 【Abstract】This article shares recommendations for the selection and configuration of VMware virtualization replacements in the securities industry, providing valuable information on core selection principles, technical route choices, and key considerations for domestic platforms, which are of practical reference significance for peers in the securities and other financial sectors using VMware.
【Abstract】This article shares recommendations for the selection and configuration of VMware virtualization replacements in the securities industry, providing valuable information on core selection principles, technical route choices, and key considerations for domestic platforms, which are of practical reference significance for peers in the securities and other financial sectors using VMware.
【Author】Yudan,an operations engineer at a securities company, mainly responsible for infrastructure operations including servers, operating systems, storage, cloud-native, and virtualization.
1. Background and Challenges
Broadcom completed its acquisition of VMware in November 2023. After the acquisition, VMware’s business model shifted from perpetual licensing to subscription-based, leading to significant dissatisfaction among users both domestically and internationally regarding the rising procurement costs. Many foreign users have expressed plans to replace VMware on social media. Similarly, the domestic securities industry is also facing considerations and challenges regarding the replacement of VMware. With the deepening of the national innovation strategy, the securities industry, as an important part of the national financial sector, has high requirements for the stability, performance, and security of virtualization platforms. Not only are foreign products continuously increasing in price, but there is also a significant risk of supply interruption. Meanwhile, domestic products have already demonstrated the capability to replace foreign products in terms of functionality maturity, cost-effectiveness, ecological compatibility, and security controllability. Therefore, considering the industry attributes, supply chain security risks, and long-term operational costs, this article aims to briefly share recommendations for the selection and configuration of VMware virtualization replacements from the perspectives of core selection principles, technical route choices, and key considerations for domestic platforms.
2. Core Selection Principles
(1) Technical Capability Assessment
-
High availability and performance: Support for hot migration, automatic failover (HA), dynamic resource pooling, and scalability to thousands of nodes in a single cluster to meet the elastic expansion needs of securities trading systems.
-
Multi-architecture support: Compatibility with x86 (including Hygon), ARM, and other chip architectures, supporting unified scheduling of “one cloud, multiple cores” resource pools, allowing for unified management of x86 and ARM architecture servers through a single platform to avoid single chip supply chain risks.
-
Storage compatibility: Support for local disk mode, centralized storage integration via FC, and hyper-converged architecture.
-
Network compatibility: Support for mainstream network virtualization technologies such as VXLAN.
(2) Ecological Compatibility
-
Operating system adaptation: Must be compatible with mainstream domestic operating systems such as Kylin, Tongxin UOS, and OpenEuler.
-
Support for managing VMware clusters and online migration of virtual machines.
(3) Autonomy and Control
-
The product must be independently developed, possess invention patents or “Computer Software Copyright Registration Certificates,” and have a product system code autonomy detection report issued by an authoritative testing institution under the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (such as Caibao Lab, China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, etc.), with overall code autonomy meeting acceptance standards.
(4) Migration and Operational Costs
-
Smooth migration capability: Support for virtual machine migration tools that minimize downtime.
-
Lower construction and expansion procurement costs, with mature product technology that meets long-term operational needs.
3. Technical Route Selection
(1) Storage-Compute Separation Architecture
The storage-compute separation architecture is a virtualization design model that decouples computing resources from storage resources, connecting them via a SAN network for independent expansion and management. VMware vSphere+ external storage is a typical application case of this architecture.
Its advantages include:
-
Decoupled computing and storage, flexible expansion (1:1 → 1:N).
-
Lower maintenance costs, with reduced dependency on software vendors’ technology.
-
Very mature architecture, reliable for production business.
The storage-compute separation architecture is suitable for users with high requirements for stability and performance, and flexible storage usage needs (local disks, external storage).
(2) Hyper-Converged Infrastructure (HCI)
Hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) is a hardware-software integrated solution that deeply integrates computing, storage, and network resources, replacing traditional centralized storage with a distributed storage engine for modular horizontal expansion. Its core feature is “software-defined everything,” with all resources centrally scheduled through a unified management platform. VMware vSphere+vSAN is a typical application case of this architecture.
Its advantages include:
-
Integration of computing and storage on the same physical node, eliminating the need for independent storage devices, simplifying architectural complexity, and saving rack space. A minimum production cluster can be built with three nodes, suitable for small and medium-sized brokerages for quick replacement.
-
Distributed storage enhances reliability through multiple copies/erasure coding mechanisms, ensuring that single node failures do not affect business operations.
-
Suitable for small and medium-sized brokerages to quickly build environments, reducing reliance on specialized storage operations teams.
Hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) is suitable for users who trust hyper-converged technology and have flexible deployment needs (such as new business pilot deployments).
(3) Private Cloud
A private cloud is a cloud infrastructure built for a single organization, integrating computing, storage, and network resources through virtualization and automation technologies to provide on-demand allocation and elastic scaling of IT service capabilities. Its core goal is to achieve efficient resource utilization and agile business delivery while meeting enterprises’ strong demands for data sovereignty, security, and compliance.
Its advantages include:
-
Strong PaaS capabilities, supporting policy-driven auto-scaling and self-healing.
-
A rich cloud service catalog, featuring self-service portals, API management, billing measurement, and automated operations.
-
Suitable for agile + stable business operations.
The private cloud architecture is suitable for large-scale deployments, with strong technical capabilities in the operations team and cloud service needs among medium to large users.
Summary: All three architectures have distinct characteristics and are widely applied in the securities industry. Notably, some leading brokerages have adopted different architectures based on business and scenario characteristics to meet their usage needs, providing reference experiences for small and medium-sized brokerages. Therefore, the author believes that technology should be combined with the company’s current situation and scenarios for selection, without being constrained by the past.
4. Key Considerations and Configuration Recommendations for Some Domestic Platforms
The author has gathered some comparative points of interest regarding domestic platforms currently used by brokerages from exchanges and company practices:
(Click to enlarge the image)
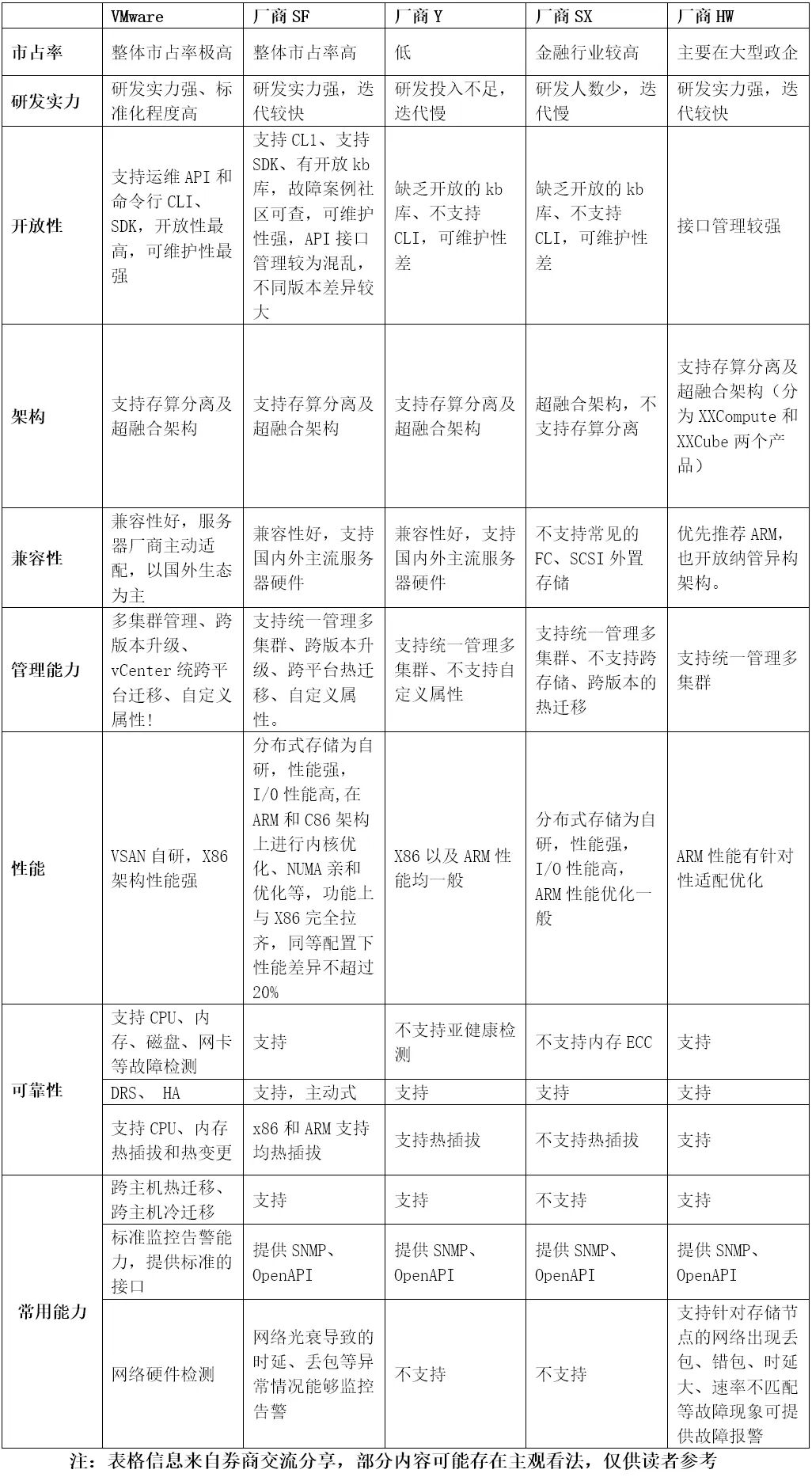
From the table above, it can be seen that although VMware still holds an undisputed dominant position in technology and market, domestic manufacturers are striving to catch up. Additionally, the author has encountered some pitfalls with default configurations in the practice of domestic platforms, and the following are some configuration items for reference:
1. UUIDRetention
|
Configuration recommendation: Enable If this option is not enabled, a new UUID will be generated after the virtual machine restarts, which may prevent some software that uses UUID for licensing (such as certain zero-trust software) from functioning. |
2. Cluster Resource Scheduling Configuration
|
Configuration recommendation: Manual Automatic configuration may pose risks of frequent balancing, and the balancing migration process may affect virtual machine performance, increasing instability factors. |
3. Host CPUConfiguration recommendation: Innovation on demand (non-innovation OS is not recommended to enable)
Enabling this option may affect the cross-cluster migration of virtual machines. The best practice is to keep it disabled, but if it is disabled during innovation acceptance, the real CPU model cannot be viewed through lscpu, which may impact on-site acceptance work.
4. Overcommit SettingsCPU overcommit recommendation: No more than 1:3Memory overcommit recommendation: 1:1Disk mode recommendation: Pre-allocated
5. Host Sub-Health ConfigurationConfiguration recommendation: Disable or enable with low sensitivity
Enabling host sub-health configuration may easily trigger the host to be kicked out of the cluster during network jitter, affecting cluster robustness. From operational practice, even if the management network is interrupted, it does not affect the normal operation of the virtual machine business network, so it is not recommended to enable sub-health configuration.
5. Conclusion
The securities industry has many mature cases of VMware virtualization replacement, and the three architectures of storage-compute separation, hyper-convergence, and private cloud have been fully validated in practice. The replacement products have evolved from being merely usable to becoming increasingly user-friendly. At the same time, they provide strong evidence for peers that under the principles of “autonomy and control, smooth migration, open adaptation, and stability and reliability,” matching mainstream mature domestic solutions and technical architectures based on the company’s scale and operational conditions, I believe that peers are confident in avoiding supply interruption risks and reducing cost pressures to build a highly available and high-performance domestic platform. Of course, the vision of continuous improvement still requires our joint efforts.
If you have any questions, feel free to click on the original article at the end of this text to discuss and exchange in the community.If you find this article useful, pleaseshare, likeor click“♡”to let more peers see it.
Recommended materials/articles:
-
Manufacturing enterprises adopting IaaS cloud platforms to replace VMware: advantages and disadvantages analysis, migration difficulties, and solutions.
-
Discussion on the replacement of key applications of VMware in urban commercial banks: strategies, alternative paths, and key selection points.
-
Application trend consensus on the migration of high-end equipment manufacturing enterprises from VMware virtualization to cloud-native platforms.
-
These 11 excellent articles will take you deeper into cloud-native.
-
From monolithic to cloud-native, how to understand the current trends in IT architecture evolution?
Welcome to follow the community’s “virtualization” technology theme, which will continuously update quality materials and articles. Address:http://www.talkwithtrend.com/Topic/23
Download the twt community client APP


Long press to recognize the QR code to download
Or search for “twt” in the app store.
Long press the QR code to follow the public account.
*The content published by this public account only represents the author’s views and does not represent the community’s position.