
#Long press the image above to recognize the QR code and participate in the OSC Year-End Celebration#
MQTT Protocol is a machine-to-machine (M2M) protocol that is widely used in IoT (Internet of Things). It is a message-oriented protocol. Because of this, it is very lightweight and widely adopted in the IoT ecosystem. Almost all IoT cloud platforms support sending and receiving data via MQTT with various implementations of IoT smart devices (such as Arduino, Raspberry Pi, etc.).
Of course, there are other IoT protocols, but MQTT is the most efficient.


MQTT was developed around 1999, primarily to create a protocol for bandwidth-constrained environments. Additionally, it has very low power consumption, which is very appealing for IoT.
This protocol uses a publish-subscribe paradigm, contrasting with the request/response paradigm of HTTP. It uses binary messages to exchange information, which is very low overhead. It is simpler to implement, more efficient, and open. Another interesting aspect is that MQTT uses TCP as its transport layer. All these factors make it more suitable for IoT.


As mentioned above, MQTT implements a publisher-subscriber model. The publisher-subscriber model decouples the client that publishes messages (the publisher) from the client that receives messages (the subscriber). Furthermore, compared to HTTP, which is mainly a synchronous protocol, MQTT is an asynchronous protocol that does not block the client while waiting for messages. Additionally, the MQTT protocol does not require subscribers and publishers to be directly connected.


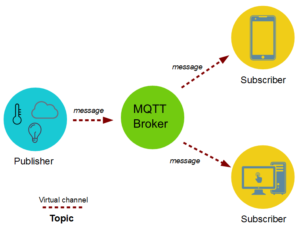
As stated above, MQTT is a protocol based on messages and implements a publisher-subscriber model. A key component of MQTT is the MQTT broker. The main task of the MQTT broker is to dispatch messages to subscribers. It receives messages from publishers and then forwards them to subscribers. When forwarding messages, the MQTT broker uses topics to filter clients. A topic is a string that can be combined by creating topic levels.
Topics act as virtual channels connecting the publisher with its subscribers. Topics are managed by the MQTT broker. Through this virtual channel, publishers and subscribers are decoupled, and clients (publishers or subscribers) do not need to know each other. Since there is no direct dependency between message producers (publishers) and message consumers (subscribers), this protocol is highly scalable.
The following diagram describes the MQTT architecture:


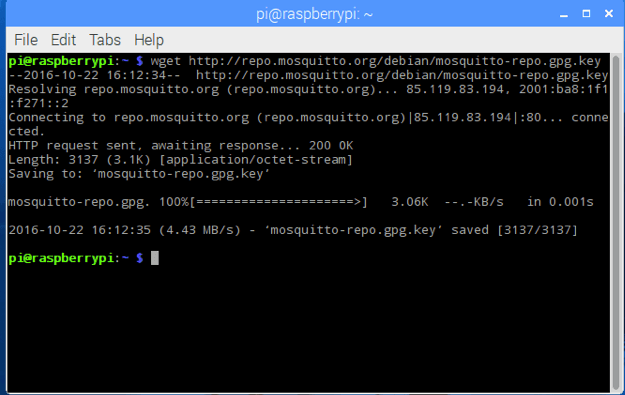
Now that we have a general understanding, let’s apply it through a practical example. MQTT has many implementations, and we will use Mosquitto, developed by Eclipse. The first step is to install the MQTT broker; for our purposes, we will install it on a Raspberry Pi. To install Mosquitto, we need to add its repository so we can download it. Before adding the repository, it is necessary to add a key to verify that the downloaded installation package is legitimate. We can connect to the Raspberry Pi via SSH or Remote Desktop Connection. Now, in the terminal, enter the following command:

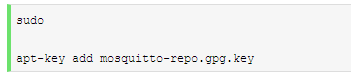
 Then, import the key:
Then, import the key:
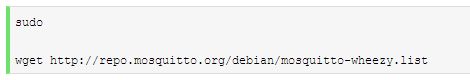
Finally, add the .list file:
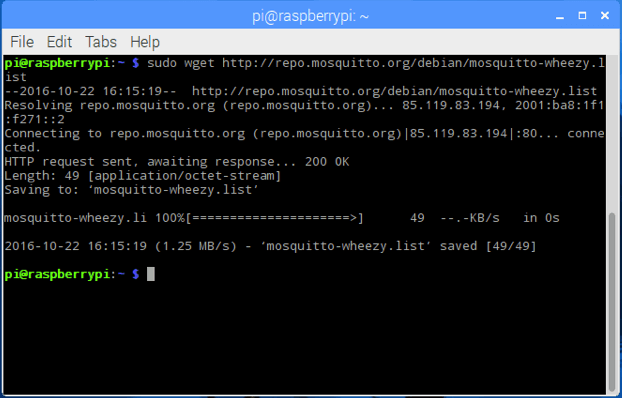 This way, the MQTT server is installed on the Raspberry Pi. This server is our MQTT broker. Now we need to install the clients (publishers and subscribers). In this example, we will install both the client and the server on the same Raspberry Pi, but you can also install them on different PCs/servers or IoT boards.
This way, the MQTT server is installed on the Raspberry Pi. This server is our MQTT broker. Now we need to install the clients (publishers and subscribers). In this example, we will install both the client and the server on the same Raspberry Pi, but you can also install them on different PCs/servers or IoT boards.
How to Send an MQTT Message
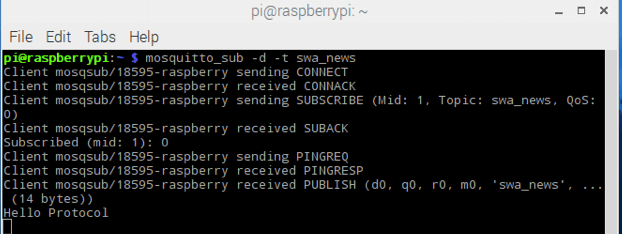
Assuming we have successfully installed and configured the client and server, we can now register a user to a specific topic and then wait for the publisher to send messages. We can use the following command to register a user:
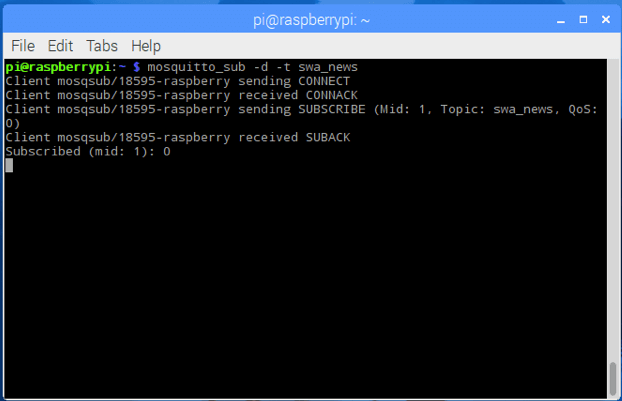
As shown, the user is waiting for messages. In this example, the topic we are using is called swa_news. Now, we will use the MQTT publisher to send a message with the topic swa_news.
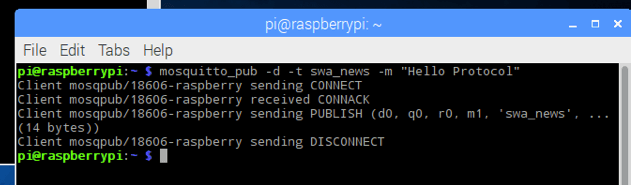
In this example, the MQTT publisher sent the message “Hello Protocol”, and on the user end, we received the following message:
How to Use MQTT on Android Devices
Finally, we will use an Android MQTT client to receive the messages we sent. The following video shows us how to configure an Android MQTT client.
https://www.youtube.com/embed/plnbafCBVtU
This article hopes you learned what the MQTT protocol is and how to use MQTT to send messages to clients.


