Source: Network Technology Alliance
Hello, this is the Network Technology Alliance.
Virtualization technology is a key technology in today’s computing field, providing great flexibility and resource utilization in areas such as data centers, cloud computing, and enterprise IT. In virtualization technology, vCPU (virtual Central Processing Unit) plays an important role, enabling multiple virtual machines to run simultaneously on a single physical computer. This article will delve into the basic concepts of virtualization and vCPU, helping readers better understand the core of this technology.
Virtualization
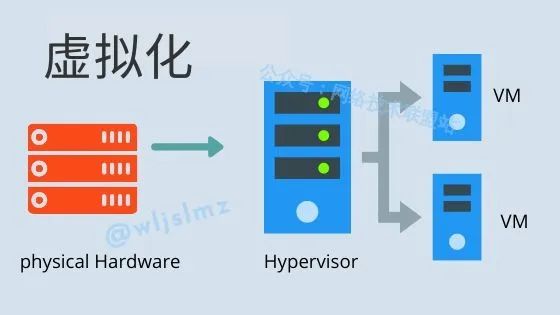
Virtualization is a technology that abstracts computing resources and logically divides them into multiple independent environments. This allows a single physical computer to run multiple virtual machines simultaneously, each with its own operating system and applications. The key goals of virtualization are to improve hardware resource utilization, simplify management, and provide a more flexible environment.
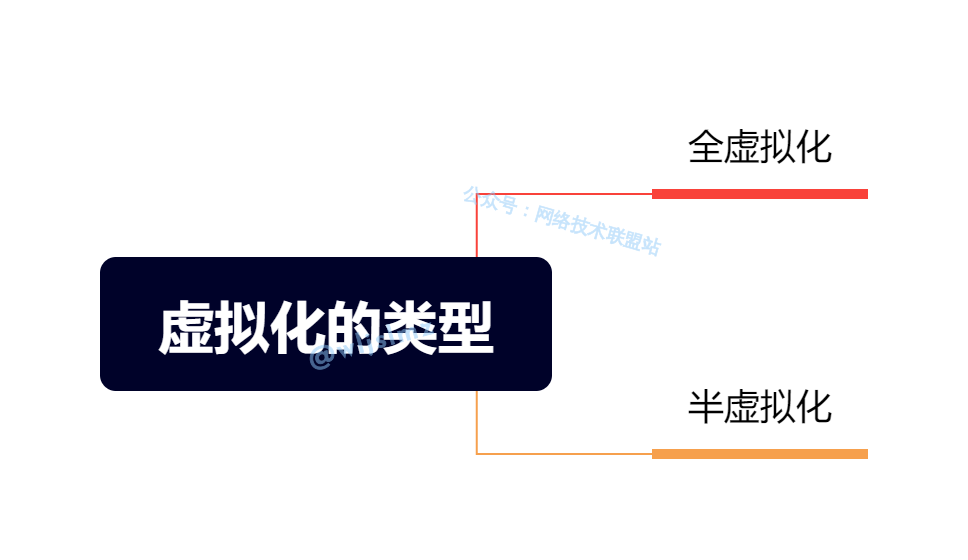
Types of Virtualization
Virtualization is mainly divided into two types: full virtualization and paravirtualization. In full virtualization, the virtual machine’s access to hardware is intercepted and simulated by the virtualization layer, allowing the virtual machine to run without modifying the applications and operating systems. Paravirtualization, on the other hand, requires the operating system within the virtual machine to be modified for more efficient communication with the virtualization layer.
vCPU is a key component in virtualization, representing the virtualization of physical processors. Each virtual machine is assigned one or more vCPUs, which are logically treated as independent processor cores. The virtualization layer is responsible for translating the virtual machine’s instructions into instructions that the physical processor can execute, enabling multiple virtual machines to run simultaneously on a single physical computer.
History of Virtualization
The history of virtualization technology dates back to the 1960s when IBM introduced virtual machine technology. However, it wasn’t until recent years, with improvements in hardware performance and growing demand, that virtualization technology truly became mainstream in the computing field. This section will review the development history of virtualization technology and introduce its evolution.
Virtualization technology has been widely applied in various fields. Cloud computing platforms, data center management, testing, and development environments all utilize virtualization technology to enhance resource flexibility and utilization. This section will explore the specific applications of virtualization technology in different scenarios.
vCPU
vCPU, short for virtual Central Processing Unit, is the processor resource used in virtual environments. It is a part of the physical CPU and can be independently used by virtual machines. Each vCPU can operate as an independent processor core to execute instructions.
In virtualization technology, vCPU is a resource abstraction that allows virtual machines to use processor resources as if they were using physical CPUs. This abstraction enables virtual machines to run multi-threaded applications without physical CPU cores.
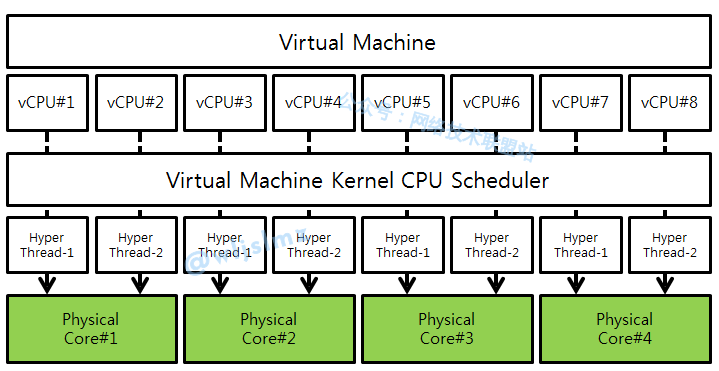
How vCPU Works
The working principle of vCPU is very similar to that of a physical CPU. When a virtual machine needs to perform a task, it sends this task to the vCPU. The vCPU converts this task into a series of instructions and then executes these instructions on the physical CPU.
During this process, the hypervisor (such as VMware or Hyper-V) is responsible for scheduling the operation of the vCPU. If multiple virtual machines request CPU resources simultaneously, the hypervisor decides which virtual machine’s task should be prioritized based on each virtual machine’s priority and resource requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of vCPU
The main advantage of vCPU is that it can improve the utilization of physical CPUs. By dividing the physical CPU into multiple vCPUs, we can run multiple tasks simultaneously, thereby increasing CPU utilization.
Additionally, vCPU provides greater flexibility. We can dynamically adjust the number of vCPUs based on the needs of each virtual machine without changing physical hardware.
However, vCPU also has some disadvantages. First, virtualization incurs a certain performance overhead. Although this overhead is minimal in most cases, it can become an issue in high-performance computing scenarios.
Secondly, over-allocating vCPUs may lead to wasted CPU resources. If a virtual machine is allocated too many vCPUs but does not fully utilize them, these vCPUs become idle resources, reducing overall CPU utilization.
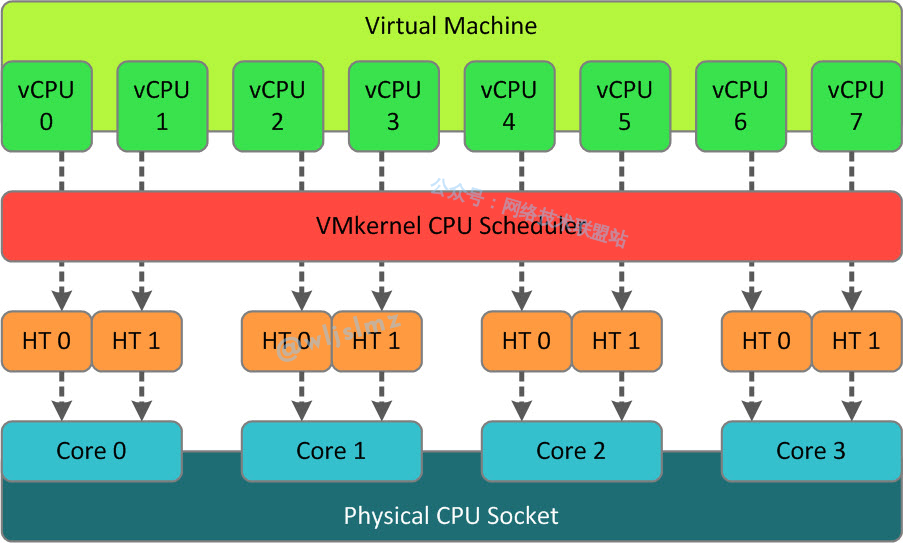
How to Optimize vCPU Usage?
Optimizing vCPU usage mainly involves two aspects: correctly allocating vCPUs and effectively managing vCPUs.
When allocating vCPUs, we need to consider the actual needs of the virtual machine. If a virtual machine runs a CPU-intensive application, we may need to allocate more vCPUs to it. Conversely, if a virtual machine has low CPU usage, we may need to reduce its number of vCPUs.
When managing vCPUs, we need to use appropriate scheduling strategies. For example, we can use priority scheduling to allow important virtual machines to access CPU resources first. We can also use fair share scheduling to ensure that each virtual machine can fairly access CPU resources.
Configuration and Management of vCPU
In a virtualization environment, configuring and managing vCPUs is an important task. This includes how to allocate vCPUs, how to schedule vCPUs, and how to monitor vCPU usage.
Allocation of vCPUs
When creating a virtual machine, we can allocate a certain number of vCPUs to it. This number can be determined based on the virtual machine’s needs and the resources of the physical CPU. Generally, we should avoid over-allocating vCPUs, as this may lead to wasted CPU resources.
Scheduling of vCPUs
The scheduling of vCPUs is handled by the hypervisor. The hypervisor decides which virtual machine’s task should be prioritized based on each virtual machine’s priority and resource requirements. During this process, the hypervisor needs to ensure that all vCPUs receive fair scheduling to avoid certain virtual machines being starved of CPU resources for extended periods.
Monitoring of vCPUs
To ensure the performance of the virtualization environment, we need to regularly monitor vCPU usage. This includes the utilization rate of vCPUs and the CPU load of each virtual machine. By monitoring this data, we can promptly identify and resolve potential performance issues.
Calculating vCPU
Before calculating vCPUs, it is important to understand some terminology.
Terms Related to vCPU
-
Hypervisor: A hypervisor, also known as a Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM), is software used to create and run virtual machines (VMs). It allows a host computer to share its resources (such as memory and processing power) to support multiple client VMs. Hypervisors can allocate one or more vCPU resources.
-
Socket: When you see the term “socket,” think of hardware. Imagine the number of slots on a motherboard. A socket is an array of pins used to secure a processor and connect the motherboard to available processing power. The number of sockets is determined by the motherboard’s capacity. There may be differences between sockets based on the supported CPU generations.
-
Thread: A thread is a path of execution within a process. A process can contain one or more threads. The main difference between threads and processes is that threads within the same process run in a shared memory space, while processes run in independent memory spaces. Threads are also referred to as lightweight processes.
-
Physical Core: A physical core, also known as a processing unit, is located within the CPU. A physical core may correspond to one or more logical cores.
-
Logical Core: A logical core allows a single physical core to execute two or more operations simultaneously.
Factors to Consider When Calculating vCPU Count
Calculating the number of vCPUs typically requires considering the following factors:
- Number of Physical CPUs: This is the actual number of CPUs in the server’s sockets.
- Number of Cores per Physical CPU: This is the number of chipsets on a CPU that can process data.
- Number of Threads per Core: If the physical CPU supports hyper-threading technology, then each CPU core can support two vCPUs.
Calculation Formula
Typically, each core has 8 vCPUs. The number of vCPUs is largely determined by the manufacturer, calculated by multiplying the number of processing threads provided for each core by the number of occupied sockets:
(Threads x Cores) x Physical CPUs = Number of vCPUsAssuming there is a physical CPU with 8 cores and 16 threads:
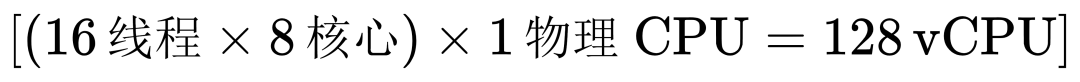
This means that on this physical CPU, 128 vCPUs can be allocated, calculated by multiplying the number of threads per core by the number of physical CPUs.
Then, the specific vCPU allocation depends on your workload and application requirements. For example, on a large database server, you might choose to allocate more vCPUs to each virtual machine to ensure sufficient computing resources. In light-load situations, fewer vCPUs can be allocated.
Here is an example calculation, assuming a total of 128 vCPUs, then calculating the number of virtual machines based on the required vCPU count for each:
- If each virtual machine requires 4 vCPUs, then:

- If each virtual machine requires 2 vCPUs, then:

- If each virtual machine requires 1 vCPU, then:
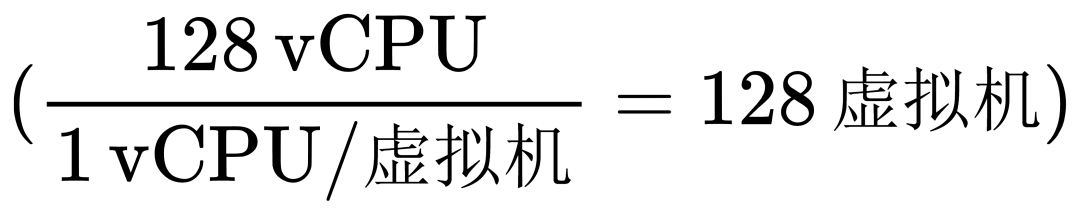
This calculation process can be adjusted based on actual needs. Overall, the key to calculating vCPUs lies in understanding the specifications of the underlying hardware and making reasonable allocations based on workload and performance requirements.
Challenges and Solutions for vCPU
Although vCPUs have many advantages, they also face some challenges. Here are some common challenges and possible solutions:
1. Performance Overhead
Virtualization technology incurs a certain performance overhead. This is because the hypervisor needs to manage and schedule vCPUs while running virtual machines. This consumes some CPU resources, thereby reducing overall system performance.
Solution: We can reduce performance overhead by optimizing the scheduling algorithms of the hypervisor and reasonably allocating vCPUs. Additionally, some hardware manufacturers are developing specialized virtualization technologies to minimize the performance overhead caused by virtualization.
2. Resource Management
In a virtualization environment, effectively managing and scheduling vCPUs is a challenge. Improper management and scheduling of vCPUs may lead to wasted CPU resources or affect the performance of virtual machines.
Solution: We can improve the management and scheduling of vCPUs by developing smarter resource management strategies and using automation tools. For example, we can dynamically adjust vCPU allocations based on the actual needs and performance metrics of virtual machines.
3. Security Issues
Virtualization technology may introduce some security issues. For example, if a virtual machine is attacked, the attacker may use vCPUs to affect other virtual machines.
Solution: We can prevent such security issues by using secure virtualization technologies and regularly updating and maintaining the hypervisor. Additionally, we can use security tools such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems to enhance the security of the virtualization environment.
Practical Applications of vCPU
vCPUs have wide applications in many scenarios.
1. Virtualization Environments
In virtualization environments, vCPUs are a key technology for achieving resource sharing and isolation. By using vCPUs, we can run multiple virtual machines on the same physical server, each with its own processing resources. This greatly improves hardware utilization and reduces IT costs.
2. Cloud Computing
In cloud computing, vCPUs are the primary unit of measurement for computing resources. Users can choose cloud servers with different numbers of vCPUs based on their needs. This provides users with great flexibility, allowing them to adjust computing resources according to business requirements.
3. High-Performance Computing
In high-performance computing, vCPUs can be used for parallel computing. By distributing computing tasks across multiple vCPUs, we can significantly increase computing speed and reduce task completion time.
vCPU vs CPU
vCPU (virtual Central Processing Unit) and CPU (Central Processing Unit) are two terms with different concepts and roles in computer architecture. Here are the main differences between them:
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
-
Physical Hardware: The CPU is the actual hardware component in a computer system, typically a chip known as a processor or central processor. It is the core of the computer, executing instructions, performing calculations, and controlling various parts of the computer.
-
Executing Instructions: The CPU is the main executor in a computer system, responsible for executing instructions in computer programs. It performs various operations such as arithmetic operations, logical operations, and data movement through its instruction set architecture.
-
Cores and Threads: A physical CPU may contain multiple cores, each capable of handling independent tasks. At the same time, each core can support multiple threads, achieving parallel processing through hyper-threading or multi-core technology.
vCPU (Virtual Central Processing Unit)
-
Virtualization Concept: vCPU is a concept in virtualization environments, representing the virtual processors allocated within virtual machines. Virtualization technology allows multiple independent virtual machines to be created on a single physical computer, each of which can have its own vCPU.
-
Virtualization Layer: vCPU is a virtual entity simulated and allocated by the virtualization layer. The virtualization layer is responsible for converting the virtual machine’s instructions into instructions that the physical processor can execute. This allows multiple virtual machines to share the resources of the same physical computer.
-
Resource Isolation: Each vCPU within a virtual machine is independent of other virtual machines, and the virtualization layer ensures resource isolation between them through scheduling and resource management. This allows multiple virtual machines running different operating systems on the same physical hardware.
Summary
- CPU is the actual physical hardware processor, the core component of a computer that executes calculations and control tasks.
- vCPU is a virtual processor in a virtualization environment, simulated and allocated by the virtualization layer, allowing multiple virtual machines to share the resources of the same physical computer.
- A physical computer can have multiple CPUs, each of which can contain multiple cores and threads.
- Multiple virtual machines can run simultaneously on a physical computer, each with one or more vCPUs.
💡💡💡 Just remember: vCPU is an abstract concept in virtualization environments used to achieve resource virtualization and isolation, while the actual CPU is a key component in computer hardware. In cloud computing and virtualization technology, the concept of vCPU allows for more flexible management and allocation of computing resources.
Previous Recommendations
What is Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW)? Beyond Traditional Network Protection!
Five Layers of IoT Architecture: Perception Layer, Network Layer, Data Layer, Application Layer, and Business Layer
The Most Comprehensive Summary of Fiber Connector Types, Very Complete!
In-Depth Understanding of Passive Optical Network (PON): Key Differences Between GPON and EPON
Ethernet Cable Categories: From CAT1 to CAT8.2, It’s Simply the History of Network Cables!

