Click the blue text above to follow us

1. Broadcast Domain
As shown in the figure, an Ethernet composed of one or more switches has all stations within the same broadcast domain. As more switches are added, the scope of this broadcast domain increases, leading to several drawbacks:
-
Broadcast Storm
-
Difficult Maintenance
-
Security Issues
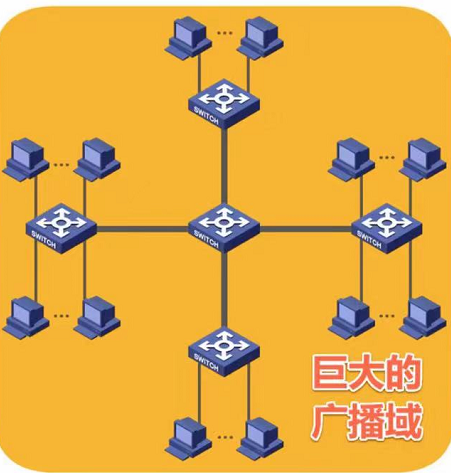
In this broadcast domain, if one host wants to obtain the MAC address of another host in a different subnet, it needs to send an ARP broadcast request to retrieve the MAC address of the other host. This broadcast request will be sent to every host, resulting in a broadcast storm. Hence, VLAN technology was introduced to address broadcast storms.
2. VLAN
To solve the broadcast domain issue, we need to segment the broadcast domain. We can use a router to segment the broadcast domain so that ARP broadcast requests do not reach every host.
As shown in the figure, the hosts connected to two switches belong to the same broadcast domain.
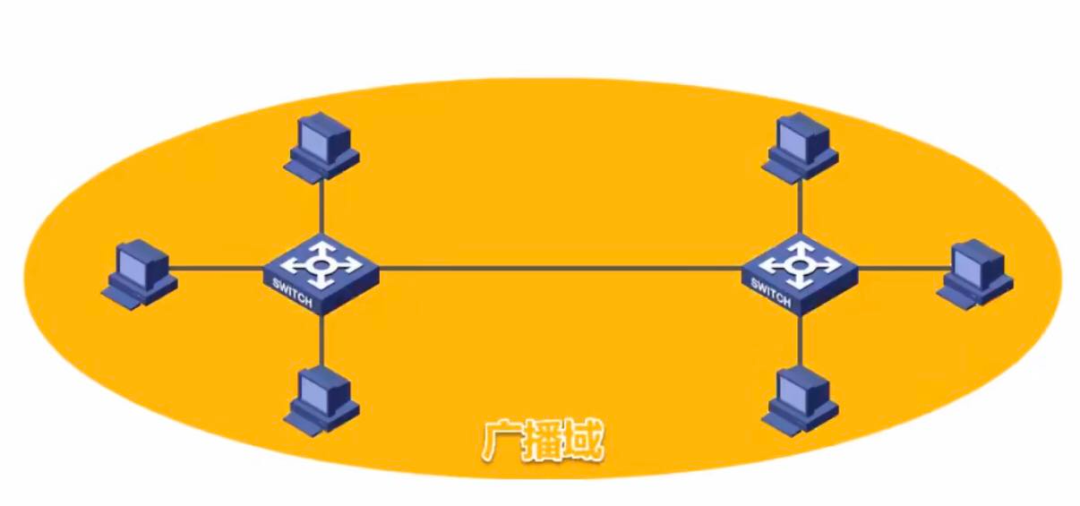
We add a router in the middle to segment the broadcast domain:
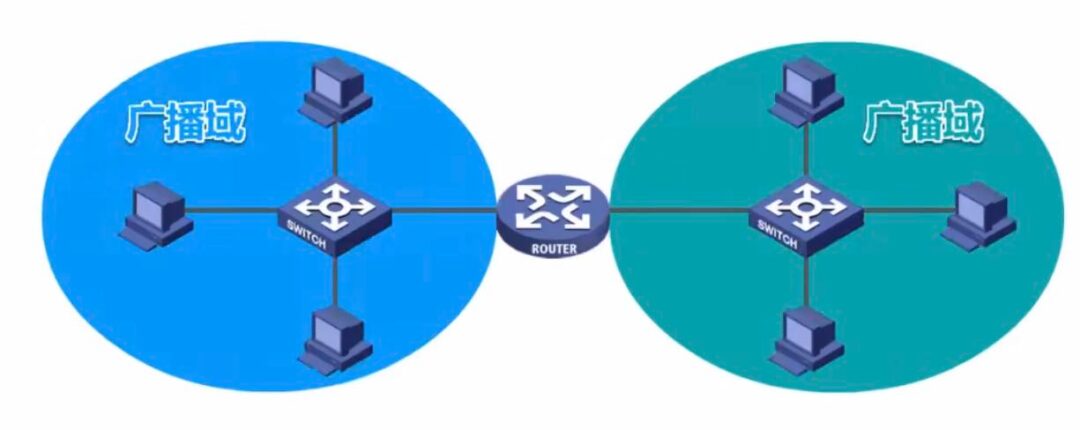
However, routers are relatively expensive, so it is not practical to use routers for broadcast isolation. We introduced Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) technology.
This is similar to virtual storage in an operating system, which saves physical storage space by dividing logical storage space to improve storage performance. The cloud desktops, cloud hosts, and various cloud products encountered in work also mean the same. The VLAN we are discussing here is an application of virtual technology in networking, and virtual technology has become a common topic.
Here, virtual technology virtualizes devices and physical locations, essentially representing a new logic for resource partitioning and flexible resource utilization. Just like in an OS where process execution is divided into time slices, the CPU only runs for a limited time in each slice, allowing for concurrent execution of multiple processes and flexible use of CPU resources.
We unify multiple local area networks into one large local area network and divide this large local area network into different VLANs, which can segment the broadcast domain.
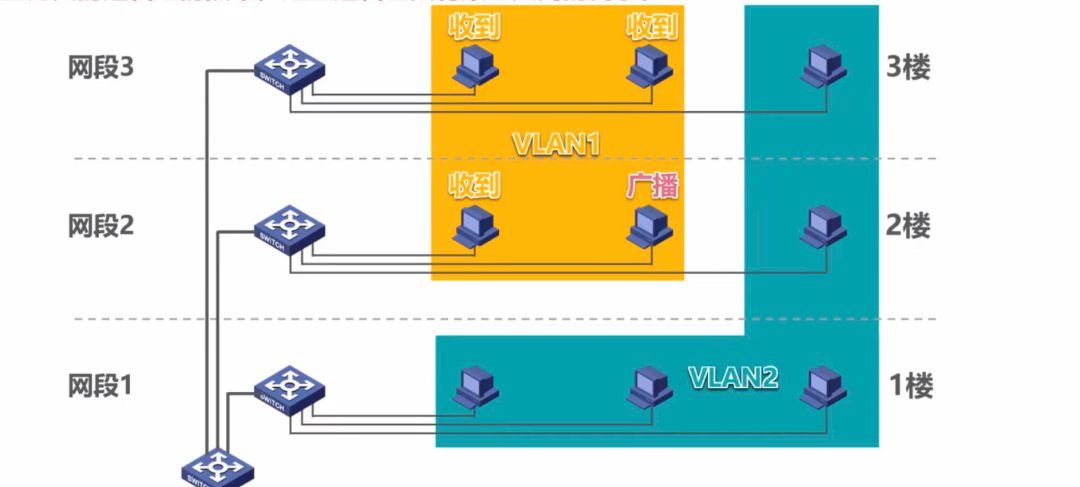
As shown in the figure, switches are allocated to floors 1, 2, and 3, each representing a local area network, where broadcast communication can be achieved within each local area network. Now, if we connect the switches from floors 1, 2, and 3 to a single switch, broadcast communication can be executed across all hosts.
This means that subnets 1, 2, and 3 achieve full broadcast; at this time, we can divide VLAN1 and VLAN2, ensuring that broadcasts from hosts in VLAN1 do not reach hosts in VLAN2, achieving isolation between subnets and broadcast domain isolation.
Summary: Hosts within the same VLAN can broadcast communicate, while hosts in different VLANs cannot broadcast communicate.


Disclaimer: Content sourced from the internet; thanks for the contributions. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal.