoT, 4G, and 5G undertake various IoT connections in stages.
In my opinion, if 2020 is the year of large-scale initiation of new infrastructure, then NB-IoT has become the “pioneer” of new infrastructure. The development history of NB-IoT over the past few years has already been practicing the role of new infrastructure. In the year of large-scale initiation of new infrastructure, NB-IoT has started to verify the effects of new infrastructure.
Why do we say this? Let’s analyze it from two aspects:
The Relationship Between NB-IoT and New Infrastructure
(1) The Infrastructure Attribute of NB-IoT
First, let’s talk about the connotation and characteristics of new infrastructure. New infrastructure is not a box; not everything can fit into it. Whether it is new infrastructure or traditional infrastructure, it is primarily about infrastructure construction, which has strict categories and characteristic definitions. Only by meeting these requirements can it become a candidate for new infrastructure.
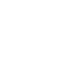
Although there is no unified concept of infrastructure in the industry, there has been a preliminary consensus on its connotation and characteristics. As early as 1994, the World Bank published its annual series report titled “World Development Report 1994” focusing on “providing infrastructure for development,” analyzing the relationship between infrastructure and economic and social development. In this report, the World Bank found through extensive empirical research that “for every 1% increase in a country’s infrastructure stock, GDP increases by 1%”, indicating the significant leverage effect of infrastructure on the entire economy.
Source: World Bank “World Development Report 1994”
The National Bureau of Statistics has a clear definition of the scope of infrastructure investment: referring to the projects and facilities that provide basic and public services for social production and life, which are the basic conditions for the survival and development of society. The first keyword is “social production and life,” meaning that these facilities must be oriented towards the whole society; facilities that only serve a few fields definitely do not qualify as infrastructure. The second keyword is “basic and public services,” meaning that they provide the most basic and underlying services to various industries, from which more specialized services and business models can be derived.
From this perspective, NB-IoT has been tasked with providing services to various sectors of the national economy since its inception, driving the realization of basic IoT connections across various industries. We can also see that NB-IoT has already penetrated industries such as water, gas, fire protection, lighting, municipal, transportation, animal husbandry, and home appliances. The purpose of this 5G NB-IoT “Billion” Journey Summit is also based on achieving 100 million connections in the already penetrated industries to further promote NB-IoT’s penetration into more industries, achieving the next 100 million connections.
This process is also the process of various industries completing digital transformation, with the NB-IoT network constituting an important underlying infrastructure for digital transformation.
(2) The New Infrastructure Attribute of NB-IoT
From an economic perspective, infrastructure has characteristics such as scale effects, positive externalities, networking, and cost charging. The scale effect means that a certain scale must be achieved to improve economic benefits; externality means that the behavior of one department will have a significant impact on others or society; networking means that the value of products or services increases faster with the number of users; cost charging mainly refers to the nature of infrastructure as a public product that does not charge users high fees.
At multiple important meetings, the central government has mentioned new infrastructure, listing contents mainly including 5G, industrial internet, artificial intelligence, IoT, and data centers, which constitute the core connotation of new infrastructure and can be said to be based on the new generation of new base technologies for ICT digital infrastructure.
The NB-IoT network constitutes a part of the digital infrastructure and largely possesses the four characteristics of the aforementioned infrastructure. For example, the scale effect of the NB-IoT network is very obvious; the breadth and depth of network coverage directly determine the level of service provided to various industries; externality is an indisputable typical feature, as the NB-IoT network mainly serves all industries outside of the communication industry, bringing a high input-output effect to various industries; networking is undeniable; Metcalfe’s law is an iron law in the communication industry, and NB-IoT is no exception; while the cost charging characteristic may not be very obvious, as the operation of the NB-IoT network is a market-oriented behavior, its cost is continuously decreasing to a large extent.
Wang Zhiqin, Deputy Director of the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, mentioned in the Xinhua News program “5G Overview”: New infrastructure itself is a representation of a new generation of information technology and a representative of digital economic development. As a new engine of the information age, new infrastructure not only has a very obvious investment and driving effect but also drives the transformation and upgrading of traditional industries.
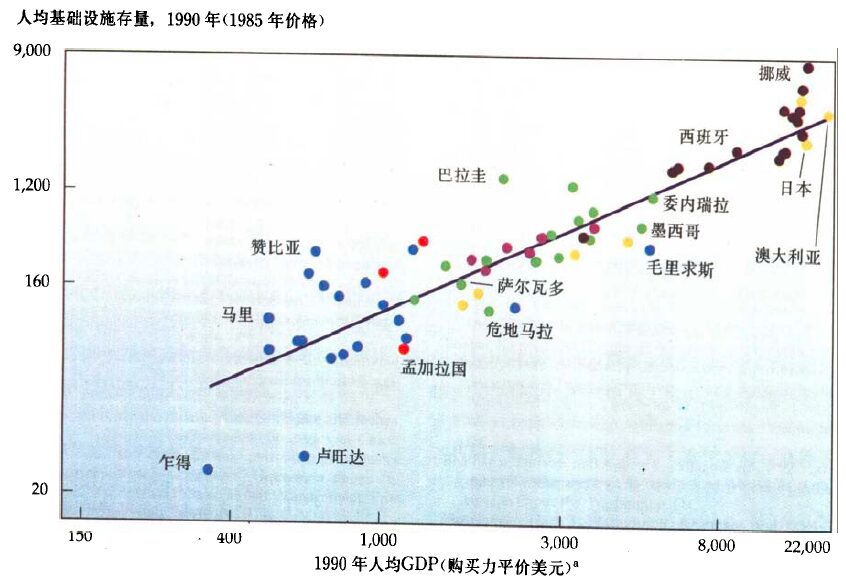
As Director Wang said, the role of new infrastructure, centered on ICT digital infrastructure, mainly manifests in enhancing the technical content of various industries, driving digital transformation, new models, and new growth. According to the White Paper on China’s Digital Economy Development and Employment released by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, in 2018, China’s digital economy reached 31.3 trillion yuan, accounting for 34.8% of GDP, an increase of 1.9 percentage points year-on-year.
Source: China Academy of Information and Communications Technology
Digital economy is divided into digital industrialization and industrial digitization, where digital industrialization refers to business forms centered around ICT, providing technology and products for the digitalization of various industries, including the new infrastructure business forms of digital infrastructure; industrial digitization refers to the integration of digitalization with various sectors of the national economy driven by digital infrastructure, technology, and products, forming a rapidly growing trend of industrial digitization. As shown in the figure above, the proportion of industrial digitization in the digital economy has shown a trend of annual increase, indicating to some extent the increasingly obvious multiplier and leverage effect of new infrastructure based on digital infrastructure, which is also the significance of new infrastructure.
Regarding NB-IoT, by the end of February this year, the number of NB-IoT connections in China has exceeded 100 million. According to Huawei’s prediction, by the end of this year, the number of NB-IoT connections will double. Of course, such a large-scale connection itself will not generate too high economic benefits; connection is not the goal. The goal is to improve quality, increase efficiency, and achieve high-quality development in various industries after the connection; achieving this goal is where NB-IoT plays its role in new infrastructure.
When IoT infrastructure, including NB-IoT, becomes an indispensable basic public product for various industries, the role of IoT new infrastructure will be fully realized.
Why is NB-IoT the “Pioneer” of New Infrastructure?
Although the central government has elevated new infrastructure to a new height this year, in fact, many fields have already been continuously promoting the construction of new infrastructure over the past few years, practicing the role of new infrastructure, and becoming the “pioneer” of new infrastructure. NB-IoT is one such representative, and the role of the “pioneer” can be reflected in the following aspects:
(1) Infrastructure is Ready
Liu Yulin, Deputy Director of the Information and Communication Development Department of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, mentioned in his speech at the summit that by the end of 2019, the number of NB-IoT base stations had exceeded 700,000. This scale of infrastructure has basically achieved coverage of most important scenarios. Next, network optimization and blind spot filling need to be carried out to make the supporting role of infrastructure for industry applications more apparent.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, several NB-IoT products became popular, such as NB-IoT smart door sensors, which, due to their convenient installation and automated management, became the best tool for isolation scenarios. These popular products and applications are backed by the basic readiness of the NB-IoT network infrastructure. In special circumstances, we can build a Huoshenshan Hospital in 10 days, ensuring various infrastructures in a short time, but in the case of nationwide isolation demands, only products and applications based on existing infrastructure can be deployed to combat the epidemic. As early as May 2017, China Telecom opened 300,000 NB-IoT base stations, followed by China Unicom and China Mobile, achieving nationwide coverage. Therefore, the readiness of infrastructure is a basic condition for NB-IoT to become the “pioneer” of new infrastructure.
(2) The Driving Effect Has Started to Show
Of course, merely having infrastructure is not enough to become a pioneer; it must also create a driving effect across multiple sectors of the national economy to reflect the characteristics of a pioneer. In my article “Milestone: Domestic 5G NB-IoT Connections Exceed 100 Million, Large Connections Accelerate Arrival,” I mentioned that under the scale-driven connections of millions and tens of millions, the NB-IoT industry has formed not only a demonstration effect but also in-depth verification of industrial landing.
As the number of connections has exceeded 100 million, this large-scale connection has brought verification of technology and business models, forming a positive cycle of landing. With experience of scaled replication, the industry with tens of millions of connections is moving towards hundreds of millions of connections, and the industry with millions of connections is accelerating towards tens of millions of connections. Besides industries that have achieved scaled applications such as water meters, gas meters, fire protection, locks, and street lights, new applications like door sensors, infrared temperature measurement, vehicle financial risk control, gas alarms, and charging sockets are also emerging, following the paths previously taken by industries like metering, smoke detection, and manhole covers, continuously forming demonstrations and receiving verification. Moreover, thanks to previous explorations, this process will be greatly accelerated.
We see that industries where NB-IoT penetration has been high over the past few years have achieved varying degrees of transformation based on NB-IoT. NB-IoT metering has brought intelligent operational means to the gas and water industries, NB-IoT anti-theft for electric bicycles has created a win-win business model for owners, government, and insurance companies, and the NB-IoT cow network has expanded income for farm operators. The case of Haier presented at this 5G NB-IoT “Billion” Journey Industry Summit shows that NB-IoT provides convenient means for industrial internet asset management. All of these reflect the support of NB-IoT as a basic service for quality improvement, efficiency enhancement, and high-quality development across various industries, and can also be seen as a validation of its role as a “pioneer” in new infrastructure.
(3) Looking Ahead, An Important Infrastructure for Driving the Marketization of Data Assets
Recently, the “Opinions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council on Building a More Perfect Market-oriented Allocation System and Mechanism for Production Factors” was officially released, one of the most notable aspects is that data is proposed as a new type of production factor, placed alongside land, labor, capital, and technology factors. The Internet of Things is an important means to accelerate the digitalization of physical assets and can promote the formation of data assets across various industries to some extent.
In the digital transformation of various industries, a large number of sensors are needed for extensive data collection, most of which collect low-frequency, small packet data that require the use of NB-IoT networks for transmission, activating relevant data to form asset attributes. For example, driven by NB-IoT smart metering, data on residents’ water and gas usage can be obtained in real-time, objectively, and centrally, allowing utility operators to explore new business models based on this livelihood data.
Vice Premier Liu He pointed out: “Data as a production factor reflects the accelerating digital transformation of economic activities, highlighting the multiplicative effect of data on improving production efficiency, becoming an important change of the most era-characteristic new production factor.” The continuous improvement of IoT infrastructure aims to “connect the unconnected scenarios,” forming data assets for various industries, achieving the digital transformation of the real economy. From this perspective, NB-IoT, as one of the core infrastructures of the Internet of Things, plays an important role in driving the formation of data assets across various industries.
In summary, NB-IoT not only possesses the characteristics of new infrastructure but also has its infrastructure ready, providing a certain degree of support for the digitalization of other sectors of the national economy and the formation of data assets. As the large-scale construction of new infrastructure begins, NB-IoT has already achieved validation in multiple industries, practicing its role as the “pioneer” of new infrastructure.
[New Infrastructure] Special Report
In-depth analysis of “New Infrastructure”, 5G, Industrial Internet, IIoT, IoT development logic sorting

A cartoon to help you understand the central government’s key mention of the “new infrastructure” that has been continuously popular in 2020

Beware of the mythologization of “new infrastructure”

From the “new infrastructure” boom, see how Baidu Smart Cloud stands out from the competition of comprehensive “upgrading”

