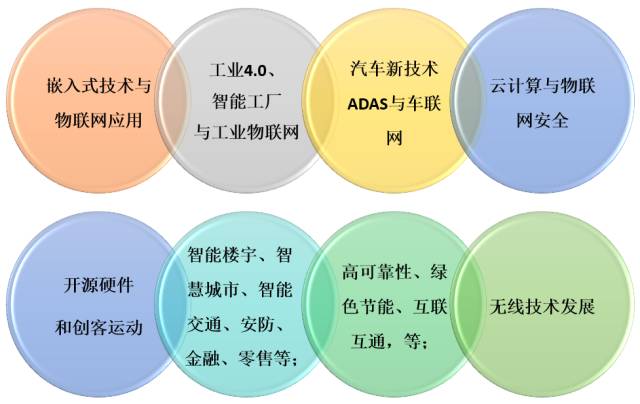
Looking back at the past year of 2016,
embedded technology and the Internet of Things (IoT) have developed rapidly.
On the basis of consolidating traditional applications,
embedded technology is exploring emerging markets,
with the IoT being one of the most extensive application markets.
In this new technological revolution driven by innovation,
the IoT will undoubtedly bring greater transformational and disruptive changes to industries.
It enables us to closely connect the digital world with the physical world,
creating profound impacts on how businesses engage with customers
and offering new services.
2017 has arrived
What will be the development trends of embedded and IoT technologies?
The author provides a brief analysis and summary ~
1. Mergers and acquisitions have a profound impact on the development of embedded processors.
In the past year and for the foreseeable future, chip suppliers are still eager to cut costs and increase profits through mergers and acquisitions. Chip suppliers need to leave enough profit on current products to fund the research and development of the next generation of products, and as costs rise, they need to figure out how to improve return rates. Recent mergers we have seen include Qualcomm with NXP, Microchip with Atmel, and Renesas with Intersil. These mergers will require 1-2 years of integration and digestion, so in the short term, mergers will affect the development of embedded processor technology and markets, but in the long term, mergers will benefit the promotion and popularization of IoT technology and systems. This is because IoT applications require processor designs to provide solutions aimed at end-users and applications. The chip designs for IoT applications emphasize power efficiency, security, ease of use of development tools, and cost reduction. All of these require chip suppliers to invest in research and development to create more integrated and better-supported embedded processor (including microcontroller) solutions. We believe that in 2018, the industry will see more innovative embedded IoT chip solutions.
Mergers will guide embedded processors toward vertical markets for IoT applications. Chip market leaders are shifting their focus to high-growth market opportunities, such as Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), autonomous driving, machine vision, artificial intelligence (AI), and 5G. Leading chip suppliers have also adopted acquisition strategies targeting these vertical markets, such as Samsung’s recent acquisition of Harman to enter the automotive market, and Intel’s acquisition of Movidius to penetrate the machine vision market. Movidius, a startup, has its machine vision chips already applied in DJI drones and Google Tango AR smartphones, which are currently very popular. Although these vertical markets are currently small in scale, they present enormous business opportunities for the future, and chip companies are unwilling to miss out on these opportunities. The trend of mergers in vertical markets will continue.
The IoT will focus on low cost, low power consumption, and power efficiency. The performance of existing embedded processors and microcontroller (MCU) products is sufficient to meet most IoT applications. Most embedded applications do not require the highest performance; they need the best power efficiency and the lowest power consumption. Leading embedded processor suppliers will continue to provide the best integration and power efficiency for targeted applications, along with appropriately sized chip products.
The microcontroller (MCU), which once successfully rose with 8-bit microcontrollers, has welcomed the wave of IoT development after years of refinement. 32-bit microcontrollers will occupy an important position in low-power and always-on IoT systems. The momentum for MCU development targeting the IoT market will not diminish, with microcontrollers becoming increasingly integrated, software platforms becoming richer, and the combination of processors with sensors and the cloud becoming closer.
Embedded processors and microcontrollers are core components of embedded and IoT systems. Currently, ARM is the market leader, with microcontrollers and processors based on ARM processor cores occupying the vast majority of embedded and IoT market share. With the rise of innovative technologies such as machine vision, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence, the role and influence of GPUs are becoming increasingly significant and cannot be ignored. The popularity of IoT has driven the development of low-power computing and wireless networks. In the future, new processor technologies and business models will emerge in this field. AI will require further enhancements in computing, and embedded edge computing will play a huge role in optimizing computing power and improving real-time capabilities. Amazon’s Alexa is an example of this. IoT and AI will drive the research and application of new processor architectures, and open-source hardware (including open-source chips) will be a development trend.
2. Merging with IoT cloud platforms into maturity.
Cloud computing has three models: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). The IoT cloud platform is an application of cloud computing PaaS. The architecture of the IoT cloud platform (IoT Platform) is illustrated in the following Figure 1. IoT devices communicate with the device gateway or smartphones through Bluetooth and Zigbee wireless communication links, and then connect to the IoT cloud platform via WiFi and 4G/LTE communication networks. It leverages public cloud IaaS basic cloud services to provide IoT devices with the capability to access the entire lifecycle of operational management services.
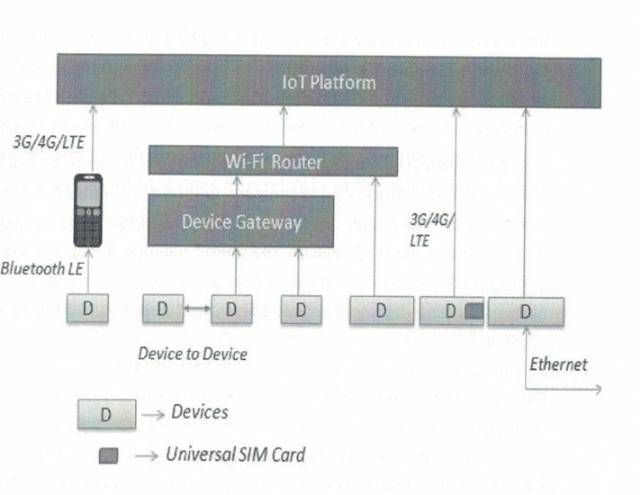 Figure 1 IoT Cloud Platform
Figure 1 IoT Cloud Platform
Currently, well-known foreign IoT cloud platforms include Amazon AWS IoT, Microsoft’s Azure IoT, General Electric’s Predix IoT (see Figure 2), IBM Watson IoT, and PTC IoT (ThingsWorks) platform. Domestic IoT cloud platforms include China Mobile’s OneNet, Guangzhou Smart Cloud, and Alibaba’s Smart Cloud. Open-source IoT cloud platforms include Kaa and Eclipse Kura projects.
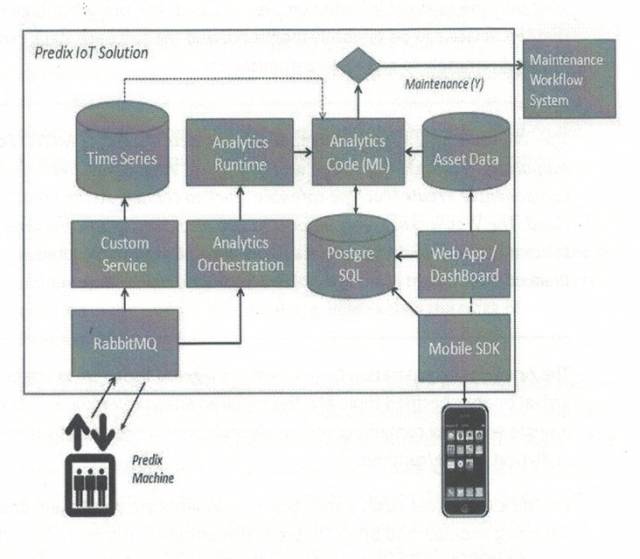 Figure 2 General Electric’s Predix IoT Platform
Figure 2 General Electric’s Predix IoT Platform
3. The rise of IoT operating systems.
With the increasing maturity of open-source software, embedded systems have widely adopted open-source software, such as the Linux operating system. Apart from fields that require high safety and reliability, such as automotive electronics, aerospace, and defense, traditional embedded operating systems are growing slowly and lack profitable business models. With the development of IoT cloud platforms, operating systems embedded on devices are also combining with cloud platforms to form a brand new IoT operating system (also known as Operating System for the Internet of Things). Currently, existing IoT operating systems include ARM mbed OS (see Figure 3), Google’s Android Things, Microsoft’s Windows 10 IoT Core, Huawei’s LiteOS, and Qingke Mico OS.
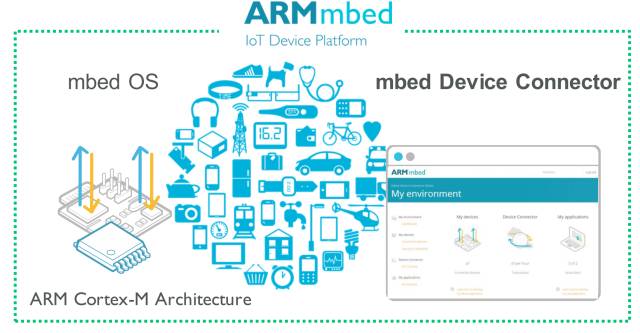
Figure 3 Application Diagram of ARM mbed OS
Despite the push from tech giants for IoT operating systems, open-source software will remain active for a long time to come. For example, FreeRTOS (which is used by the Pebble smartwatch and many IoT devices), TinyOS, etc. This is because the demand for IoT systems is unclear, the business model is immature, and the technology for IoT operating systems is still developing and needs to be validated in products. Some users may prefer to choose open-source software to customize their IoT operating systems..
4. IoT security remains a significant challenge.
On October 21, 2016, a massive cyberattack in the United States, including Amazon and Twitter, caused widespread network paralysis, which was attributed to a DDoS attack on the DNS service provider Dyn. Dyn stated that the attack was likely caused by 100,000 IoT devices infected with the Mirai malware, which brought IoT security concerns to the forefront. On October 26, the American security research team Shellphish demonstrated the ability to hack the fingerprint unlock feature of Huawei P9 Lite at a geek conference, along with the 2015 security breach incident of a video surveillance device company in Hangzhou, highlighting the growing attention to IoT device security issues.
Previously, smart product manufacturers only considered protecting the functional safety of their devices and the security of the data they generated. Even with this requirement, many device manufacturers, especially in consumer electronics, have struggled to meet this task. Now they are required to help protect the security of devices and networks, even for customers that do not belong to them. Moreover, IoT security design is still in the exploratory stage, and there are currently no mature design and implementation methods.
Another layer of meaning for embedded systems security is the functional safety of embedded devices. The demand for functional safety is most urgent in industrial IoT (IIoT) fields such as automotive electronics, factory automation, industrial control, railway traffic signaling, and smart grids. The design and implementation methods for this aspect are also relatively standardized, and commercial companies have mature software and tools to provide project consulting and services.
2017 will be a year of adjustment and development for embedded and IoT technologies. As the integration of chip companies following mergers gradually completes, some IoT applications will come to fruition and scale up. The narrowband IoT technology (LPWAN) will develop rapidly in 2017, with standards such as LoRa, Sigfox, and NB-IoT advancing simultaneously. China has just announced the establishment of the world’s largest 5G experimental field in Huairou, Beijing, which can provide an end-to-end testing environment and will help promote the formation of 5G standards and industrial development. One of the key technologies of 5G for IoT is aimed at low-power, large-connection, and low-latency, high-reliability scenarios, which is a new direction for 5G expansion.
2018 will usher in a year of breakthrough developments in embedded and IoT technologies. Operating system technology and network security technology targeting IoT applications will become increasingly mature, and processor technology will see refreshing developments driven by rapid advancements in virtual reality and artificial intelligence. Supported by new generation network technology, IoT development will enter a new era of rapid growth.
The 6th Shenzhen International Embedded Systems Exhibition EMBEDDED EXPO 2017 will be held from December 21-23, 2017, at the Shenzhen Convention and Exhibition Center. As an annual event in the embedded field in China, the Embedded Systems Exhibition gathers professionals, buyers, and decision-makers from the embedded and various application industries, providing a one-stop communication platform for the entire industry chain, from components, modules, embedded boards, to smart systems and IoT solutions in various industries. For more details, please follow the official website: www.embeddedexpo.com
Further Reading:
1. For more market information on IoT operating systems, you can read the article “Hunting for IoT Operating Systems” by journalist Zhou Yuan published on January 23, 2017, in Caijing. This article is currently the most detailed discussion on the development of the IoT operating system market.
2. For information on IoT operating systems and the technology and evolution history of open-source embedded operating systems, you can refer to the book “The Chronicles of Embedded Operating Systems: Historical Evolution and the Future of IoT” authored by the author and published by the Machinery Industry Press in November 2016.
3. For information on embedded system security, you can refer to the book “Embedded System Security: Practical Approaches to Secure and Trusted Software Development” by David Kleidermacher, translated by Zhou Qingguo et al., published by the Machinery Industry Press in 2015. This book is one of the very few good books on embedded system security available both domestically and internationally.
4. For analysis of enterprise IoT technology and market, it is recommended to refer to the book “Enterprise IoT: Strategies & Best Practices for Connected Products & Services” authored by Dirk Slama, Frank Puhlmann, and others, published by O’Reilly. The two main authors of this book come from Bosch in Germany, combining theory with practice, and the content is close to current application scenarios.
Author Biography:
He Xiaoqing is a renowned embedded systems expert and one of the earliest entrants in embedded OS in China. He founded Beijing Maikete Software Technology Co., Ltd. and has 30 years of experience in embedded technology and markets. He is also a council member of the China Software Industry Association, vice-chairman of the Embedded Systems Branch, and secretary-general of the Embedded Systems Association. He has published several books, including “The Chronicles of Embedded Operating Systems: Historical Evolution and the Future of IoT,” “Embedded Real-Time Operating System μC/OS-III Application Development,” and “Embedded Software Essentials.”

Date: December 21-23, 2017
Location: Shenzhen Convention and Exhibition Center Halls 1/2/9