
 Introduction to Low Energy Bluetooth
Introduction to Low Energy BluetoothGuangzhou Zhiyuan Electronics Co., Ltd. has launched multiple series of low energy Bluetooth modules for different application scenarios, including the ZLG52810 series slave Bluetooth module, ZM52820 series master-slave Bluetooth module, and ZM8258 series master-slave Bluetooth module. The products meet the needs of low-power wireless communication for small battery-powered devices and support two low-power modes, with the lowest power consumption reaching nA level. Users can configure the appropriate power mode for their devices based on usage scenarios using AT commands.
-
Normal sleep mode: The serial port stops working, and the module’s power consumption reaches uA level, while the protocol stack operates normally, waking up through the wake-up pin or when the module receives BLE data.
-
Deep sleep mode: Most peripherals are turned off, the protocol stack stops operating, entering deep sleep mode, with the lowest power consumption reaching nA level. To wake the Bluetooth module, the wake-up pin can be used.
 How Low Energy Bluetooth Achieves Low Power Consumption
How Low Energy Bluetooth Achieves Low Power ConsumptionBLE has 40 channels, of which 37, 38, and 39 are advertising channels, also known as primary advertising channels. The primary advertising channel can advertise a maximum of 31 bytes, while the remaining 37 are data channels, also known as secondary advertising channels. When large data packets need to be broadcasted, they must be sent through secondary advertising channels with lengths ranging from 0-255 bytes. To achieve low power consumption, Bluetooth typically broadcasts once on each of the three primary advertising channels, with the radio frequency on time reduced from the traditional 22.5ms to 0.6-1.2ms.
Low energy Bluetooth replaces the idle state of traditional Bluetooth with a deep sleep state. In the deep sleep state, the host remains in an ultra-low load cycle state for a long time, and many interfaces are turned off during sleep, activated only when needed by the controller, saving the most energy and achieving deep sleep.
-
Efficient encoding methods can send the same amount of data in less time, thereby reducing power consumption; -
Compared to traditional Bluetooth, low energy Bluetooth supports ultra-short packets, which requires less time to send, while faster startup times shorten the waiting time for transmission and reception; -
Low energy Bluetooth uses only one protocol to achieve server discovery, name discovery, and information reading and writing, requiring less overhead than classic Bluetooth that uses multiple protocols, thus reducing power consumption; -
The low energy Bluetooth protocol adopts a client-server architecture, reasonably distributing tasks between the client and server to reduce communication overhead in the system.
 Common Low Energy Application Scenarios
Common Low Energy Application ScenariosIn the application scenario of smart door locks, by installing a Bluetooth module inside the lock, users can read the Bluetooth information of the smart lock in real-time through an app, pair it, and send an unlock request to the server. The server then sends the unlock command to the phone, which receives the unlock information and sends the command to the smart lock via the Bluetooth module, making unlocking convenient, fast, and secure.
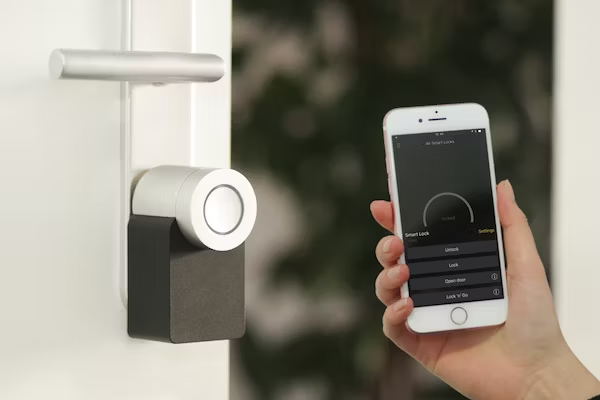


Figure 2 Healthcare Products
Low energy Bluetooth smart MESH lights utilize low energy Bluetooth technology and MESH networking technology. By simply installing an app on a smartphone, users can achieve smart networking control of lighting, which is more convenient and flexible, while also supporting remote control devices.
Figure 3 Smart Lighting System

Figure 4 HID Device
In traditional home appliances, such as soymilk machines and rice cookers, low energy Bluetooth control can upgrade them to smarter devices. Users can control home appliances through smartphones for switching, scheduling, and other functions, as well as conduct self-diagnosis and firmware upgrades.
Figure 5 Smart Home Appliance Products
6. iBeacon Applications
iBeacon broadcasts information to phones based on low energy Bluetooth, helping businesses optimize their operational strategies by providing services based on users’ geographic locations. Utilizing low energy Bluetooth offers more stable and reliable performance with lower power consumption, allowing devices to maintain longer operational times.

Figure 6 iBeacon Application Scenario
 Technical Communication Group
Technical Communication Group
For more articles, please click “ Read Original ”.






