Author: Levin
IoT Think Tank Original
The competition in the IoT industry is developing towards an ecosystem, with companies including internet giants and operators actively laying out upstream key technologies and downstream solutions based on platforms.
According to data released by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, by the end of August this year, the three major basic telecom operators have developed 1.698 billion cellular IoT terminal users, surpassing the total number of mobile phone users at 1.678 billion, marking the first historic moment for the domestic cellular IoT industry to welcome “IoT surpassing people.” Moreover, with the continuous improvement of new infrastructure dominated by underlying technologies, the IoT industry will continue to maintain high-speed growth over the next 5 to 10 years. It is expected that by 2025, the number of connections in the domestic IoT sector will exceed 8 billion, and will continue to grow to a scale of 10 billion, with the market size expected to reach trillions.
Similar to the development trajectory experienced during the internet and mobile internet eras over the past few decades, the IoT era will also undergo stages of a significant increase in the number of devices, and users will demand better services and experiences, all of which place higher requirements on the hardware and software of IoT devices, necessitating continuous development and innovation across the entire industry.
For IoT devices, operating systems are equally indispensable. The operating system sits between the underlying hardware and the user, serving as a bridge for communication. Users can input commands through the user interface of the operating system, which is responsible for interpreting the commands and driving the hardware devices to fulfill user requests.
On computers, there are well-known operating systems like Windows and Linux, while Android and iOS systems are almost installed on all smartphones. Naturally, IoT devices should also have their own unique operating systems to address the different needs in various fragmented scenarios.
Building Operating Systems for the IoT Era
Compared to computers and smartphones, the types and applicable scenarios of IoT devices have greatly increased, being used in high-performance and real-time demanding scenarios like connected vehicles, as well as in power-sensitive fields like smart metering. Therefore, the problems faced by IoT terminal devices are also more complex, such as hardware fragmentation, diverse network protocols, complex platform access, and the materialization of security attacks. Traditional open-source embedded operating systems can solve some problems but cannot meet more challenges, nor can they form a unified IoT application ecosystem across devices, chip platforms, and the cloud.
Against this backdrop, large internet companies are investing resources to develop their own IoT operating systems, such as Amazon FreeRTOS, ARM Mbed OS, Huawei LiteOS, and Alibaba AliOS Things. Operators with deep accumulations in the communication field are no exception.
Since 2019, China Mobile has begun to invest in the research and development of a lightweight real-time operating system for the IoT field. After more than a year, China Mobile’s subsidiary, China Mobile IoT, officially launched the 5G-oriented IoT operating system—OneOS—in June 2020. This system can carry business applications upward while shielding hardware differences downward, connecting various fragmented scenarios to better meet the application needs of the era of interconnected things.
Overall, the architecture of OneOS adopts a layered design, consisting of drivers, a kernel, components, and a security framework. Through a lightweight kernel combined with multiple system components, along with extensive hardware adaptation support, OneOS boasts high scalability and usability.
Since version 1.0, OneOS has employed an extremely minimalist kernel, featuring characteristics such as being customizable, cross-platform, low-power, and highly secure. It supports mainstream chip architectures like ARM Cortex-A/M, MIPS, RISC-V, and is compatible with standards such as POSIX and CMSIS. It supports development modes in advanced languages like Javascript and MicroPython, providing graphical development tools that effectively enhance development efficiency and reduce costs, helping users in fields like smart wearables, smart locks, smart charging, and environmental monitoring to quickly develop stable, reliable, and user-friendly IoT applications.
Faster and Stronger! OneOS3.0 Achieves Comprehensive Upgrades
This month, focusing on real-time performance, security, and efficiency, OneOS3.0 has achieved comprehensive upgrades, creating a faster, stronger, and safer kernel, and providing various service components such as GUI, audio and video, and positioning, offering a safe, reliable, and convenient development experience for personal wearables, smart homes, and industrial control fields.
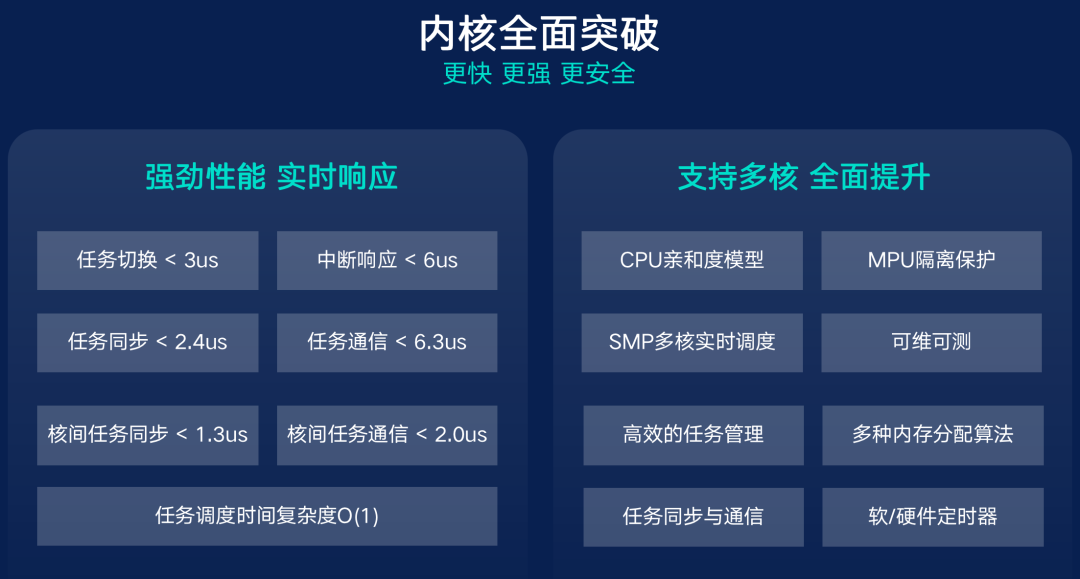
 For operating systems, the kernel is the most core and important part. By version 3.0, the kernel functionality of OneOS has further enriched. Firstly, OneOS3.0 supports symmetric multiprocessing platforms, helping advanced applications improve running efficiency; the CPU affinity model enhances task execution efficiency, avoiding unnecessary context switching by the CPU, thereby conserving performance; MPU isolation protection achieves separation between kernel and user access spaces, prohibiting tampering of critical data areas and protecting code segments, enhancing the system’s security and reliability; additional maintainable and measurable features, such as IPC tracing, interrupt detection, task trajectory tracing, and partner monitoring, help developers detect system status and quickly analyze issues.
At the same time, the kernel performance of OneOS3.0 has also further improved. On the Cortex-M4 platform, task switching is less than 3us, the maximum interrupt response delay is less than 6us, task synchronization is less than 2.4us, and task communication is less than 6.3us; on the multi-core Cortex-A9 platform, inter-core task synchronization is less than 1.3us, and inter-core task communication is less than 2.0us; the task scheduling time complexity also ranks among the best in mainstream RTOS systems.
For operating systems, the kernel is the most core and important part. By version 3.0, the kernel functionality of OneOS has further enriched. Firstly, OneOS3.0 supports symmetric multiprocessing platforms, helping advanced applications improve running efficiency; the CPU affinity model enhances task execution efficiency, avoiding unnecessary context switching by the CPU, thereby conserving performance; MPU isolation protection achieves separation between kernel and user access spaces, prohibiting tampering of critical data areas and protecting code segments, enhancing the system’s security and reliability; additional maintainable and measurable features, such as IPC tracing, interrupt detection, task trajectory tracing, and partner monitoring, help developers detect system status and quickly analyze issues.
At the same time, the kernel performance of OneOS3.0 has also further improved. On the Cortex-M4 platform, task switching is less than 3us, the maximum interrupt response delay is less than 6us, task synchronization is less than 2.4us, and task communication is less than 6.3us; on the multi-core Cortex-A9 platform, inter-core task synchronization is less than 1.3us, and inter-core task communication is less than 2.0us; the task scheduling time complexity also ranks among the best in mainstream RTOS systems.
Security and Reliability are the Cornerstones of Achieving IoT
As of now, OneOS has obtained 92 invention patents and 8 software copyrights, and is widely used in consumer electronics, smart cities, industrial control, and other fields, serving over 350 partners and achieving 30 million application installations.
Facing a scale of tens of millions of terminals, the security and protection capabilities of the operating system are crucial for all customers. As a new type of critical infrastructure, most data in IoT devices is real-time sensing data in specific application scenarios, including sensitive data from important industries. Data security assurance is an important foundation for the healthy development of the IoT industry. With the arrival of the interconnected era, more and more smart terminals will require operating systems that are more compatible and secure.
For lightweight IoT operating systems, it is even more essential to comprehensively consider the collaboration between software and hardware as well as the system’s footprint. In IoT environments, data generally undergoes a lifecycle of sensing, transmission, and processing; the security components provided by OneOS can offer lightweight solutions for each stage of data security, safeguarding IoT data. Moreover, the newly released OneOS3.0 is an LTS version (Long Term Support version), which has undergone extensive and in-depth testing, incorporating numerous security accumulations and stability improvements.
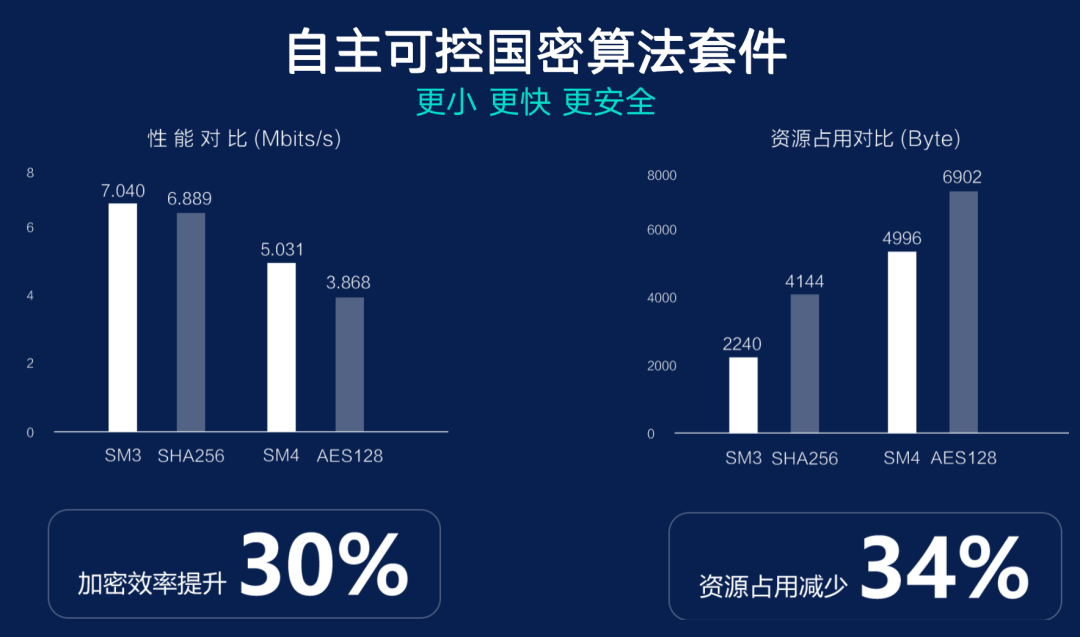
Regarding Terminal Data Protection, the OneOS security team has developed a lightweight domestic commercial encryption SM series algorithm suite, specifically optimized for the characteristics of small resources in IoT terminals, greatly reducing the suite’s resource occupation on terminals. In equivalent hardware environments, the resource occupation of the OneOS national encryption algorithm suite can be reduced by 34%, while encryption efficiency can be improved by 30%, significantly relieving resource pressure on terminal devices and providing data protection for a broader range of devices.
 Regarding Network Data Transmission, to provide a secure channel for communication parties and ensure the security and reliability of transmitted data, OneOS has developed a lightweight DTLS 1.3 security transmission protocol stack for IoT scenarios, which reduces memory resource occupation by 54% while improving handshake efficiency by 43%, meeting the sensitive data transmission needs of data collection terminals and smart devices across various network environments.
Currently, China Mobile IoT’s OneOS has passed multiple security certifications, including PSA, IEC 61508, CCRC EAL4+, and the system’s kernel performance has achieved breakthroughs in key indicators such as task switching and interrupt handling, reaching internationally advanced levels, capable of meeting the high-security requirements of special industries such as finance and payment. Among them, IEC 61508 has been recognized as the authoritative global standard for functional safety since its official release in 2000. OneOS’s successful acquisition of this certification signifies that in terms of system reliability and overall technical strength, OneOS has entered the ranks of internationally leading embedded operating systems, providing strong guarantees for the reliability of the basic system when enterprises and developers use OneOS to develop software products, and allowing for faster passage through relevant security certifications in related fields, accelerating product industry access and market sales.
Regarding Network Data Transmission, to provide a secure channel for communication parties and ensure the security and reliability of transmitted data, OneOS has developed a lightweight DTLS 1.3 security transmission protocol stack for IoT scenarios, which reduces memory resource occupation by 54% while improving handshake efficiency by 43%, meeting the sensitive data transmission needs of data collection terminals and smart devices across various network environments.
Currently, China Mobile IoT’s OneOS has passed multiple security certifications, including PSA, IEC 61508, CCRC EAL4+, and the system’s kernel performance has achieved breakthroughs in key indicators such as task switching and interrupt handling, reaching internationally advanced levels, capable of meeting the high-security requirements of special industries such as finance and payment. Among them, IEC 61508 has been recognized as the authoritative global standard for functional safety since its official release in 2000. OneOS’s successful acquisition of this certification signifies that in terms of system reliability and overall technical strength, OneOS has entered the ranks of internationally leading embedded operating systems, providing strong guarantees for the reliability of the basic system when enterprises and developers use OneOS to develop software products, and allowing for faster passage through relevant security certifications in related fields, accelerating product industry access and market sales.
All Industries Urgently Need Comprehensive Solutions
For IoT, one of the most prominent features is the severe phenomenon of “fragmentation”; the hardware devices in different industries vary widely, and software is also “diverse”, which not only leads to much unnecessary redundant development but also causes devices to be disconnected from each other, making it difficult to form a true interconnected experience. To solve this problem, many companies are proposing industry solutions for IoT, covering applications, operating systems, terminals, and various levels. For the operating system level, various upper-layer applications shield the different operational modes of underlying hardware through it, allowing developers to focus solely on the implementation of functionalities, breaking down barriers between devices, thereby promoting more rapid and efficient development and deployment of applications.
In Consumer Electronics, OneOS has partnered with several foreign professional service providers to offer developers a set of globally reliable, low-latency, low-cost, high-quality real-time audio and video communication services. Specifically, the system supports 48kHz full-band sampling, providing an ultra-high-quality experience; supports 1080P resolution with freely switchable bit rates, integrating various video encoding processing algorithms for better picture quality and lower bit rates; provides millisecond-level latency services, with real-time call quality exceeding the industry average; additionally, it can still support high-quality communication under weak network conditions and during network switching, maintaining normal communication even with a 70% packet loss rate; moreover, developers can easily achieve one-to-one voice and video calls for smart hardware devices by integrating RTC SDK, significantly reducing the development costs of real-time audio and video applications.
In Industrial Control, OneOS integrates industry foundational capabilities and optimizes them according to the market demand for industrial digitization. In the PLC product direction, OneOS has developed a soft PLC development suite in collaboration with Germany’s CODESYS, adhering to the IEC61131-3 standard, addressing the pain points of remote debugging and operation and maintenance in the industrial internet, utilizing 5G technology to facilitate wireless communication and cloud channels between upper-level machines and PLC devices, reducing on-site wiring while enabling flexible operation and maintenance across wide area networks; in the motion control direction, following CNC programming specifications, OneOS employs efficient CNC algorithms to achieve high-efficiency G-code parsing and execution capabilities. Thanks to OneOS’s extremely low resource occupation and efficient real-time response, multi-task CNC technology has become feasible on ordinary MCU platforms; in terms of communication capabilities, OneOS not only provides mainstream fieldbus protocol stacks including Modbus, CANopen, EtherCAT, and Ethernet, but also deeply supports 5G and 4G network characteristics, offering low-latency and high-reliability industrial communication capabilities to industrial customers.
Open Source Collaboration is the Lifeblood of IoT Operating Systems
For foreign IoT operating systems that have developed earlier, both open-source and ecosystem development are already relatively mature. In contrast, domestic IoT operating systems have started relatively late and require greater collaboration with upstream chip manufacturers, downstream capability developers, and application developers to jointly build the industrial ecosystem.
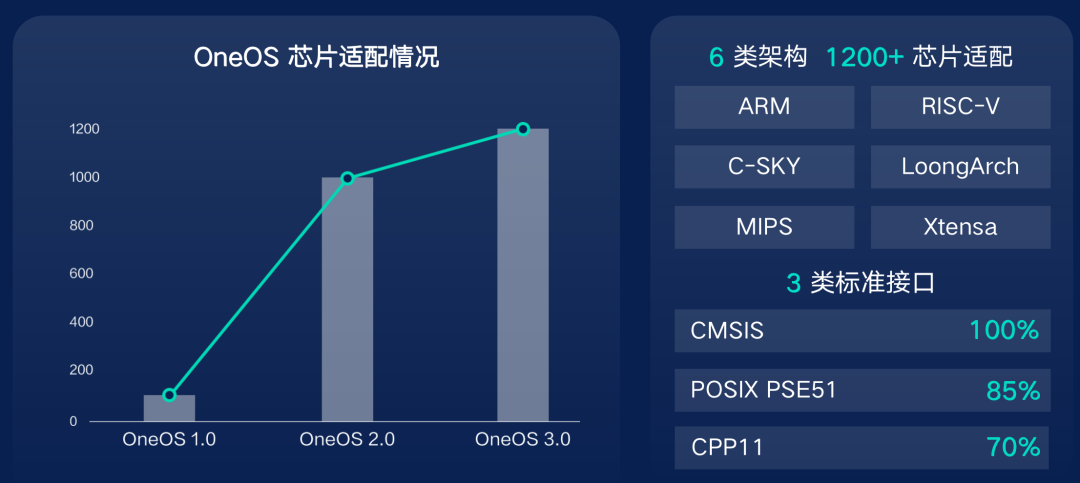
Since the inception of OneOS, it has been committed to providing a more friendly development experience for a wide range of developers and offering higher access efficiency for partners. In terms of compatibility, OneOS supported only over 100 chip types in version 1.0; now, OneOS3.0 supports six mainstream chip architectures: ARM, RISC-V, MIPS, LoongArch, C-SKY, Xtensa, covering mainstream manufacturers’ MCUs such as STMicroelectronics, NXP, GigaDevice, Huada Semiconductor, Fudan Micro, Loongson, and Feiteng, with a cumulative adaptation of over 1200 chips, supporting over 80 modules, and running stably on more than 50 development boards.
 Furthermore, to maximize support for cross-platform and cross-system networking communication, OneOS is now compatible with and supports most cloud service platforms, including Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, and China Mobile’s OneNET cloud platform, sinking various service capabilities from cloud platforms into terminals and underlying components, providing more choices for developers.
In addition, in terms of system source code, open-source community, and development tools, China Mobile IoT is also providing comprehensive technical support services for developers, helping partners access China Mobile IoT product libraries, IoT malls, and other channels; at the same time, China Mobile IoT is also closely collaborating with universities through joint laboratories, student competitions, and open courses to provide comprehensive and multi-dimensional services for enterprise and individual developers.
Furthermore, to maximize support for cross-platform and cross-system networking communication, OneOS is now compatible with and supports most cloud service platforms, including Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, and China Mobile’s OneNET cloud platform, sinking various service capabilities from cloud platforms into terminals and underlying components, providing more choices for developers.
In addition, in terms of system source code, open-source community, and development tools, China Mobile IoT is also providing comprehensive technical support services for developers, helping partners access China Mobile IoT product libraries, IoT malls, and other channels; at the same time, China Mobile IoT is also closely collaborating with universities through joint laboratories, student competitions, and open courses to provide comprehensive and multi-dimensional services for enterprise and individual developers.

Currently, “autonomy and controllability” has become one of the main themes of China’s technological development, which can avoid issues such as being “choked” by core technologies. As China’s exploration and practice of domestically produced autonomous IoT operating systems, OneOS is also of great significance for the entire IoT industry. Against this backdrop, OneOS has adapted to IoT chip products from domestic manufacturers like Feiteng and Loongson, providing domestic solutions for clients across various industry sectors, helping them break free from dependence on foreign technology and promoting the localization process in the industrial internet sector.
In the future, China Mobile IoT’s OneOS will continue to consolidate system foundational capabilities, layout industry applications, and deeply cultivate consumer electronics, smart cities, and smart industries, collaborating with upstream and downstream enterprises to jointly build an autonomous and controllable industrial chain ecosystem centered on operating systems, driving industry development through technological strength and accelerating the digital and intelligent transformation and upgrading of the industry.