Last weekend, I received an order worth 1200. The customer service took a 10% commission, leaving me with 1000. I completed it in two hours, feeling quite happy. Such orders are actually rare; they have low technical difficulty but high prices, which we colloquially refer to as ‘easy pickings’. I thought about treating my goddess to a meal with the money I made, but was ruthlessly rejected!
Effect Display

Tool Preparation
-
Data Source: https://maoyan.com/board/4?offset=1
-
Development Environment: Windows 10, Python 3.7
-
Development Tools: PyCharm, Chrome
Project Idea Analysis
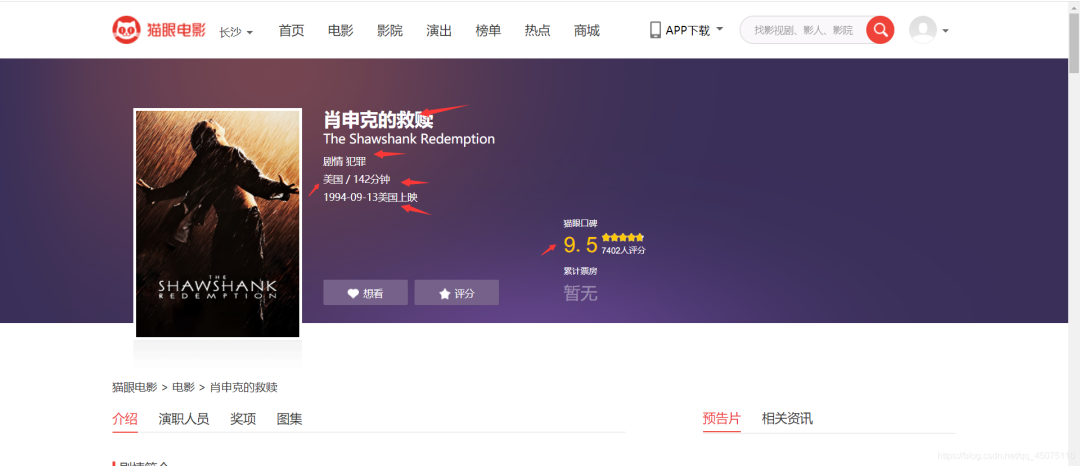
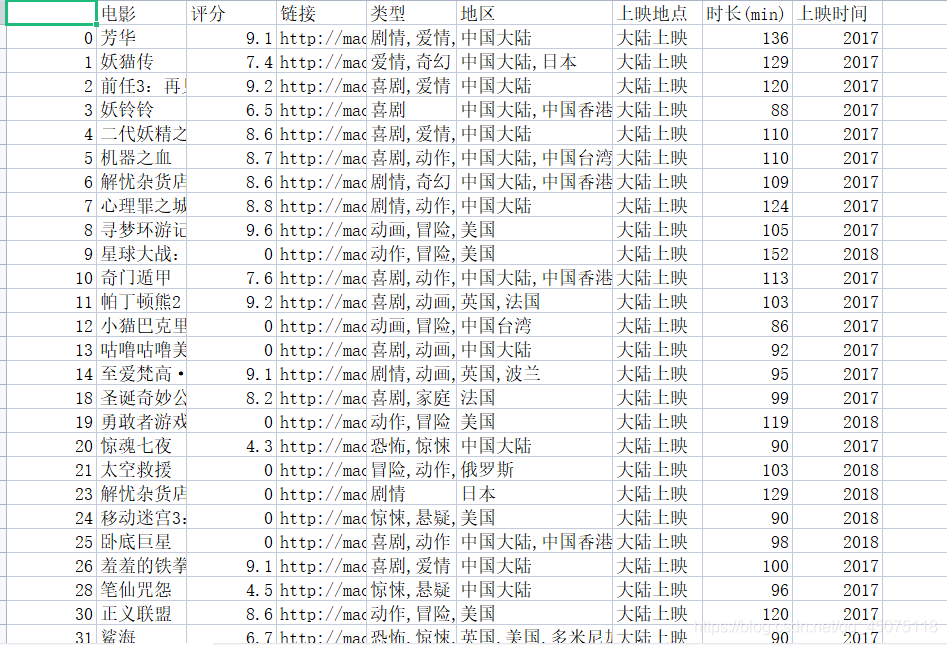
First, I collected all movie information from Maoyan. Here, I took the top 100 list as an example to obtain movie information:
-
Movie Name
-
Movie Rating
-
Movie Link
-
Movie Genre
-
Movie Release Location
-
Location
-
Movie Duration
-
Movie Duration
Parsing webpage data information
Parsing the redirect links from the homepage
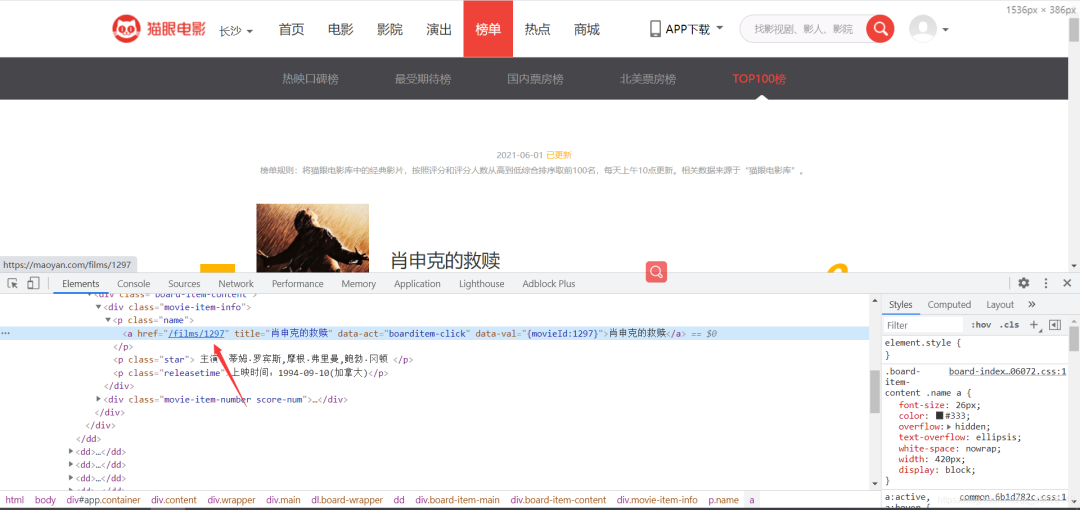 The rating on the Maoyan detail page is encrypted, so we directly extract the rating information from the homepage.
The rating on the Maoyan detail page is encrypted, so we directly extract the rating information from the homepage.
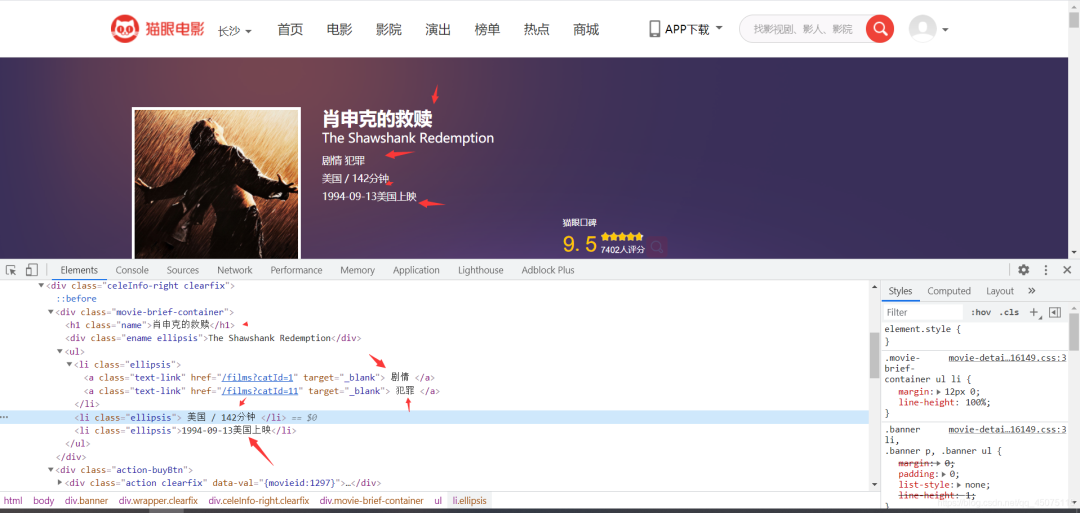
Extracting data from the detail page
 Saving the data in a CSV file for easy future data visualization.
Saving the data in a CSV file for easy future data visualization.
Tools Needed for Data Visualization
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import jieba
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# get_ipython().run_line_magic('matplotlib', 'inline')Effect Display

Source Code Display:
Web Crawler:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2021年06月05日
# @File : demo4.py
import requests
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
from lxml import etree
import time
# Random request header
ua = UserAgent()
# Construct request. You need to change it on the webpage. If you can't request, refresh the webpage and deal with the captcha.
headers = { 'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9', 'Cookie': '__mta=244176442.1622872454168.1622876903037.1622877097390.7; uuid_n_v=v1; uuid=6FFF6D30C5C211EB8D61CF53B1EFE83FE91D3C40EE5240DCBA0A422050B1E8C0; _csrf=bff9b813020b795594ff3b2ea3c1be6295b7453d19ecd72f8beb9700c679dfb4; Hm_lvt_703e94591e87be68cc8da0da7cbd0be2=1622872443; _lxsdk_cuid=1770e9ed136c8-048c356e76a22b-7d677965-1fa400-1770e9ed136c8; _lxsdk=6FFF6D30C5C211EB8D61CF53B1EFE83FE91D3C40EE5240DCBA0A422050B1E8C0; ci=59; recentCis=59; __mta=51142166.1622872443578.1622872443578.1622876719906.2; Hm_lpvt_703e94591e87be68cc8da0da7cbd0be2=1622877097; _lxsdk_s=179dafd56bf-06d-403-d81%7C%7C12', 'User-Agent': str(ua.random)}
def RequestsTools(url): ''' Crawler request tool function :param url: request address :return: HTML object for xpath extraction ''' response = requests.get(url, headers=headers).content.decode('utf-8') html = etree.HTML(response) return html
def Index(page): ''' Homepage function :param page: page number :return: ''' url = 'https://maoyan.com/board/4?offset={}'.format(page) html = RequestsTools(url) # Detail page address suffix urls_text = html.xpath('//a[@class=image-link]/@href') # Rating pingfen1 = html.xpath('//i[@class=integer]/text()') pingfen2 = html.xpath('//i[@class=fraction]/text()')
for i, p1, p2 in zip(urls_text, pingfen1, pingfen2): pingfen = p1 + p2 urs = 'https://maoyan.com' + i # Request too frequently time.sleep(2) Details(urs, pingfen)
def Details(url, pingfen): html = RequestsTools(url) dianyan = html.xpath('//h1[@class=name]/text()') # Movie name leixing = html.xpath('//li[@class=ellipsis]/a/text()') # Genre diqu = html.xpath('/html/body/div[3]/div/div[2]/div[1]/ul/li[2]/text()') # Read total timedata = html.xpath('/html/body/div[3]/div/div[2]/div[1]/ul/li[3]/text()') # Time for d, l, b, t in zip(dianyan, leixing, diqu, timedata): countyr = b.replace('\n', '').split('/')[0] # Location shichang = b.replace('\n', '').split('/')[1] # Duration f = open('猫眼.csv', 'a') f.write('{}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}
'.format(d, pingfen, url, l, countyr, shichang, t)) print(d, pingfen, url, l, countyr, shichang, t )
for page in range(0, 11): page *= 10 Index(page)Data Visualization
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
# Load commonly used data analysis libraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import jieba
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# get_ipython().run_line_magic('matplotlib', 'inline')
# In[3]:
path='./maoyan.csv'
df=pd.read_csv(path,sep=',',encoding='utf-8',index_col=False)
df.drop(df.columns[0],axis=1,inplace=True)
df.dropna(inplace=True)
df.drop_duplicates(inplace=True)
df.head(10)
# Check the structure of the data
df.info()
print(df.columns)
# In[11]:
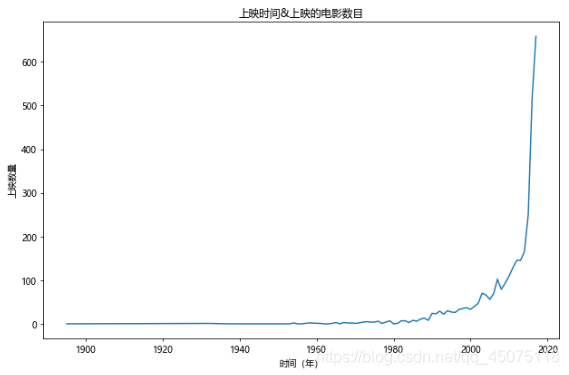
# Year and number of movies released. The number of releases after 2018 is uncertain, so we exclude it for now.
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(9,6),dpi=70)
df[df[u'上映时间']<2018][u'上映时间'].value_counts().sort_index().plot(kind='line',ax=ax)
ax.set_xlabel(u'Year')
ax.set_ylabel(u'Number of Releases')
ax.set_title(u'Release Year and Number of Movies Released')
# Based on the above figure, create a relationship chart between release year, number of releases, and ratings.
# However, due to the small amount of data before 1980, the ratings are inaccurate, so we focus on the analysis area from 1980 to 2017.
x=df[df[u'上映时间']<2018][u'上映时间'].value_counts().sort_index().index
y=df[df[u'上映时间']<2018][u'上映时间'].value_counts().sort_index().values
y2=df[df[u'上映时间']<2018].sort_values(by=u'上映时间').groupby(u'上映时间').mean()[u'评分'].values
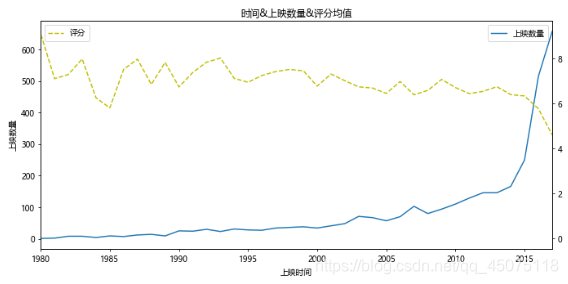
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(10,5),dpi=70)
ax.plot(x,y,label=u'Number of Releases')
ax.set_xlim(1980,2017)
ax.set_xlabel(u'Release Year')
ax.set_ylabel(u'Number of Releases')
ax.set_title(u'Release Year, Number of Releases, and Average Ratings')
ax2=ax.twinx()
ax2.plot(x,y2,c='y',ls='--',label=u'Ratings')
ax.legend(loc=1)
ax2.legend(loc=2)
# Solve Chinese garbled characters and the issue of negative values on the axes.
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] =['Microsoft YaHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# In[12]:
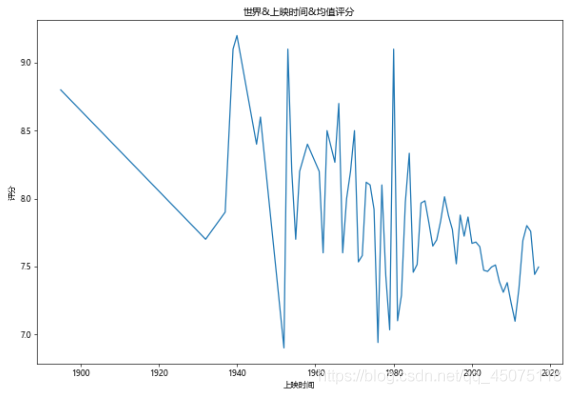
# World, Release Year, and Average Ratings
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(10,7),dpi=60)
df[df[u'评分']>0].groupby(u'上映时间').mean()[u'评分'].plot(kind='line',ax=ax)
ax.set_ylabel(u'Ratings')
ax.set_title(u'World, Release Year, and Average Ratings')
# In[13]:
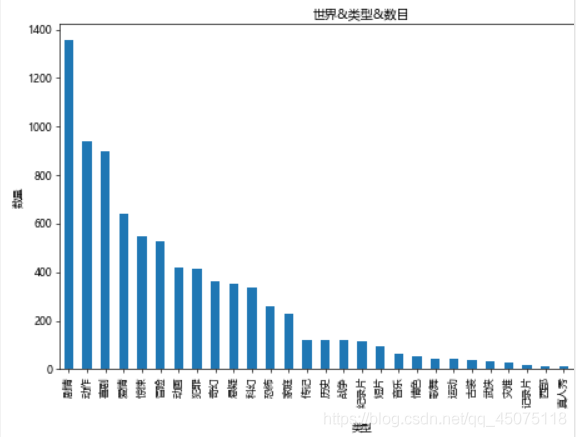
# Number of movies by genre in the world.
# Split the genres into the smallest units and then count.
types=[]
for tp in df[u'类型']:
ls=tp.split(',')
for x in ls:
types.append(x)
tp_df=pd.DataFrame({u'类型':types})
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(9,6),dpi=60)
tp_df[u'类型'].value_counts().plot(kind='bar',ax=ax)
ax.set_xlabel(u'Genre')
ax.set_ylabel(u'Number')
ax.set_title(u'World, Genre, and Number')
# In[14]:
# Distribution of movie duration and ratings.
# Note: Some movies have not been rated, so those need to be filtered out.
x=df[df[u'评分']>0].sort_values(by=u'时长(min)')[u'时长(min)'].values
y=df[df[u'评分']>0].sort_values(by=u'时长(min)')[u'评分'].values
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(9,6),dpi=70)
ax.scatter(x,y,alpha=0.6,marker='o')
ax.set_xlabel(u'Duration (min)')
ax.set_ylabel(u'Number')
ax.set_title(u'Distribution of Movie Duration and Ratings')
# It can be seen that the ratings...
# Data filtering for China
i=0
c0=[]
c1=[]
c2=[]
c3=[]
c4=[]
c5=[]
c6=[]
c7=[]
for x in df[u'地区']:
if u'中国大陆' in x:
c0.append(df.iat[i, 0])
c1.append(df.iat[i, 1])
c2.append(df.iat[i, 2])
c3.append(df.iat[i, 3])
c4.append(df.iat[i, 4])
c5.append(df.iat[i, 5])
c6.append(df.iat[i, 6])
c7.append(df.iat[i, 7])
i=i+1
china_df=pd.DataFrame({u'电影':c0, u'评分':c1,u'链接':c2, u'类型':c3,u'地区':c4, u'上映地点':c5,u'时长(min)':c6,u'上映时间':c7})
# In[16]:
# Comparing average ratings between China and the world in the time range of 1980-2017.
x1 = df[df[u'评分']>0].groupby(u'上映时间').mean()[u'评分'].index
y1 = df[df[u'评分']>0].groupby(u'上映时间').mean()[u'评分'].values
x2 = china_df[china_df[u'评分']>0].groupby(u'上映时间').mean()[u'评分'].index
y2 = china_df[china_df[u'评分']>0].groupby(u'上映时间').mean()[u'评分'].values
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(12,9),dpi=60)
ax.plot(x1,y1,ls='-',c='DarkTurquoise',label=u'World')
ax.plot(x2,y2,ls='--',c='Gold',label=u'China')
ax.set_title(u'Average Ratings: China vs World')
ax.set_xlabel(u'Time')
ax.set_xlim(1980,2017)
ax.set_ylabel(u'Ratings')
ax.legend()
# In[17]:
# Number of movies by genre: Comparison between China and the world.
# Since genres are mixed, we need to write a function to split them first.
# In[18]:
# Function to split genres: input a Series object and return a DataFrame of split genres.
# Here, we input a Series of genres.
def Cuttig_type(typeS): types=[] types1=[]
for x in typeS: if len(x)<4: # print x types1.append(x) ls=x.split(',') for i in ls: types.append(i)
types.extend(types1) df=pd.DataFrame({u'类型':types}) return pd.DataFrame(df[u'类型'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))
# In[19]:
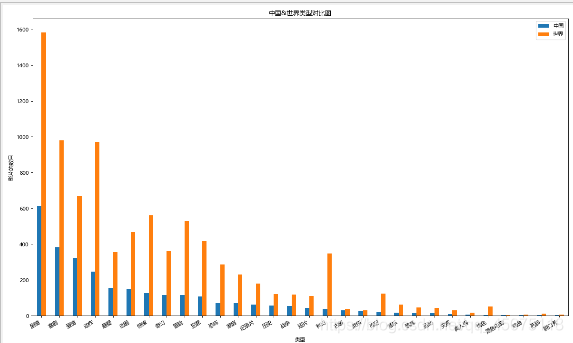
# Comparing movie types between China and the world.
df1=Cuttig_type(china_df[u'类型'])
df2=Cuttig_type(df[u'类型'])
trans=pd.concat([df1,df2],axis=1)
trans.dropna(inplace=True)
trans.columns=[u'中国',u'世界']
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(15,9),dpi=80)
trans.plot(kind='bar',ax=ax)
fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation=30)
ax.set_title(u'Comparison of Movie Types: China vs World')
ax.set_xlabel(u'Genre')
ax.set_ylabel(u'Number of Movies')
# In[20]:
# Then there is the scatter distribution: China, World, Duration, and Rating Distribution.
y = df[df[u'评分'] > 0].sort_values(by=u'时长(min)')[u'评分'].values
x = df[df[u'评分'] > 0].sort_values(by=u'时长(min)')[u'时长(min)'].values
y2 = china_df[china_df[u'评分'] > 0].sort_values(by=u'时长(min)')[u'评分'].values
x2 = china_df[china_df[u'评分'] > 0].sort_values(by=u'时长(min)')[u'时长(min)'].values
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,7), dpi=80)
ax.scatter(x, y, c='DeepSkyBlue', alpha=0.6, label=u'World')
ax.scatter(x2, y2, c='Salmon', alpha=0.7, label=u'China')
ax.set_title(u'Distribution of Ratings: China vs World')
ax.set_xlabel(u'Duration (min)')
ax.set_ylabel(u'Ratings')
ax.legend(loc=4)
# In[25]:
dfs=df[(df[u'上映时间']>1980)&(df[u'上映时间']<2019)]
# for x in range(0,len(dfs)):# print(dfs.iat[x,0],dfs.iat[x,-1])
df666 = dfs['电影'][:15]
wl = ,.join(df666.values)# Write the tokenized txt to a text file# fenciTxt = open(fenciHou.txt,w+)# fenciTxt.writelines(wl)# fenciTxt.close()
# Set the word cloud
lwc = WordCloud(background_color='white', # Set background color # mask=imread('shen.jpg'), # Set background image# max_words=2000, # Set maximum number of words font_path='C:\Windows\Fonts\simkai.ttf', # Set to KaiTi Regular # Set Chinese font so that the word cloud can display (the default font for word clouds is 'DroidSansMono.ttf', which does not support Chinese) max_font_size=60, # Set maximum font size random_state=30, # Set how many random generation states, i.e., how many color schemes )
myword = wc.generate(wl) # Generate word cloud
wc.to_file('result.jpg')
# Display the word cloud image
plt.imshow(myword)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
# In[41]:Conclusion
The source code is already provided, so I won’t explain it. If it is useful to you, please give me a thumbs up, thank you! Finally, let me show you my order-taking process.
PS: Always go through a third-party platform for order-taking!
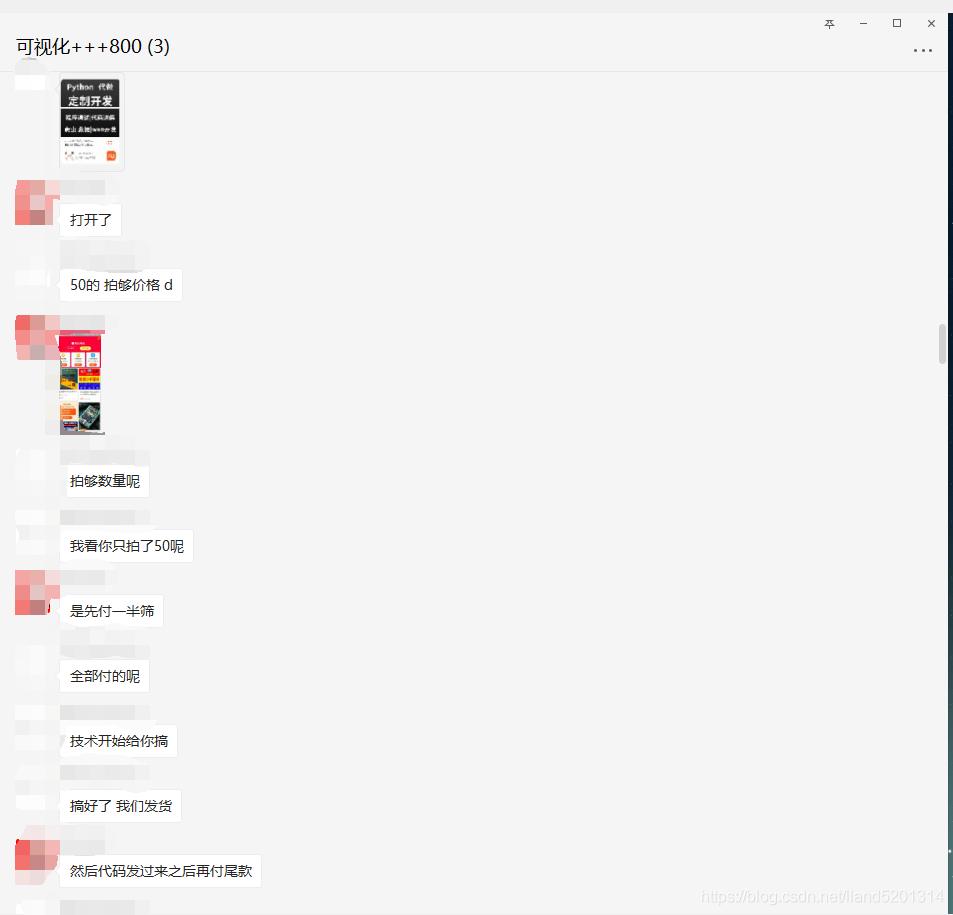
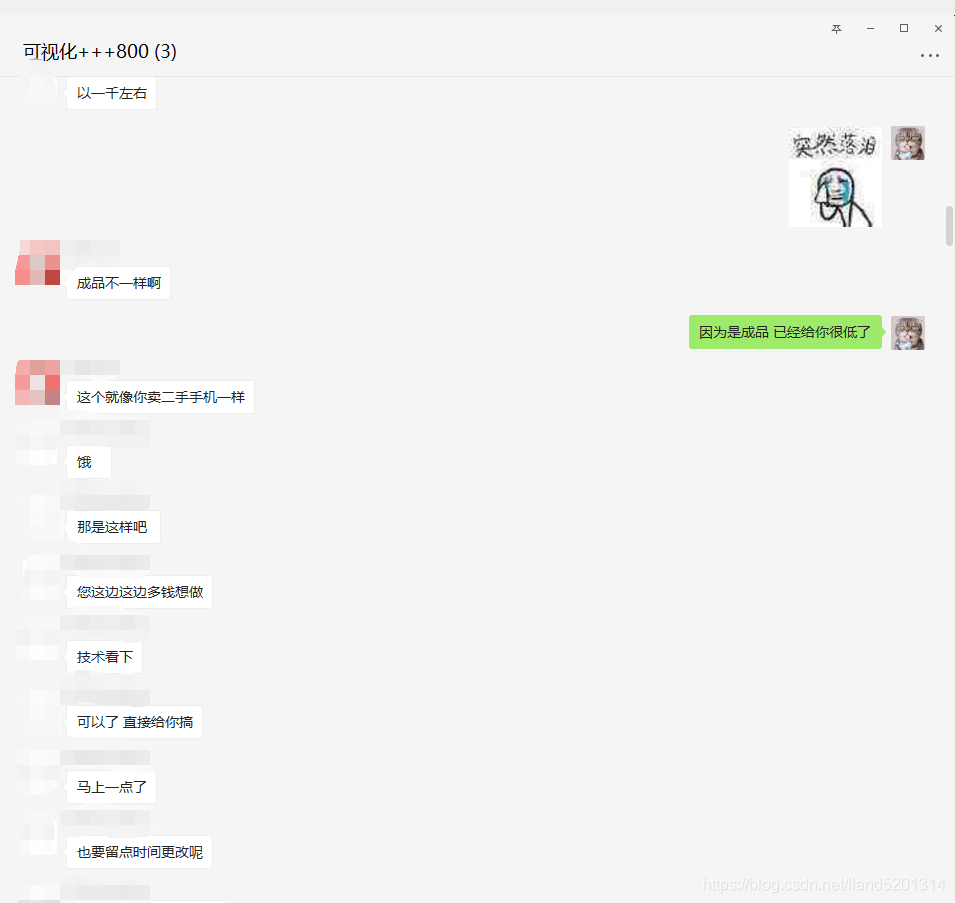
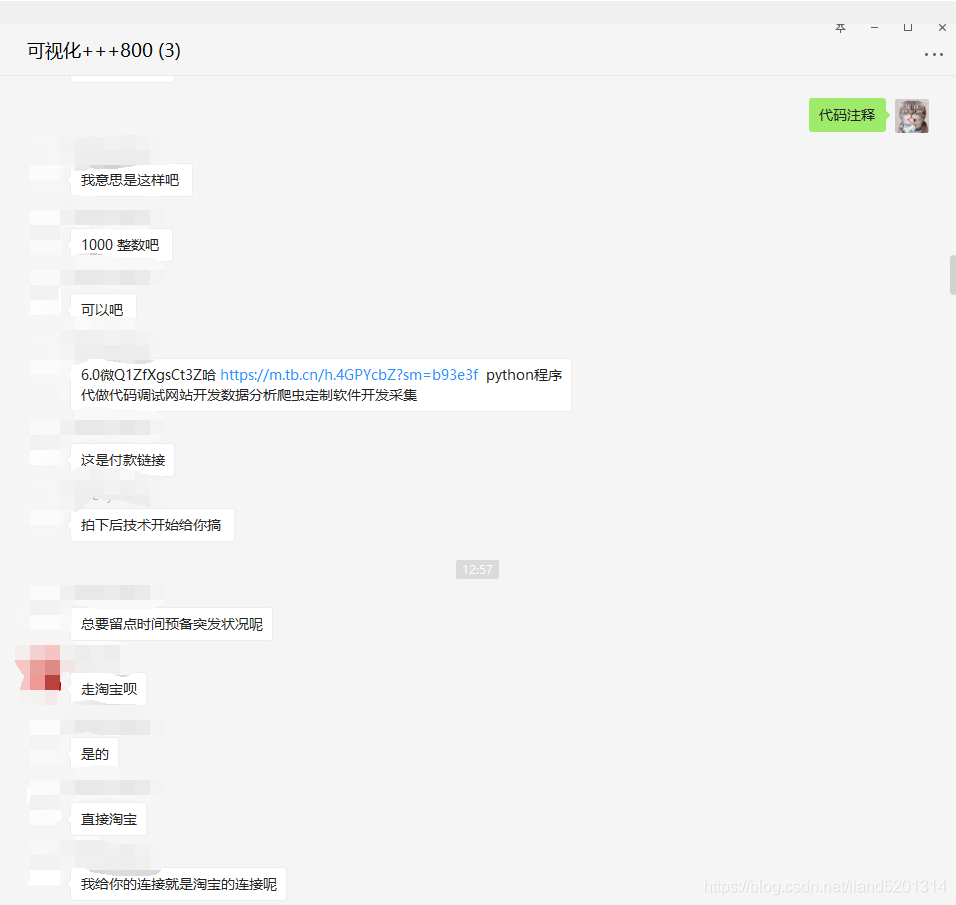
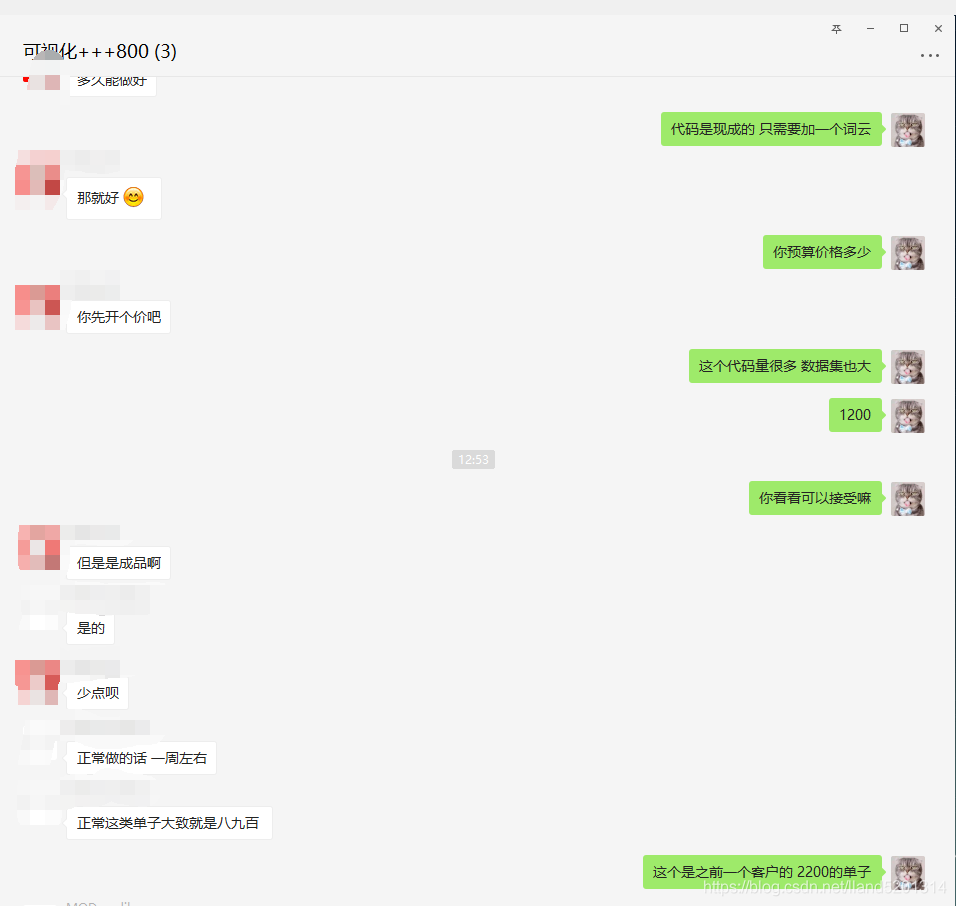
PS: Always go through a third-party platform for order-taking!PS: Always go through a third-party platform for order-taking!PS: Always go through a third-party platform for order-taking!
Copyright Notice: This article is the original work of the author, following the CC 4.0 BY-SA copyright agreement. Please attach the original source link and this statement when reprinting. Article link:
https://blog.csdn.net/lland5201314/article/details/117606268
Recommended Reading
18 Great One-Liner Python Codes
Generate Internet Slang with Python
Daughter, be obedient and change your avatar quickly!
Python from Beginner to Master: One Month is Enough!
How Valuable is the Computer Level 2 Certificate?
2021 National Worst University Dormitory Rankings.
Send Python Books|
|
 Long press the QR code aboveReply533756 to download for free(Not from this account) Long press the QR code aboveReply533756 to download for free(Not from this account) |
If useful, reward with a👍 and a look~
