 Click “Industrial Control Lao Xu” to follow me
Click “Industrial Control Lao Xu” to follow me
Introduction
“Why does my PLC program crash while running?”
“Clearly the logic is fine, but the output signals are jumping around?”
PLC programming may seem simple, but beginners (and even experienced engineers) often fall into pitfalls due to some detail issues. This article summarizes the ten most common and fatal programming errors, along with real cases and solutions, helping you save 80% of debugging time!
1: Error in Reusing Output Points
Error Case:
In the PLC programming of an automated production line, to save output points, the same output point was used to control two different devices: one for the extension action of a cylinder and the other for the illumination of an indicator light. When the program ran, it was found that the actions of the cylinder and the indicator light were confused and could not work properly.
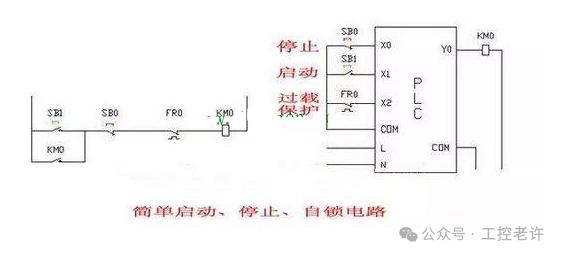
Error Reason:
Each output point in a PLC can only correspond to a unique output signal. If the same output point is used for controlling multiple different devices, it will lead to signal conflicts, causing the device actions to become chaotic.
Solution:
Reassign output points, giving each device a separate output point. Ensure that each output point controls only one device to avoid signal conflicts. Additionally, carefully plan the use of output points during programming to prevent similar errors.
2: Error in Timer Usage
Error Case:
In a timed control project, a timer was used to control the running time of a motor. A timer was set for 10 seconds, and when the timer reached 10 seconds, the motor was supposed to stop running. However, in actual operation, the motor did not stop as expected, but rather stopped early or late.
Error Reason:
The timing accuracy of the timer is affected by the PLC’s scan cycle and program execution time. If there are a lot of complex logic and loops in the program, it can lead to inaccurate timing. Additionally, the timing unit of the timer also needs to be set correctly; if set incorrectly, it will also lead to inaccurate timing.
Solution:
Optimize program logic, reduce unnecessary loops and complex logic, and improve program execution efficiency. At the same time, set the timer’s timing unit and timing duration reasonably based on the PLC’s scan cycle and actual needs. During programming, consider using a combination of multiple timers to improve timing accuracy.
3: Program Logic Error
Error Case:
In the PLC programming of an automated warehouse, a program was written to control the inbound and outbound of goods. There was a logic error in the program, causing the system to incorrectly send goods to the outbound port when they were supposed to be stored, leading to confusion of goods.
Error Reason:
Program logic errors are usually due to the engineer’s insufficient understanding of the system’s workflow and requirements, or carelessness during programming. When writing the program, various possible situations and exceptions were not fully considered, leading to the program not functioning properly in certain cases.
Solution:
Carefully analyze the system’s workflow and requirements to ensure an accurate understanding of the system. During programming, conduct thorough testing and validation, considering various possible situations and exceptions, and write corresponding handling programs. Additionally, develop good programming habits by providing detailed comments in the program for easier maintenance and modification.
4: Data Processing Error
Error Case:
In a data collection and processing project, data collected from sensors needed to be processed and analyzed. During programming, the engineer used incorrect data types and operation methods, resulting in inaccurate data processing results.
Error Reason:
Data processing errors are usually due to a lack of understanding of data types and operation methods, or carelessness during programming. Different data types have different storage methods and operation rules in PLCs; using the wrong data type for operations can lead to inaccurate results.
Solution:
Before programming, fully understand the characteristics and usage rules of data types and operation methods. Choose appropriate data types and operation methods for data processing based on actual needs. During programming, conduct thorough testing and validation to ensure the accuracy of data processing results.
5: Communication Error
Error Case:
In a multi-PLC communication project, engineers needed to enable communication between multiple PLCs to achieve data sharing and exchange. However, during actual operation, it was found that communication between PLCs was unstable, often resulting in data loss and communication interruptions.
Error Reason:
Communication errors are usually caused by incorrect communication parameter settings, communication line faults, electromagnetic interference, etc. During programming, ensure that communication parameters are set correctly, including baud rate, data bits, stop bits, and parity bits. Additionally, check whether the communication lines are normal to avoid line faults and electromagnetic interference.
Solution:
Carefully check communication parameter settings to ensure they are correct. Check whether the communication lines are normal, eliminating line faults and electromagnetic interference. Communication diagnostic tools can be used to monitor and debug communication, allowing for timely detection and resolution of communication issues. During programming, write corresponding communication error handling programs to handle and recover from communication errors promptly.
6: Unreasonable Program Structure
Error Case:
In the PLC programming of a large automation project, the program structure written by the engineer was chaotic, lacking reasonable modular design. The program contained a lot of duplicate code and nested loops, resulting in poor readability and maintainability.
Error Reason:
Unreasonable program structure is usually due to a lack of overall planning and design by the engineer, who did not properly modularize the program. When writing the program, the engineer did not consider the program’s scalability and maintainability, leading to difficulties in subsequent development and maintenance.
Solution:
Before programming, conduct overall planning and design of the program, and perform reasonable modular division. Divide the program into multiple functional modules, with each module responsible for a specific function. Modules should communicate and interact through interfaces to improve program readability and maintainability. Additionally, avoid using a lot of duplicate code and nested loops to enhance program execution efficiency.
7: Non-standard Variable Naming
Error Case:
In a PLC programming project, the engineer used arbitrary variable names such as “a”, “b”, “c”, etc. During program debugging and maintenance, it was difficult to understand the meaning of these variables, leading to low efficiency in debugging and maintenance work.
Error Reason:
Non-standard variable naming is usually due to a lack of awareness of standards by the engineer, who did not follow a unified naming convention. Arbitrary variable names reduce the readability of the program, making subsequent debugging and maintenance difficult.
Solution:
Establish a unified variable naming convention and adhere to certain naming standards. Variable names should have clear meanings that can express the purpose and function of the variable. Use English words or abbreviations for variable naming, avoiding arbitrary characters. Additionally, provide comments for variables to explain their meanings and purposes, improving program readability.
8: Insufficient Program Comments
Error Case:
In a PLC programming project, the program written by the engineer lacked sufficient comments. During program debugging and maintenance, other engineers found it difficult to understand the program’s logic and functionality, leading to low efficiency in debugging and maintenance work.
Error Reason:
Insufficient program comments are usually due to a lack of awareness of the importance of comments by the engineer. Comments can help other engineers quickly understand the program’s logic and functionality, improving program maintainability.
Solution:
During programming, develop good commenting habits by adding detailed comments to key parts and complex logic in the program. Comments should clearly and accurately express the program’s logic and functionality, avoiding vague and ambiguous language. Additionally, provide a brief explanation of the overall functionality and design ideas of the program to help other engineers quickly understand the program’s overview..
9: Program Not Backed Up
Error Case:
In a PLC programming project, after completing the programming, the engineer did not back up the program. Later, due to a PLC failure, the program needed to be re-downloaded, but it was found that the original program had been lost, severely affecting the project schedule.
Error Reason:
Failure to back up the program is usually due to a lack of awareness of the importance of backups by the engineer. Backups can quickly restore the program in case of PLC failure or program loss, reducing project losses.
Solution:
After completing programming, promptly back up the program. Programs can be backed up to external storage devices such as USB drives or hard disks. Additionally, regularly update backups to ensure that the backed-up program is the latest version. In case of PLC failure or program loss, the program can be quickly restored to ensure the normal progress of the project.
10: Lack of Testing and Validation
Error Case:
In a PLC programming project, after completing the programming, the engineer did not conduct sufficient testing and validation before directly downloading the program to the PLC for operation. As a result, during actual operation, many errors and issues were found in the program, causing the equipment to malfunction.
Error Reason:
Lack of testing and validation is usually due to a lack of rigorous attitude by the engineer during programming, who did not recognize the importance of testing and validation. Testing and validation can identify errors and issues in the program, allowing for timely modifications and optimizations to improve the program’s reliability and stability.
Solution:
After completing programming, conduct thorough testing and validation of the program. A combination of simulation testing and actual testing can be used to test various functions of the program. During testing, carefully observe the program’s operation, promptly identifying and recording errors and issues in the program. For identified problems, timely modifications and optimizations should be made to ensure the program’s reliability and stability.

In summary, PLC programming is a task that requires a rigorous attitude and rich experience. During the programming process, it is important to avoid the common errors mentioned above, continuously summarize experiences and lessons, and improve programming skills. I hope this article can be helpful to everyone.
If you need further optimization or specific case details, feel free to leave a comment for discussion.

 Scan to receiveElectrical/PLC/Robot learning materials
Scan to receiveElectrical/PLC/Robot learning materials Share
Share Collect
Collect View
View Like
Like