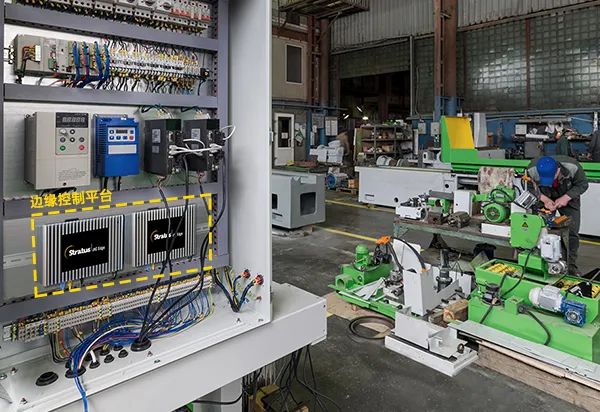

Edge computing can help equipment manufacturers integrate existing applications like monitoring and control software into a single platform, while allowing other critical applications to run on the same platform. This makes it easier to develop intelligent Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) machines and devices, and future applications that support customers in developing Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing needs can be easily added.
Currently, the global manufacturing industry is moving towards smart factories!
Building a smart factory fundamentally requires smarter machines and equipment. These machines are equipped with sensors, smart controllers, and HMI/SCADA systems with IoT capabilities, leveraging the innovative advantages of digital technology. To fully realize the benefits of these technologies while ensuring they operate safely and reliably, an edge computing platform is essential.
Smart factories require smarter devices
Just as the use of PLC and PAC in machine automation revolutionized the design of previous generation equipment, smart factories and smart manufacturing are again driving development in the industrial sector. Applying the concept of digital transformation enables companies to utilize data collected from control systems and sensors to operate at optimal performance. This approach provides operators with real-time analytics, inputs that help improve Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE), and data that can be collected and analyzed locally. Data can also be sent to the cloud for deeper analysis in various applications. These applications may include optimized maintenance, flexible supply chains, and increased output from multiple factories engaged in similar production.
Machines and OEM equipment are fundamental elements of production. Smart factories and smart manufacturing can only be achieved through OEM-designed or end-user specified intelligent machines. By adopting digital transformation, machine and equipment manufacturers can enhance design and support the development of new services around equipment performance and maintenance. An important question is: what is the best way to develop a new generation of smart devices or to adapt existing designs and deployments to meet customer needs? The answer is edge computing. Edge computing is a method that can address many critical design requirements.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing takes many forms, and its broad definition encompasses any computing that occurs outside of data centers. Given such a broad definition, it is not surprising that many confusing definitions have emerged in the IT industry and in automation and control sectors, collectively referred to as Operational Technology (OT).
Large analytics firm Gartner released a simple topology to help everyone understand what types of edge computing may be useful to them. This topology illustrates the infrastructure technology stack, showing the types of servers, devices, or platforms that can be described as edge computing, as well as their physical endpoint locations at the “edge” of data sources. It highlights the computing capabilities available outside of actual data centers, as well as the types of data collection, analysis, and movement. The edge offers significant benefits to equipment manufacturers and their customers.
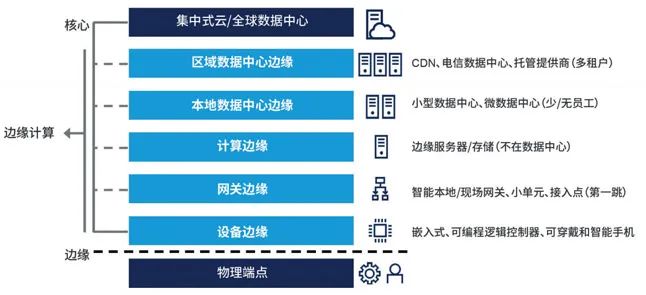
Why Do Intelligent Machines Need Edge Computing Platforms?
It is easy to see from the aforementioned topology that devices at the edge of computing are suitable for machine and equipment manufacturers. In fact, today all machines and equipment involve edge devices with PLCs, some even have gateway edge devices. In some respects, the industrial PCs and tablet PCs used by machines or devices fall into this gateway category. They may be the first “touchpoint” for the edge PLC of the device.
However, IPCs have limited computing and analytical capabilities, or face common reliability and availability issues similar to typical PCs or servers not specifically designed for harsh environments. Therefore, other types of dedicated edge computing platforms are needed to meet customer needs.
When modernizing machine control and automation systems, the computing edge should be a focus for equipment manufacturers. Edge computing provides all the necessary features and functions for machine and equipment manufacturers to enhance their current designs and transition to providing smarter devices.
Application Architecture of Edge Computing Platforms
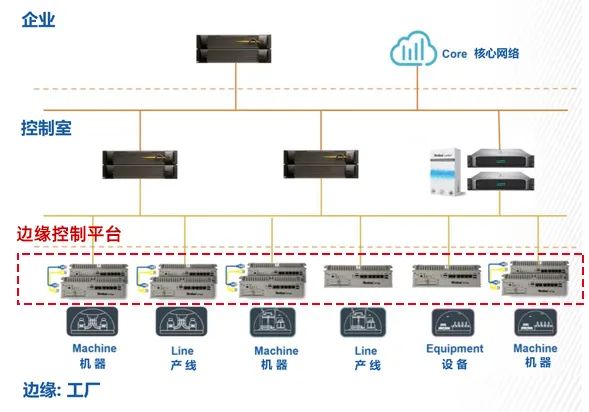
The Four Basic Functions of Edge Computing Platforms
Edge computing platforms provide equipment and machine manufacturers with new revenue service possibilities and help reduce costs and improve total ownership costs. “Machines as a Service” or “Devices as a Service” will become possible. Edge computing platforms have the following four basic functions.
1
Support existing automation and control applications
Capable of running existing control and automation applications in a modular way without extensive re-architecture.
2
Modify and upgrade existing control applications
Allows for greater flexibility in the operation and monitoring of machines and devices.
3
Add new analytics and digital transformation applications
New virtual machines can be created on the platform, making it easier to add new applications without impacting existing applications.
4
Support OT/IT convergence
Can simultaneously meet OT and IT requirements, ensuring that platforms supporting various types of operational applications are easy to deploy and maintain, and manageable by both OT and IT professionals.

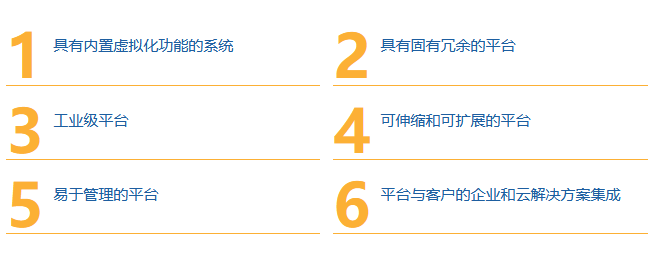
Six Features of Edge Computing Platforms Different from IPC and IT Servers
There are various computing platforms available for machine and equipment manufacturers, such as IPCs or traditional IT servers, but dedicated edge computing platforms undoubtedly outperform both. IPCs are suitable for industrial-grade applications but do not provide any redundancy, meaning manual intervention in your machines and customer operations must be performed periodically. Traditional IT servers are not suitable for industrial-grade applications and need to be placed in environmentally controlled locations, such as server rooms or server farms, which is not conducive to smart manufacturing. Edge computing platforms must possess the following six features:
– END –
Disclaimer: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author. If there are copyright issues with the videos, images, or text used in this article, please notify us immediately, and we will confirm copyright based on the materials you provide and pay remuneration according to national standards or delete the content immediately! The content of this article reflects the views of the original author and does not represent the views of this public account or assume responsibility for its authenticity.


To publish your products, please click “Read the original text”
