The humanoid robot industry has a broad prospect.
Humanoid robots are robots that imitate human appearance and behavior, possessing a high level of intelligence. Compared to traditional industrial robots and service robots, their most significant feature is their human-like “limb” structure, movement patterns, and perception methods. Empowered by large models of artificial intelligence, they achieve imitation of humans in terms of physical ability, skills, and intelligence.
Figure 1 Characteristics of Humanoid Robots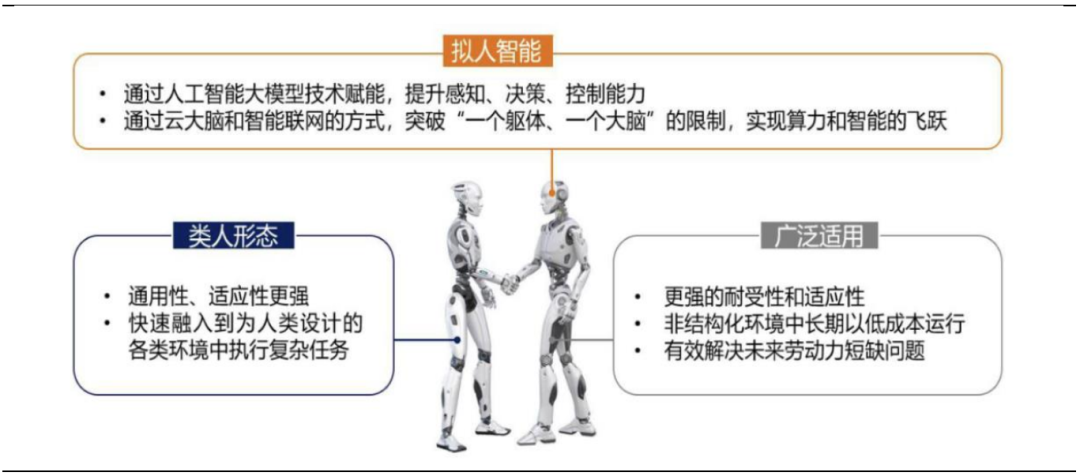 Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) |
Although humanoid robots are developing rapidly and product iterations are quick, they are still in the early stages of development. The future market scale is enormous, and currently, the vast majority of versatile humanoid robot products are at Level 1, with a few gradually exploring Level 2.
Figure 2 Different Development Levels of Humanoid Robots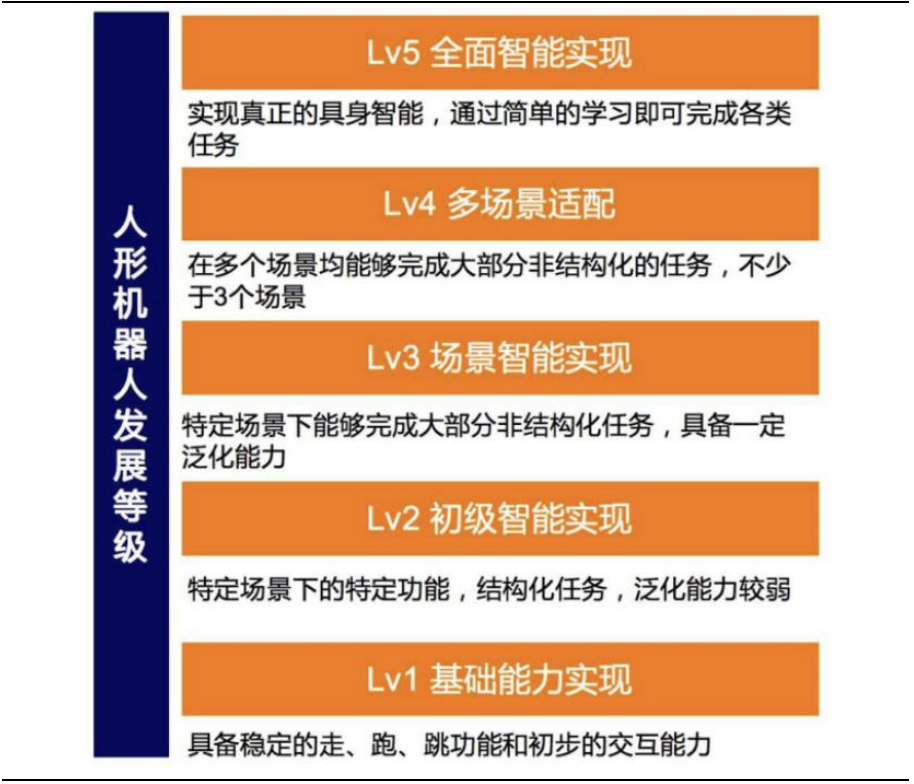 Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) |
The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has issued the “Guiding Opinions on the Innovative Development of Humanoid Robots,” which proposes that by 2025, an innovative system for humanoid robots will be initially established, with breakthroughs in key technologies such as “brain, cerebellum, limbs,” ensuring the safe and effective supply of core components. According to the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, the market space for humanoid robots in China is vast and requires several developmental stages to advance.
Figure 3 Different Development Levels and Expected Industry Scale of Humanoid Robots in China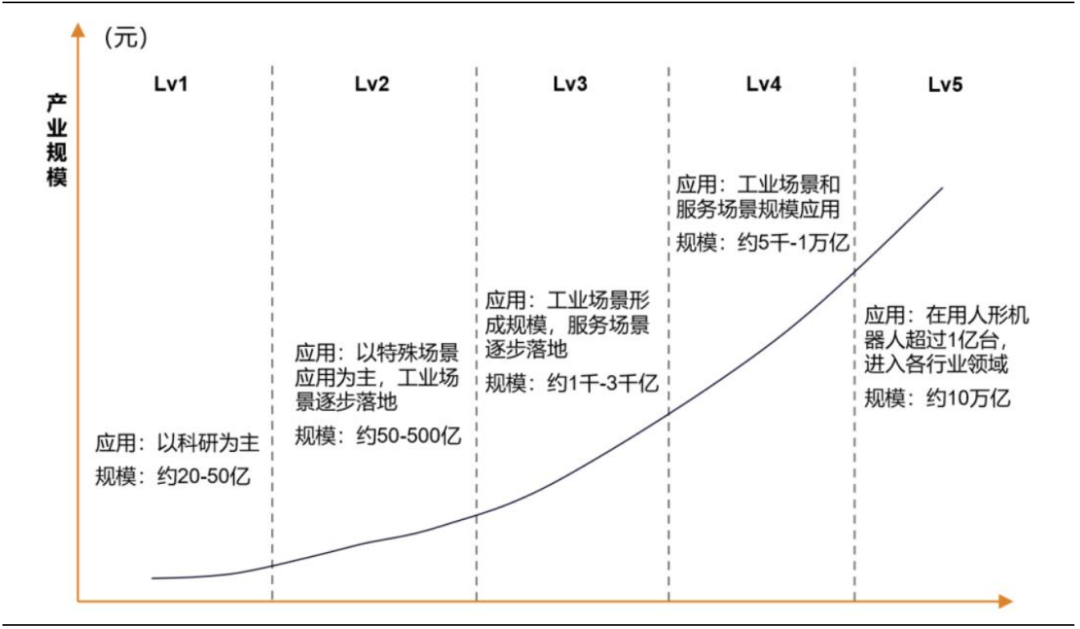 Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) |
Humanoid robots have complex structures; what chemical materials are involved?
Humanoid robots mainly consist of three parts: the “brain,” “cerebellum,” and “limbs.”
Figure 4 Composition of Humanoid Robots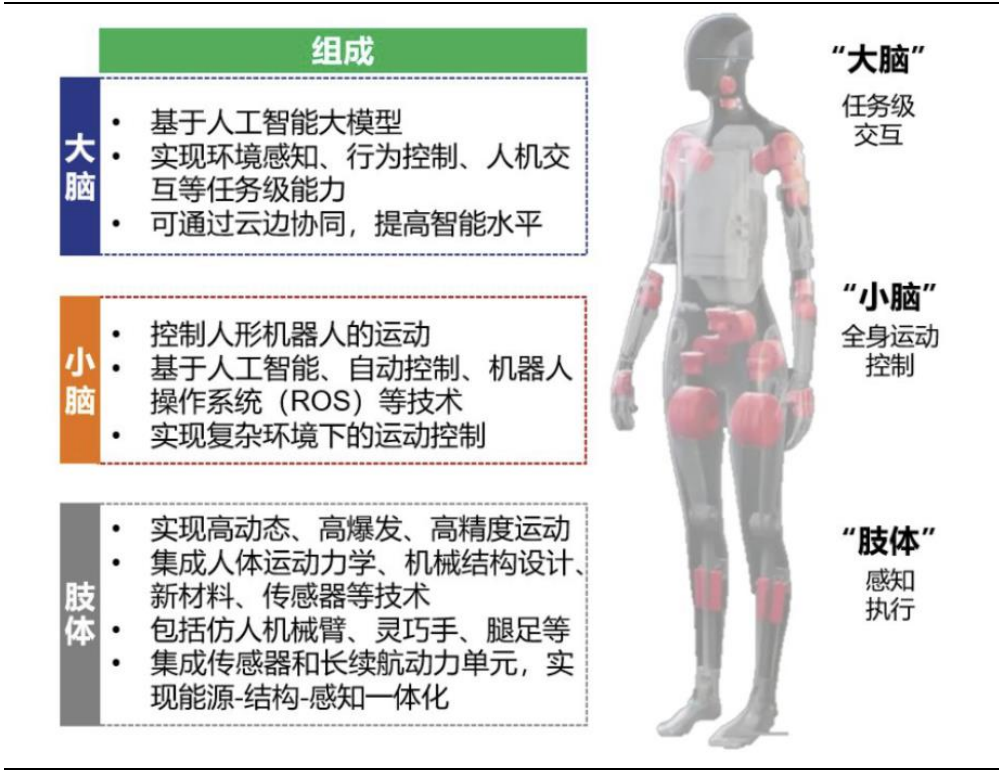 Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) |
1 Brain and Cerebellum
The current technology for the “brain” of humanoid robots is centered around large models, which require innovative algorithm support and are also dependent on powerful computing capabilities. The “cerebellum” aspect is similar. The relevant chemical materials mainly involve:
Figure 5 AI-related Chemical Materials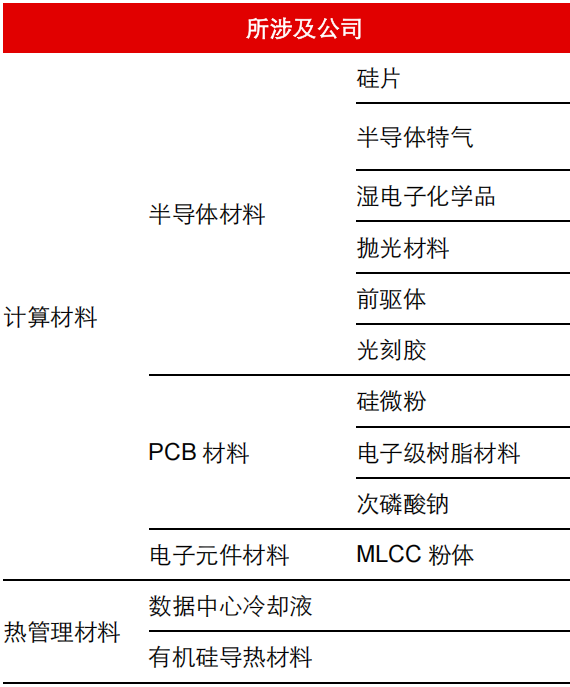 Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) |
2 Limbs
The “limbs” are the carriers and foundations for humanoid robots to achieve all anthropomorphic functions, mainly including actuators, chips, sensors, power sources, and many advanced technologies in new materials.
2.1 Actuators: Upgrading of Motor and Tendon Materials
The actuators of humanoid robots mainly include rotary actuators, linear actuators, and end effectors. The materials involved include: samarium-cobalt permanent magnet materials primarily used in motors, and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene and PBO fibers mainly used in the tendons of humanoid robot dexterous hands.
Figure 6 Three Major Actuators of Humanoid Robots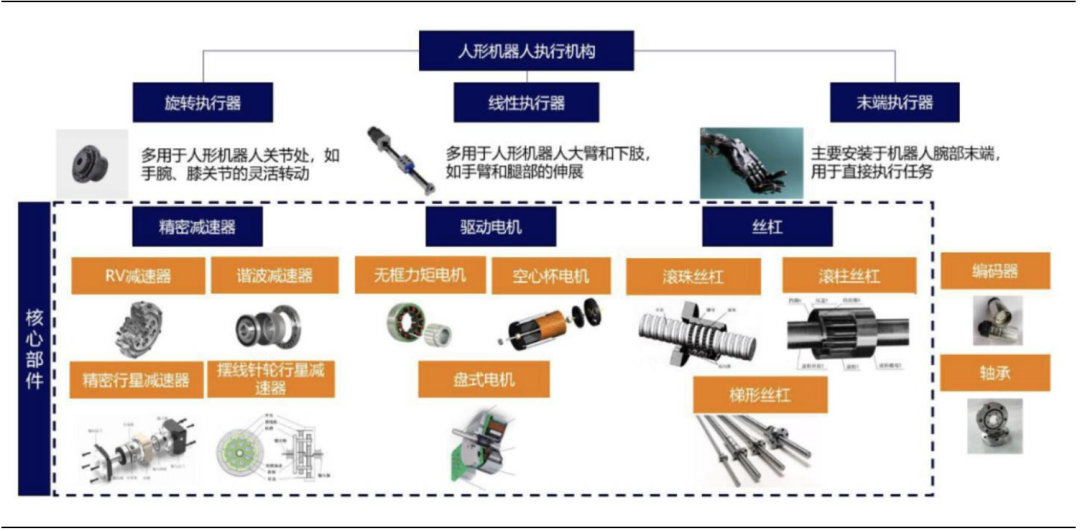 Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) |
2.2 Sensors: Electronic Tactile Skin as a Key Breakthrough Point
A large number of sensing units are the basis for achieving complex perception functions and interacting with the environment. The types of sensors required for humanoid robots include various types. Among them, electronic tactile skin has become the main development direction for tactile sensors. The materials involved include:
Substrate materials: Polydimethylsiloxane, polyethylene terephthalate, polyimide, polyethylene, polyurethane, etc.
Active layer materials: Graphene, carbon nanotubes, conductive polymers, ionic conductors, etc.
Electrode materials: Graphene, carbon nanotubes, etc.
Figure 7 Main Types of Electronic Tactile Skin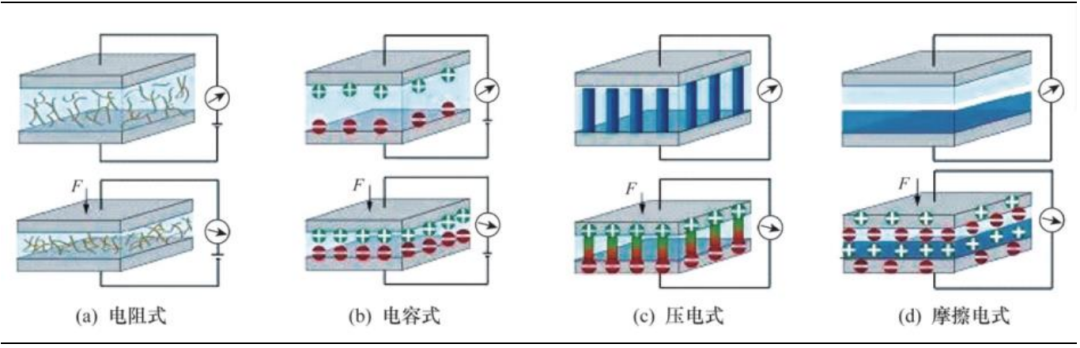 Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) |
Figure 8 Multimodal Soft Magnetic Sensors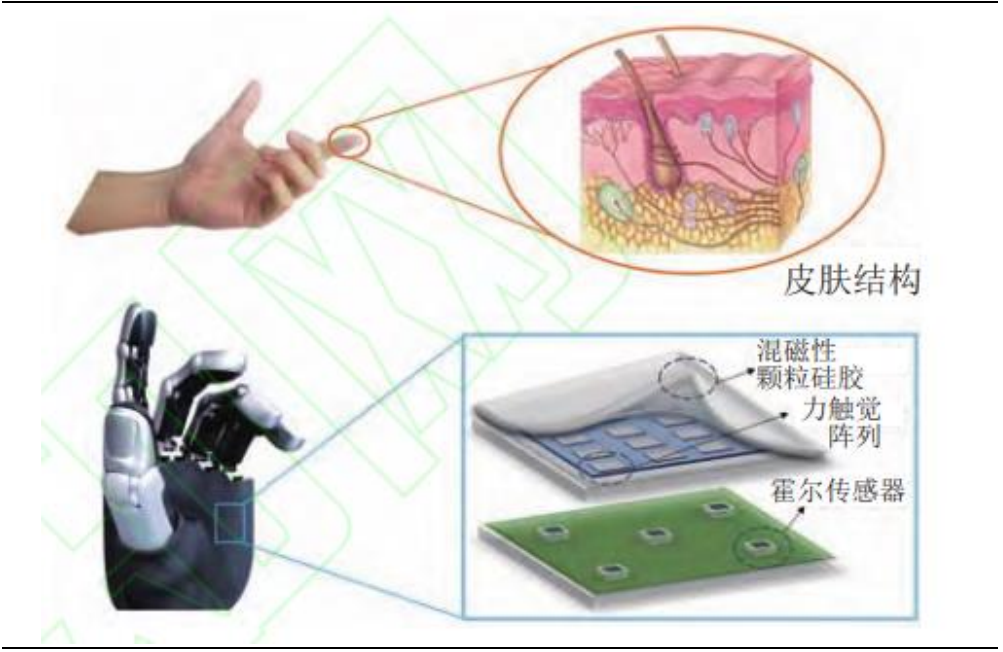 Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) |
2.3 Batteries: Development of New Generation Batteries Provides Power
Humanoid robots require high-performance power sources to provide lasting power, thus necessitating the continuous development of new generation battery systems, with solid-state batteries being an important direction. The solid-state battery-powered humanoid robot planned by GAC Group is expected to operate for 6 hours continuously without charging by 2026.
Figure 9 GAC Group’s Third Generation Embodied Intelligent Robot – GoMate Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) |
2.4 Other New Materials: PEEK Material Has Broad Prospects
The new materials for humanoid robots are mainly applied in the skeleton, shell, etc., which form the basic framework supporting humanoid robots in various actions. The new high-performance polymer PEEK (polyether ether ketone) achieves lightweight while maintaining high strength and rigidity. The production process of PEEK is complex, with high technical requirements and a high entry barrier. Humanoid robots are expected to become one of the fastest-growing application areas for its usage.
Figure 10 PEEK Industry Chain Overview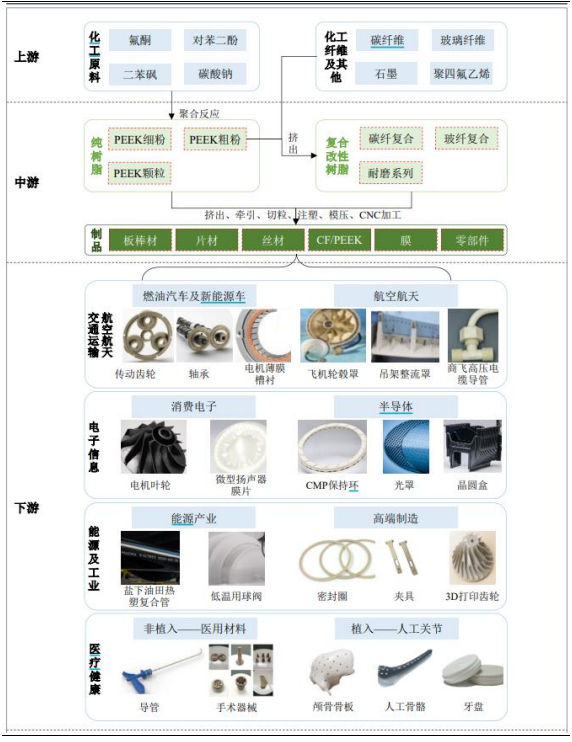 Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) Source: Changjiang Securities (Matai et al., 2025.02.06) |
Figure 11 Chemical Materials Related to Humanoid Robots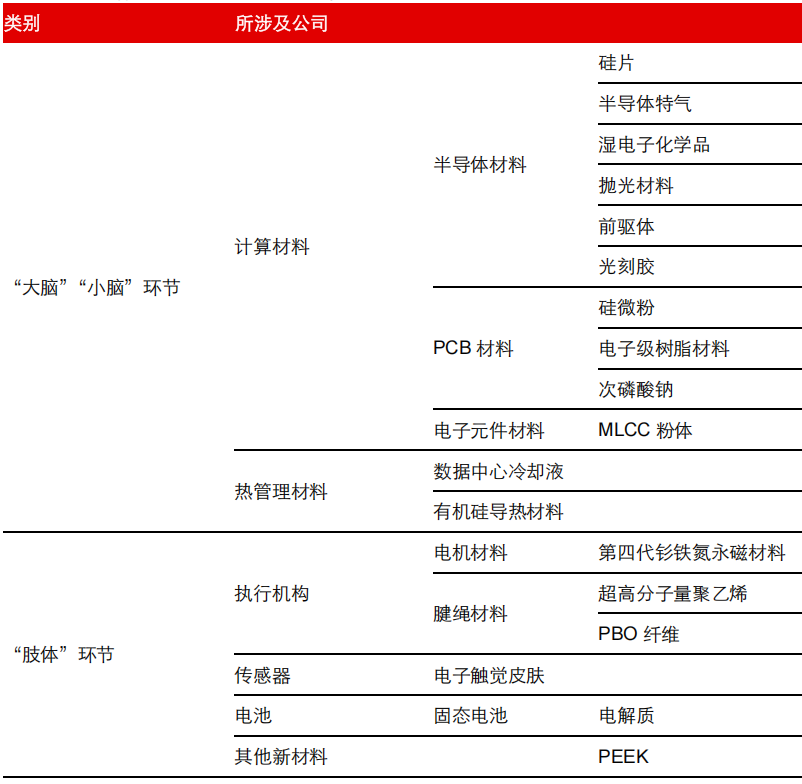 |
Source/Author: Shiquan Laoshi
Statement: Cheqian Information adheres to the principle of respecting originality and serving the industry together. This public account will indicate the source for reprints based on sharing purposes. The copyright of reprinted articles belongs to the original author or original public account. If there is any infringement, please contact 021-31656996.