As a fashionable tech youth, there are several products in life that enhance personal charm: Bluetooth headphones, Bluetooth mice, Bluetooth speakers, smart wristbands… Just buying one, even if you haven’t started using it, makes you feel like your life has instantly leveled up in style and technology.
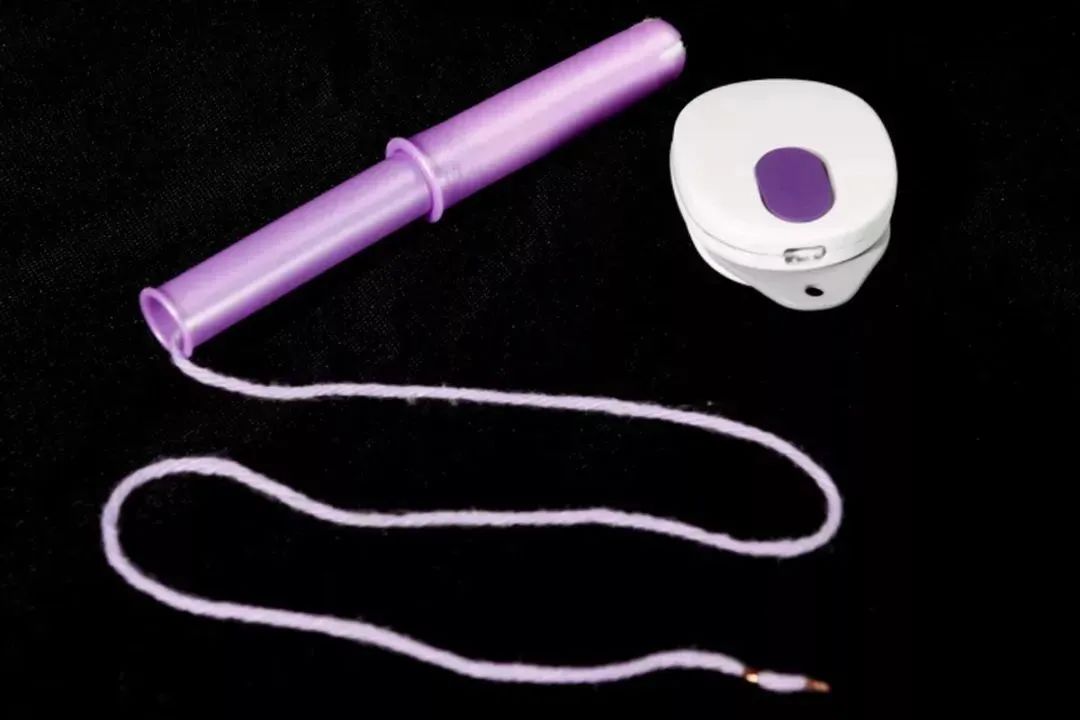

A certain company abroad produces Bluetooth tampons, you just say geek or not | my.Flow
We are all too familiar with the term Bluetooth. However, if you keep saying Bluetooth and using Bluetooth, what exactly is Bluetooth?
This story starts with a Danish king
Bluetooth is actually a short-range wireless communication technology, a global open standard for wireless transmission of voice and data. But why is Bluetooth so “blue”? This traces back to King Harald Blåtand of Denmark in the 10th century. King Harald ruled Denmark from approximately 958 to 986 AD, known for his military prowess, ending the age of pirates and unifying the vast Nordic regions of present-day Norway, Sweden, and Denmark.
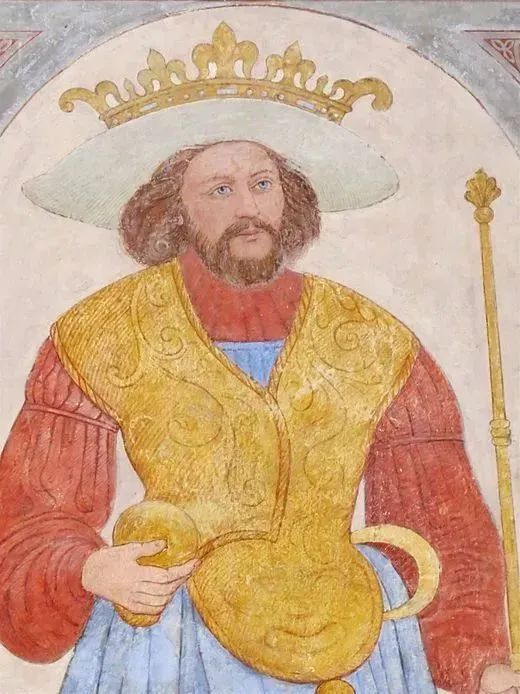

King Harald Blåtand | wikipedia
The Danish word Blåtand translates to Bluetooth in English, hence this king is also known as Harald Bluetooth. There are many versions of the origin of this name; one legend suggests that the king loved eating blueberries, which stained his teeth blue; other historians speculate that one of the king’s teeth decayed, giving it a blue appearance.
In 1996, Ericsson, Nokia, Toshiba, IBM, and Intel planned to establish an industry association to jointly develop a short-range wireless connection technology. The development team hoped this wireless communication technology could coordinate and unify the work across different industrial sectors, much like King Bluetooth. Thus, this technology was named Bluetooth. The Bluetooth logo is a combination of the ancient Nordic runes ᚼ and ᛒ, which represent the initials HB of King Harald Blåtand. Thanks to this magical logo, the story of this Danish king will be remembered for generations.
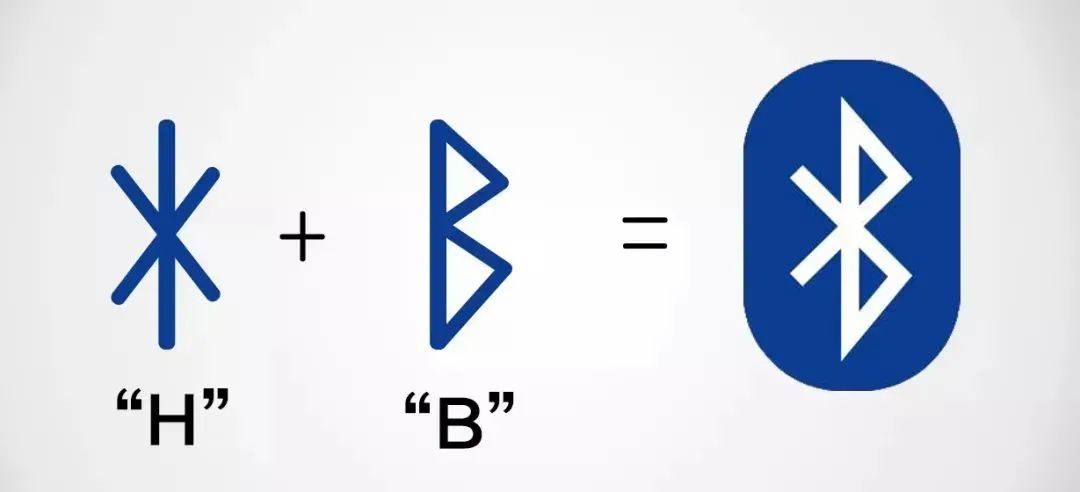
The meaning of the Bluetooth logo
Why do I need Bluetooth when I have Wi-Fi?
Both are short-range communication technologies, and Bluetooth inevitably gets compared with Wi-Fi technology. So what are the differences between the two?

Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are often compared
First, in terms of usage, we often connect multiple devices to one Wi-Fi to access the internet, which is a one-to-many connection method, while Bluetooth allows two devices to transfer data between each other, which is a point-to-point connection method. In this regard, Bluetooth has a higher level of data security.
Secondly, Bluetooth uses microstrip antennas, which are small and easy to integrate into devices, and Bluetooth modules are very low-cost, leading to a high prevalence of Bluetooth devices. In contrast, Wi-Fi devices require separate network cards and routing devices, which are more expensive and consume more power.
In some scenarios, Bluetooth is more suitable than Wi-Fi. For example, friends in Shanghai often use an app called Metro when taking the subway.

Image | Shanghai Local Treasure
To protect passengers’ property security and prevent QR codes from being stolen, this app requires users to turn on Bluetooth to allow the turnstile and phone to verify each other; access will only be granted if verification is successful. If this app used the internet or Wi-Fi for authentication, poor network conditions could affect passenger access through the turnstile. In this case, using Bluetooth for secure authentication is a more appropriate solution.
Does turning on Bluetooth consume a lot of power?
However, if you keep Bluetooth on just to take the subway, will it drain your phone’s battery quickly? To understand this, you need to know the new developments in Bluetooth technology.
Currently, there are two types of Bluetooth we use: traditional Bluetooth and BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy). Traditional Bluetooth uses a point-to-point communication method, which is a continuously maintained connection, typically used for scenarios with larger data volumes, such as Bluetooth headphones and speakers.

Listening to music with Bluetooth headphones relies on the traditional Bluetooth connection method | Oriental IC
BLE is a low-power Bluetooth technology. Compared to traditional Bluetooth, BLE’s biggest advantage is that it has a very fast search and connection speed, and low power consumption. A BLE connection (scanning devices, establishing connections, sending data, etc.) takes about 3ms, and after the task is completed, it quickly switches to a “non-connected” state, minimizing power consumption. However, BLE has a physical bandwidth of only 1M, resulting in a lower data transmission rate, so BLE is generally used for devices with high real-time requirements but small data packets, such as keyboards and remote controls.

Low-power Bluetooth technology is generally used for devices like Bluetooth keyboards | Oriental IC
Using the “Metro” app as an example, it utilizes BLE technology. When passengers pass through the turnstile, the app can quickly establish a connection and complete verification with the turnstile through BLE, making this process nearly imperceptible to passengers, without increasing their waiting time at the turnstile. Moreover, due to the use of BLE technology, Metro only needs to send a very small data packet to the turnstile, and after verification, Bluetooth quickly enters a “non-connected” state, significantly reducing power consumption, making the energy used negligible for the phone.
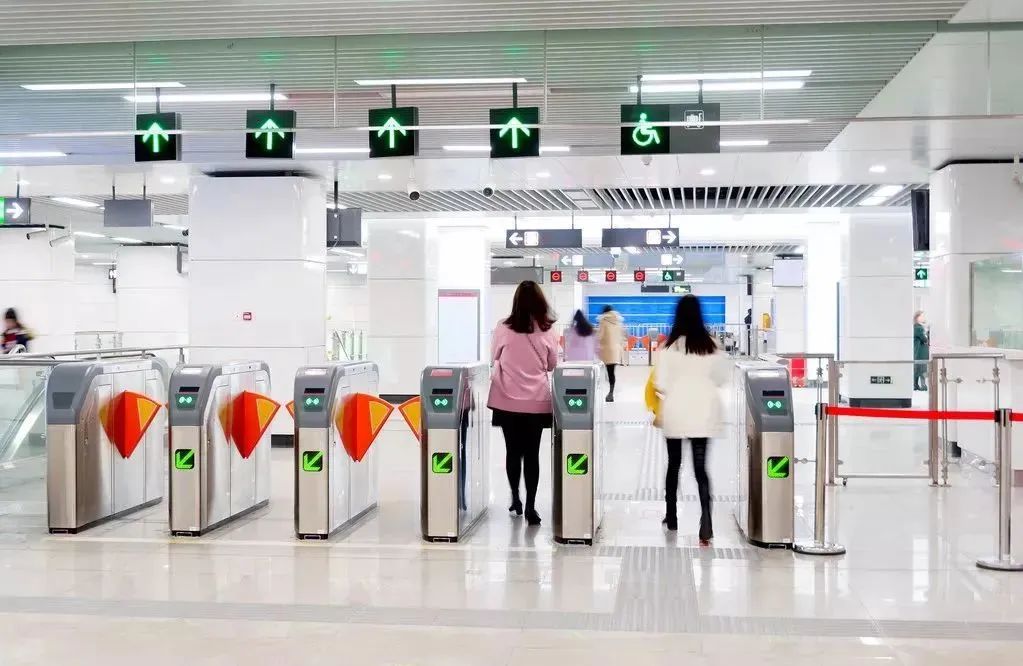

It just “whooshed” by | Oriental IC
Whether commuting to work, listening to music on the subway, or working wirelessly, the use of Bluetooth technology makes our lives more convenient. The next time you turn on Bluetooth, don’t forget to thank that Nordic engineering romance and the distant Danish king from the Viking era.
References
[1]https://gizmodo.com/bluetooth-is-named-after-a-medieval-king-who-may-have-h-1671450657
[2]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Harald_Bluetooth
Author: Ban Zhi
Editor: Da Linza
This article is from Guokr and may not be reproduced without permission.
If needed, please contact [email protected]
