In the ever-evolving battlefield of web application security, firewalls are becoming increasingly intelligent, and scanners are becoming more aggressive, yet some vulnerabilities still **slip silently through the cracks**.
One of these — **HTTP Request Smuggling (HRS)** — has once again emerged as a *high-impact*, *low-visibility* threat capable of bypassing authentication, hijacking sessions, poisoning caches, and causing complete destruction… all without **triggering any alarms**.
Surprisingly, many production systems — even in 2025 — remain vulnerable. For offensive security experts, this means one thing:🧨 **Opportunity**.

But to exploit these complex behaviors, you need more than just intuition — you need Param Miner.
This article is your tactical blueprint:
- 🧠 Understand the mechanics of HTTP Request Smuggling– 🔍 Use Param Miner to discover logic flaws, IDOR, and authentication bypasses– ⚙️ Craft precise real-world attack chains– 🧯 Implement appropriate mitigations (if you are on the blue team)
What Makes HTTP Request Smuggling So Dangerous?
**HTTP Request Smuggling** is not just a bug — it is a collapse of trust between infrastructure components.
It exploits how different systems (such as reverse proxies and backend servers) interpret HTTP requests differently, especially when it comes to headers like:
– `Content-Length`– `Transfer-Encoding`
When these components disagree on where the request ends, an attacker can “smuggle” a second request into the body of the first request — often bypassing edge protections, WAFs, and logging systems.
###🔥 Asynchronous Scenario Example

- Frontendrespects
<span>Content-Length</span>→ considers the body to be 6 bytes. - Backendrespects
<span>Transfer-Encoding: chunked</span>→ interprets<span>G</span>as the second request.
🔁Result: Requests are out of sync, allowing the attacker to exploit this desynchronization to:
- Bypass authentication
- Poison caches
- Hijack sessions
- Deliver undetected payloads
- Fully exploit RCE, IDOR, or SSRF
🛠️ Param Miner: The Reconnaissance Tool for HTTP Desync and Logic Errors
Param Miner is not your ordinary Burp extension. It is a targeted fuzzing engine that can automatically discover the following:
- 🕵️ Hidden and undocumented parameters
- 🧩 Legacy fields still processed by backend systems
- 🔐 Headers worth bypassing (e.g.,
<span>X-Original-URL</span>) - 🔁 Endpoints prone to desynchronization
- ⚖️ Logic flaws triggered by rare or duplicate parameters

✅ Use Case #2 — IDOR Caused by Parameter Pollution
Original request:
GET /profile?userId=111 HTTP/1.1
Param Miner attempts:
GET /profile?userId=111&userId=222
If the backend processes the second parameter, you have triggeredIDOR, gaining unauthorized access to other users’ data.
✅ Use Case #3 — Asynchronous Payload Discovery
Using Param Miner, you find an endpoint prone to desynchronization. You can craft:
POST / HTTP/1.1Host: target.comContent-Length: 50Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0GET /admin HTTP/1.1
Host: target.com
X-Forwarded-For: 127.0.0.1
X-Original-URL: /admin
X-Forwarded-Host: internal-api.target.com
Result: complete bypass of<span>/admin</span>. 🔥 This is where desync + Param Miner = game over.
🔥 Chained Attack: Param Miner + HTTP Desync = 💣
Once Param Miner reveals the correct endpoints and payload prefixes (<span>X-Forwarded-Host</span>, <span>X-Original-URL</span>, etc.), you can:
- Launch large-scale desynchronization attacks
- Poison shared cache layers
- Silently hijack cookies and sessions
- Conduct full-scale attacks leveraging SSRF or logic flaws
This is not just testing; it is surgical-level protocol manipulation.
📤 5. HTTP/2 to HTTP/1 Smuggling
WAF supportsHTTP/2, while the backend supportsHTTP/1.1. Now you can desynchronize protocol parsing instead of headers.
- Tool: Smuggler
- Send backend interpretations as raw HTTP/1 frames of HTTP/2
→ WAF cannot properly inspect HTTP/2 frames = bypass..

💡 Professional Advice for Advanced Hunters
- UseBurp Collaborator to detect blind interactions
- Use Logger++ to monitor response lengths and headers
- Use Turbo Intruder to automate attacks
- Use HTTP/2 → HTTP/1.1 downgrade to trigger desynchronization




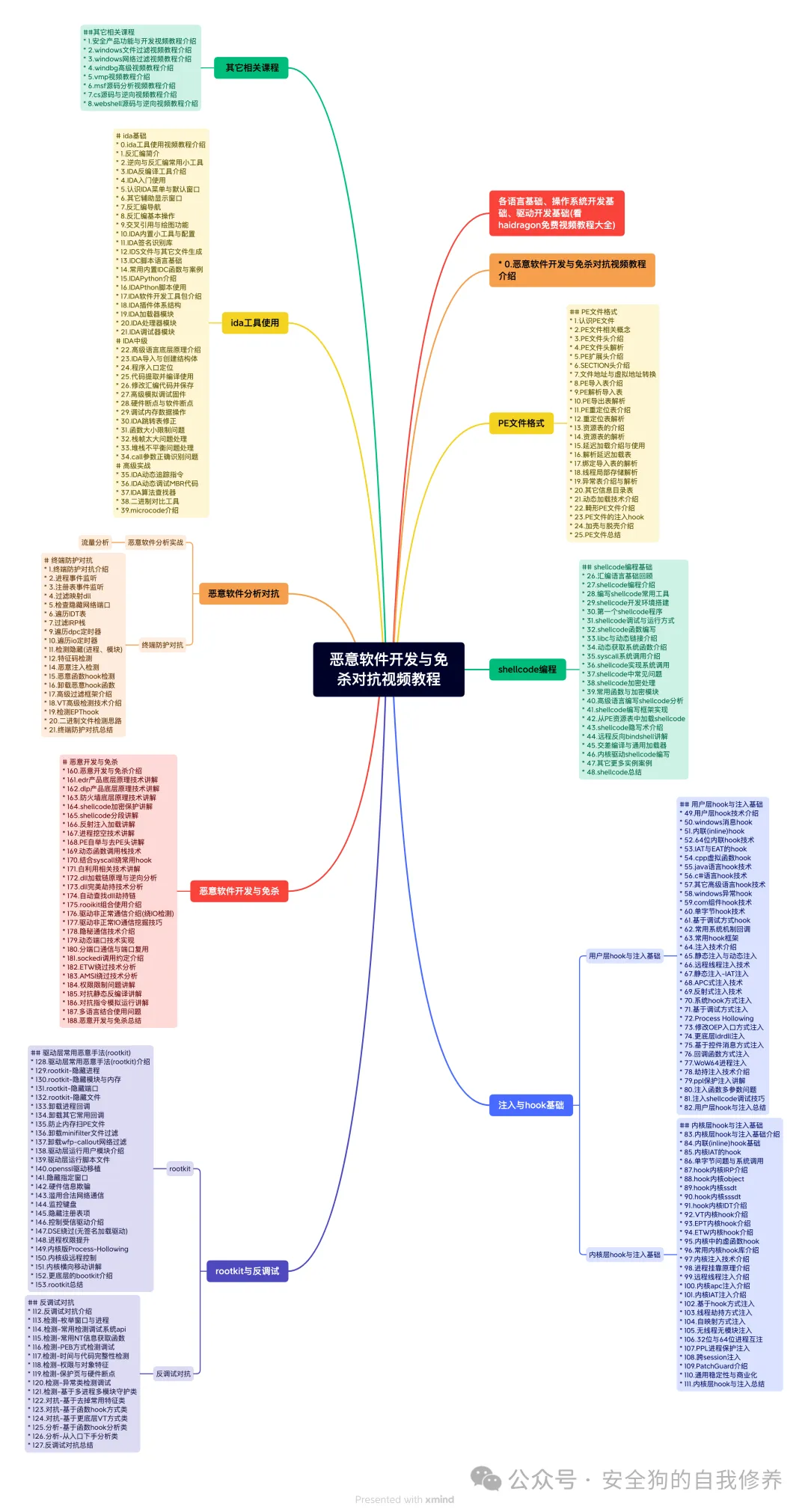
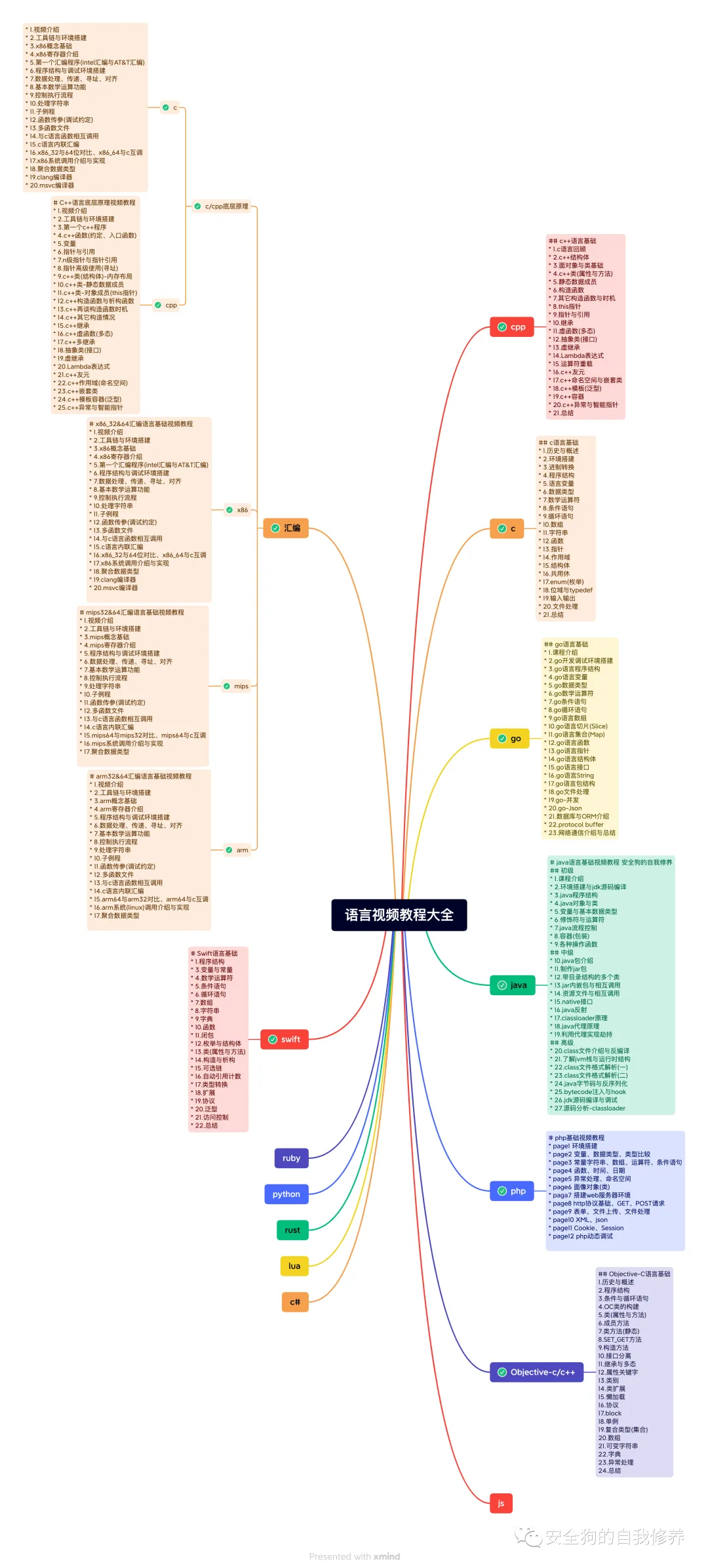
Rust Language Full-Stack Development Video Tutorial – Season 1 (Latest 2025)


Detailed Directory
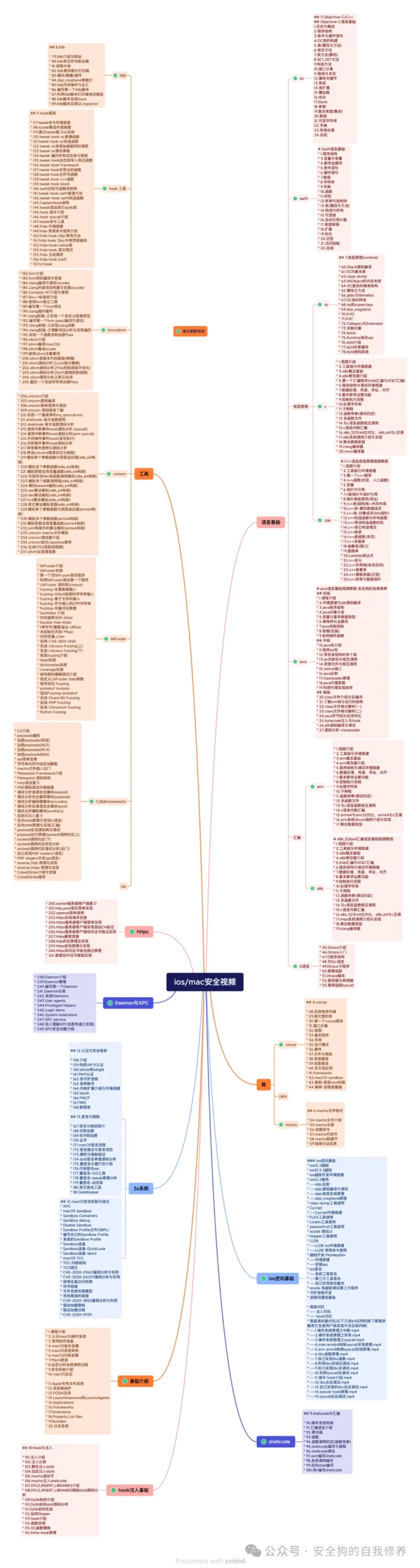
Mac/iOS Security Video
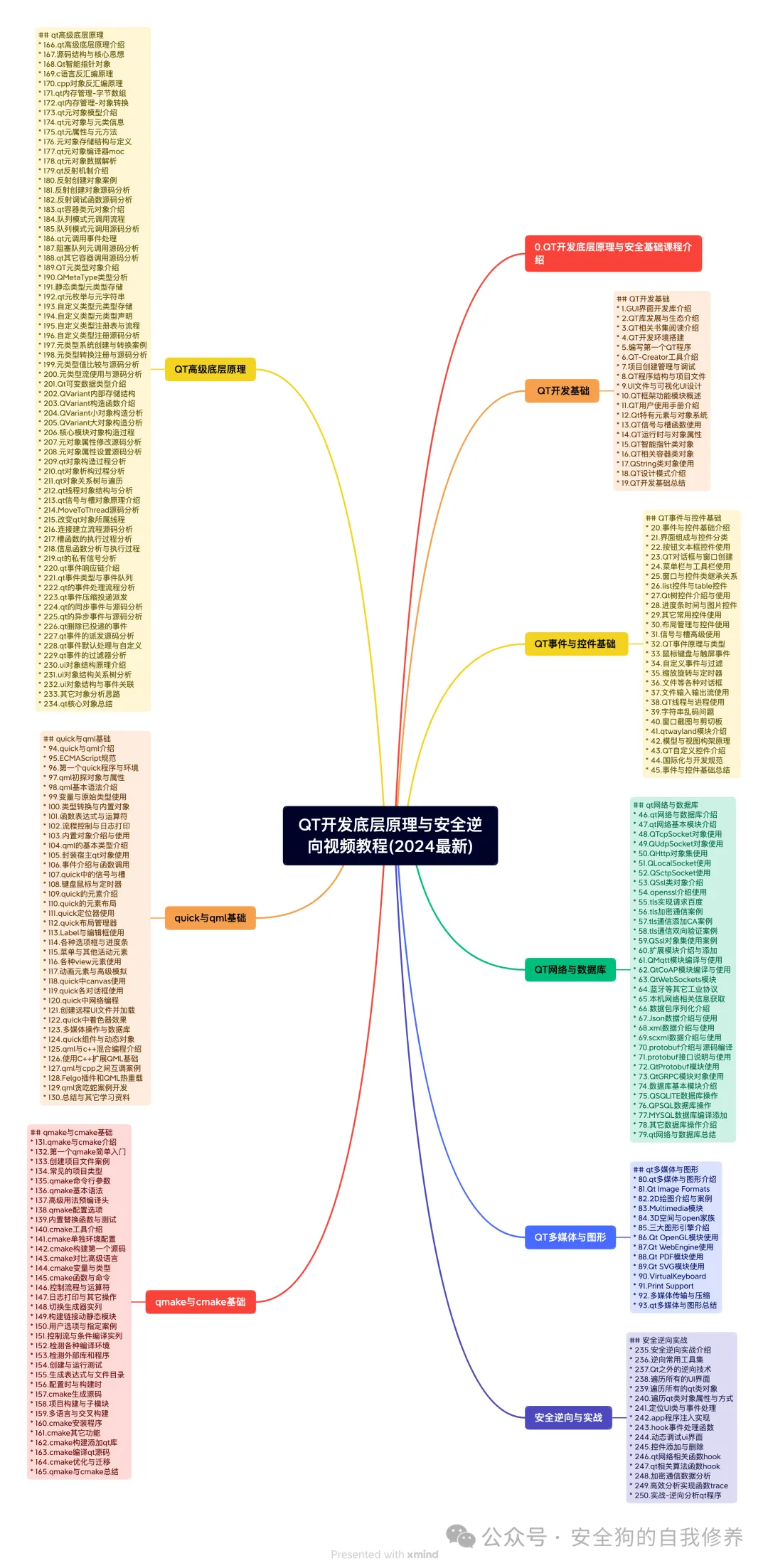
QT Development Underlying Principles and Security Reverse Engineering Video Tutorial
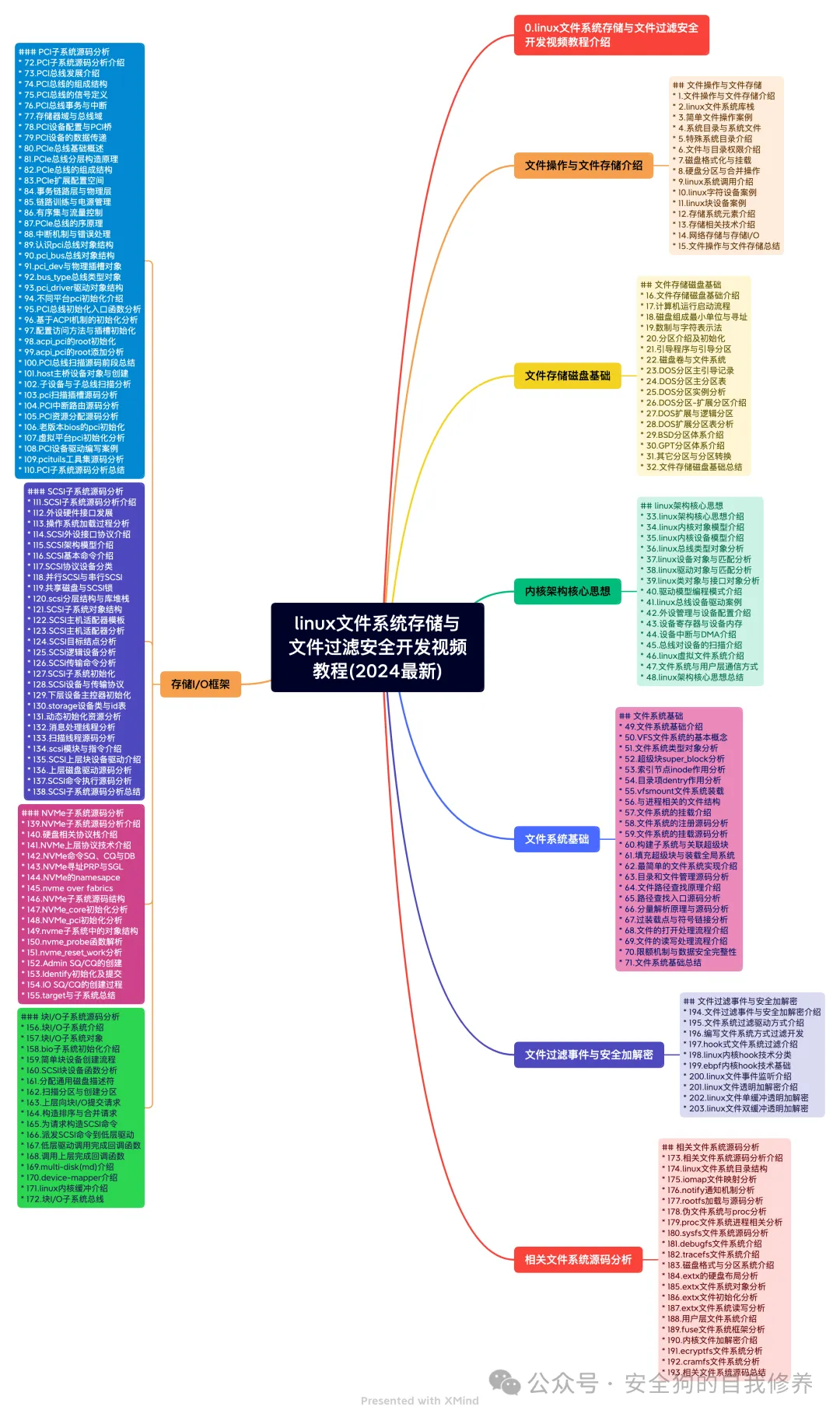
Linux File System Storage and File Filtering Security Development Video Tutorial (Latest 2024)
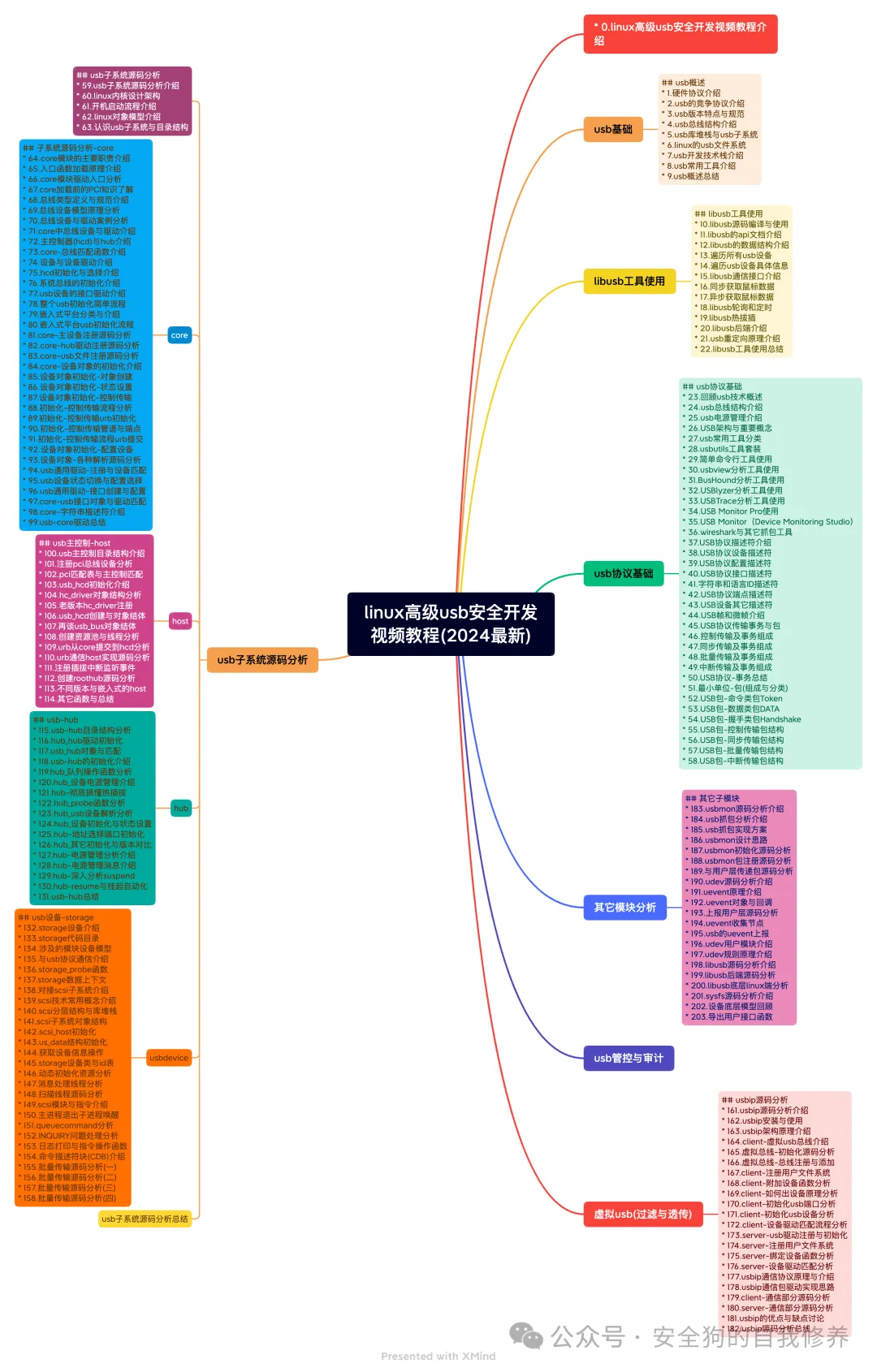
Linux Advanced USB Security Development and Source Code Analysis Video Tutorial
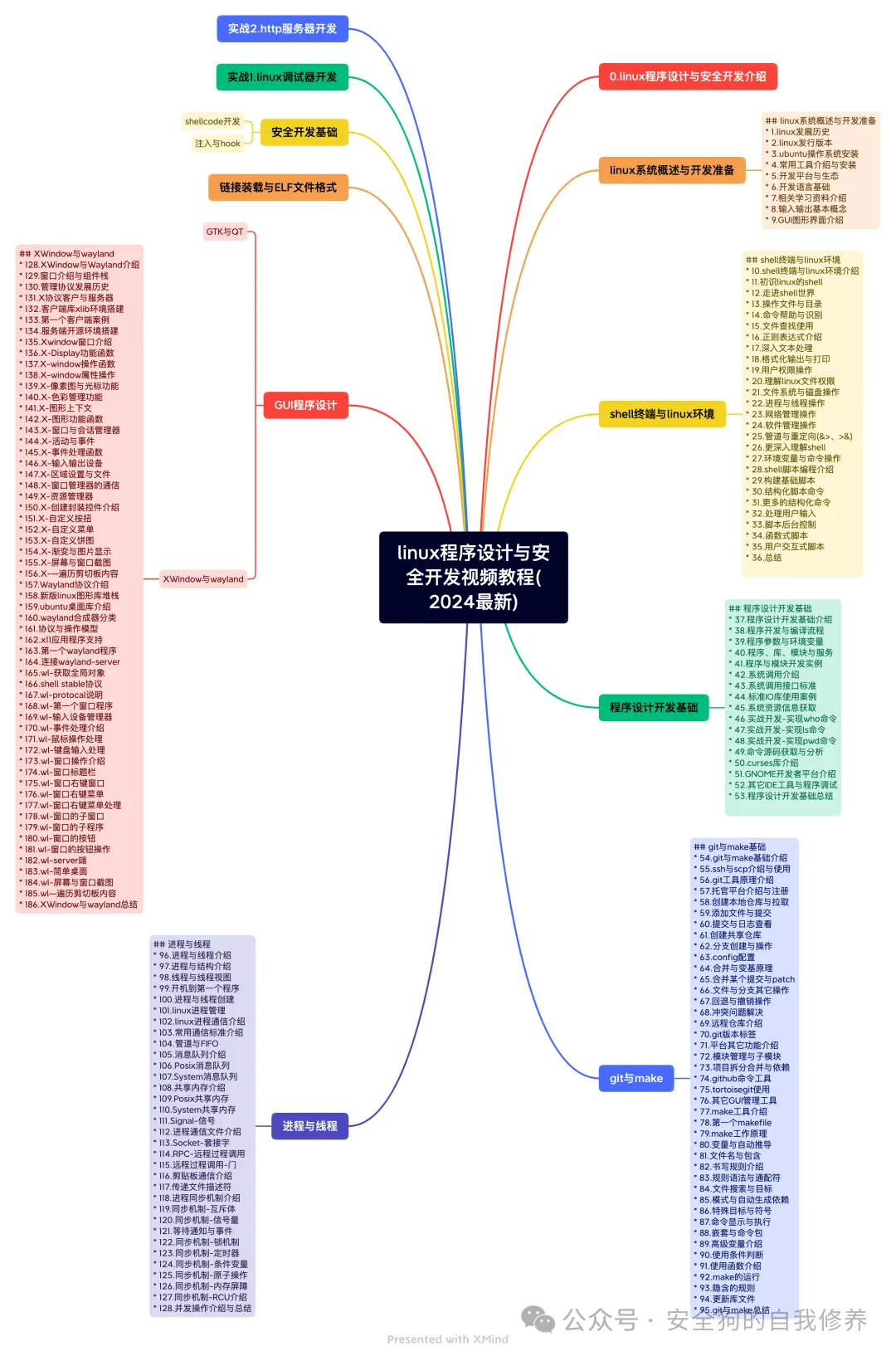
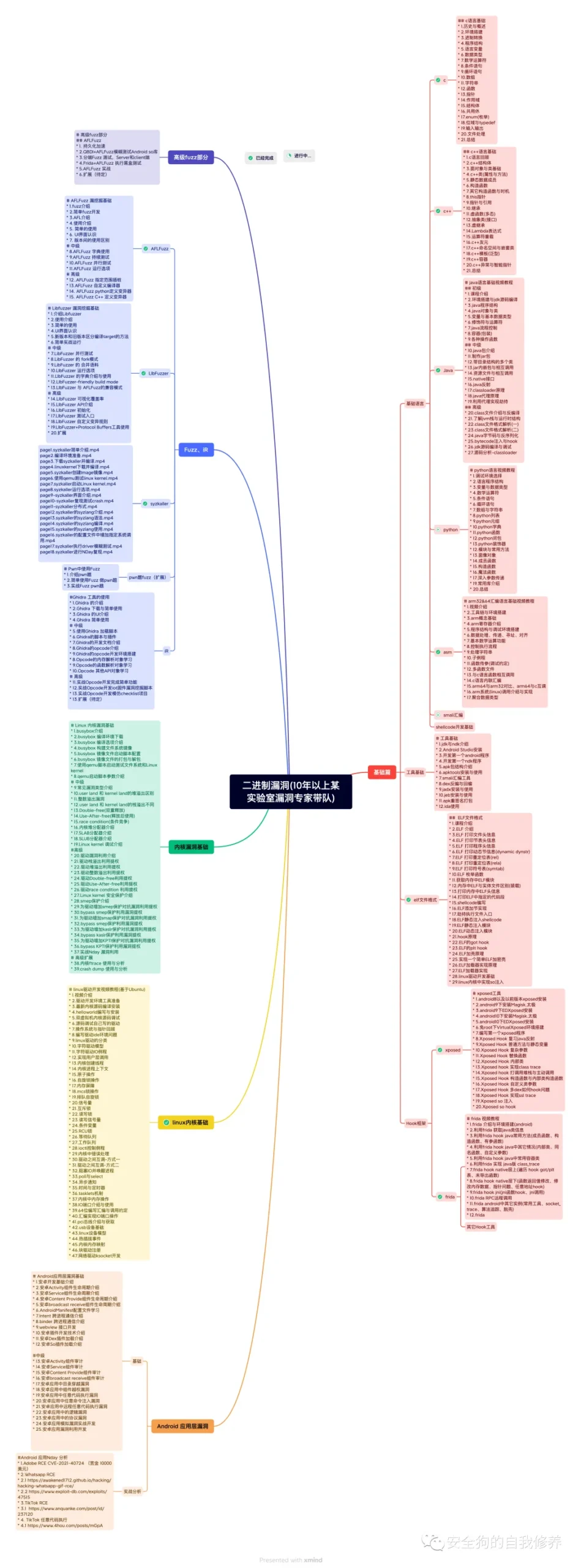
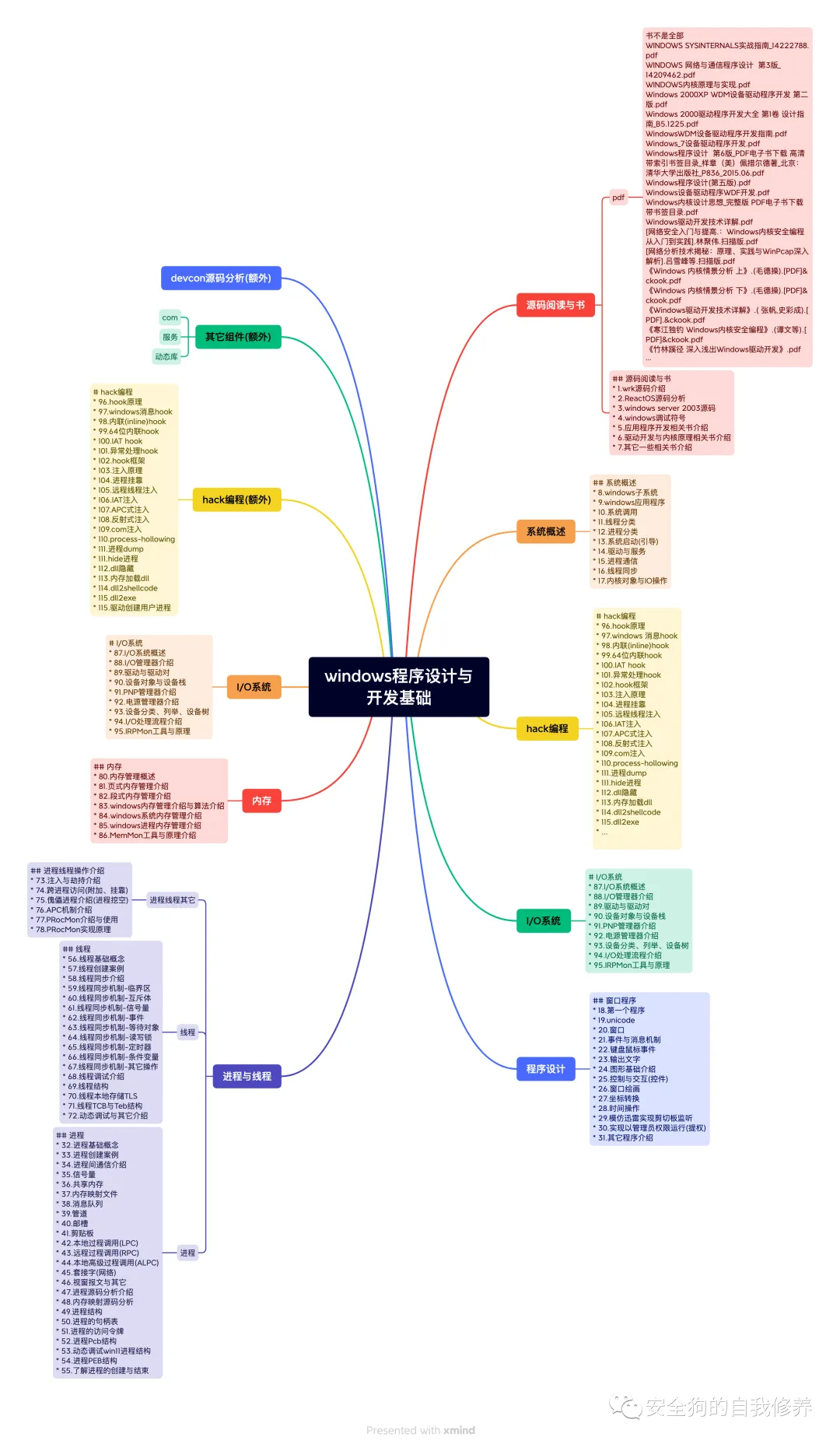
Linux Program Design and Security Development
-
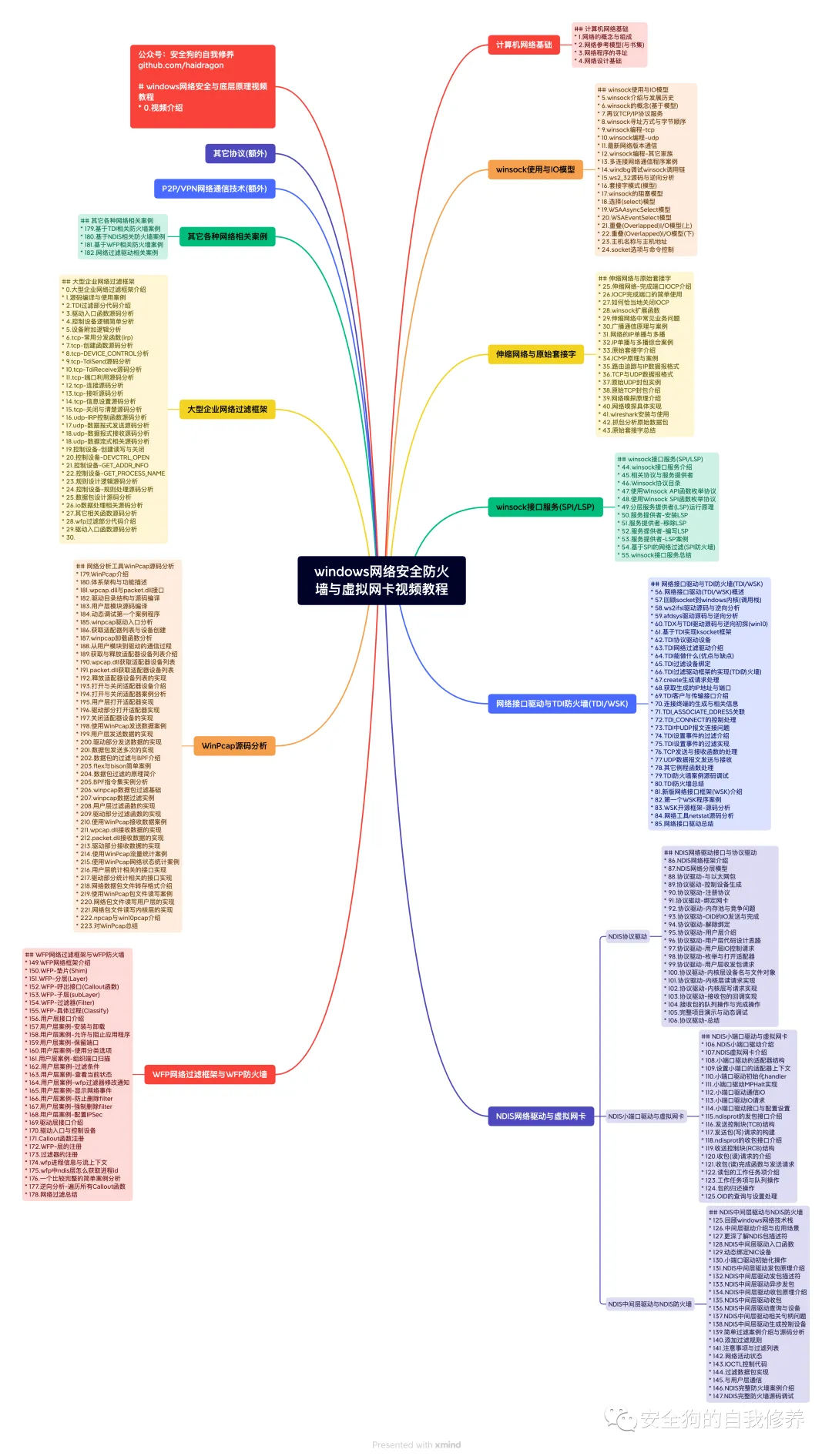
windows网络安全防火墙与虚拟网卡(更新完成
-
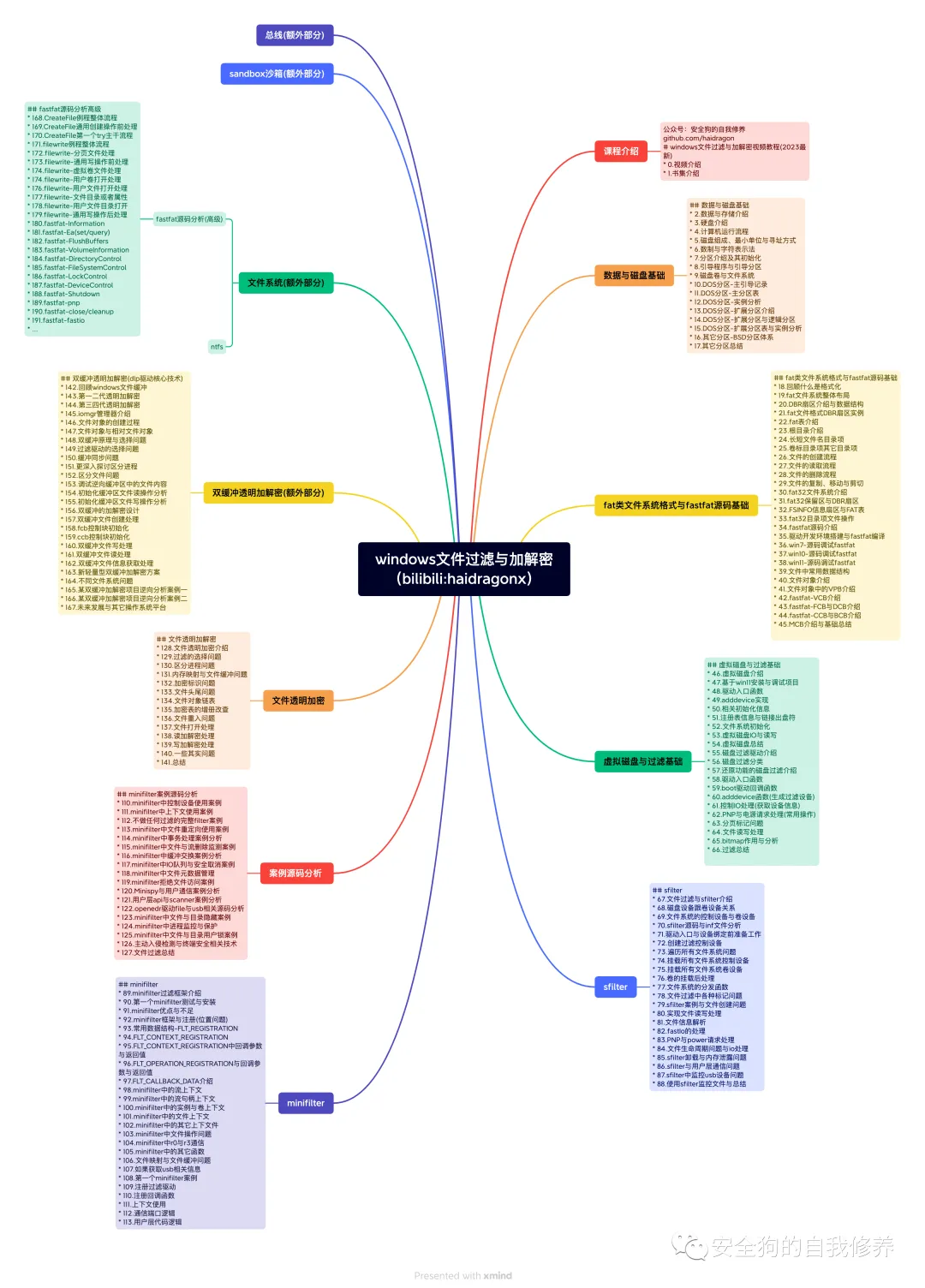
windows文件过滤(更新完成)
-
USB过滤(更新完成)
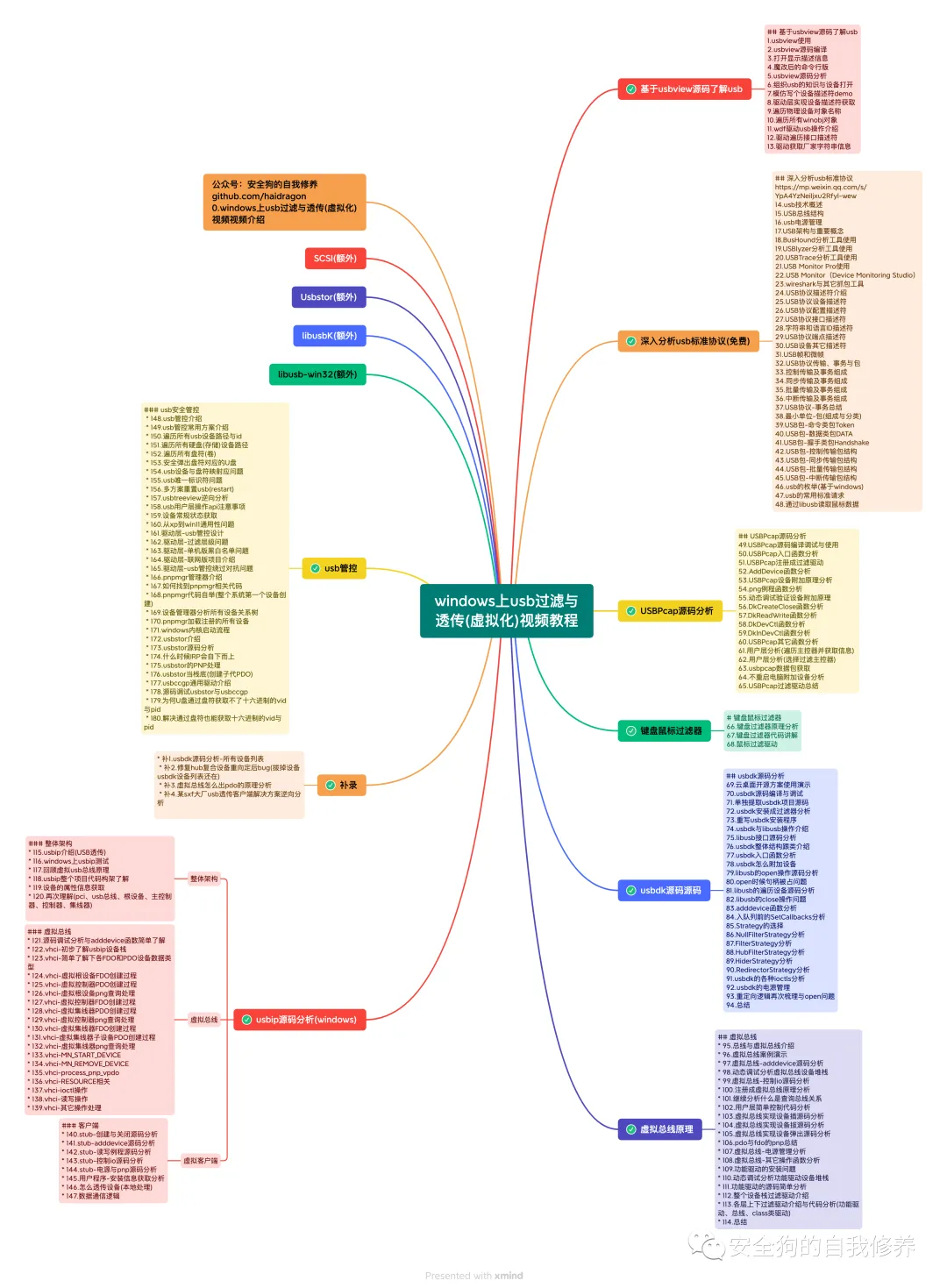
-
游戏安全(更新中)
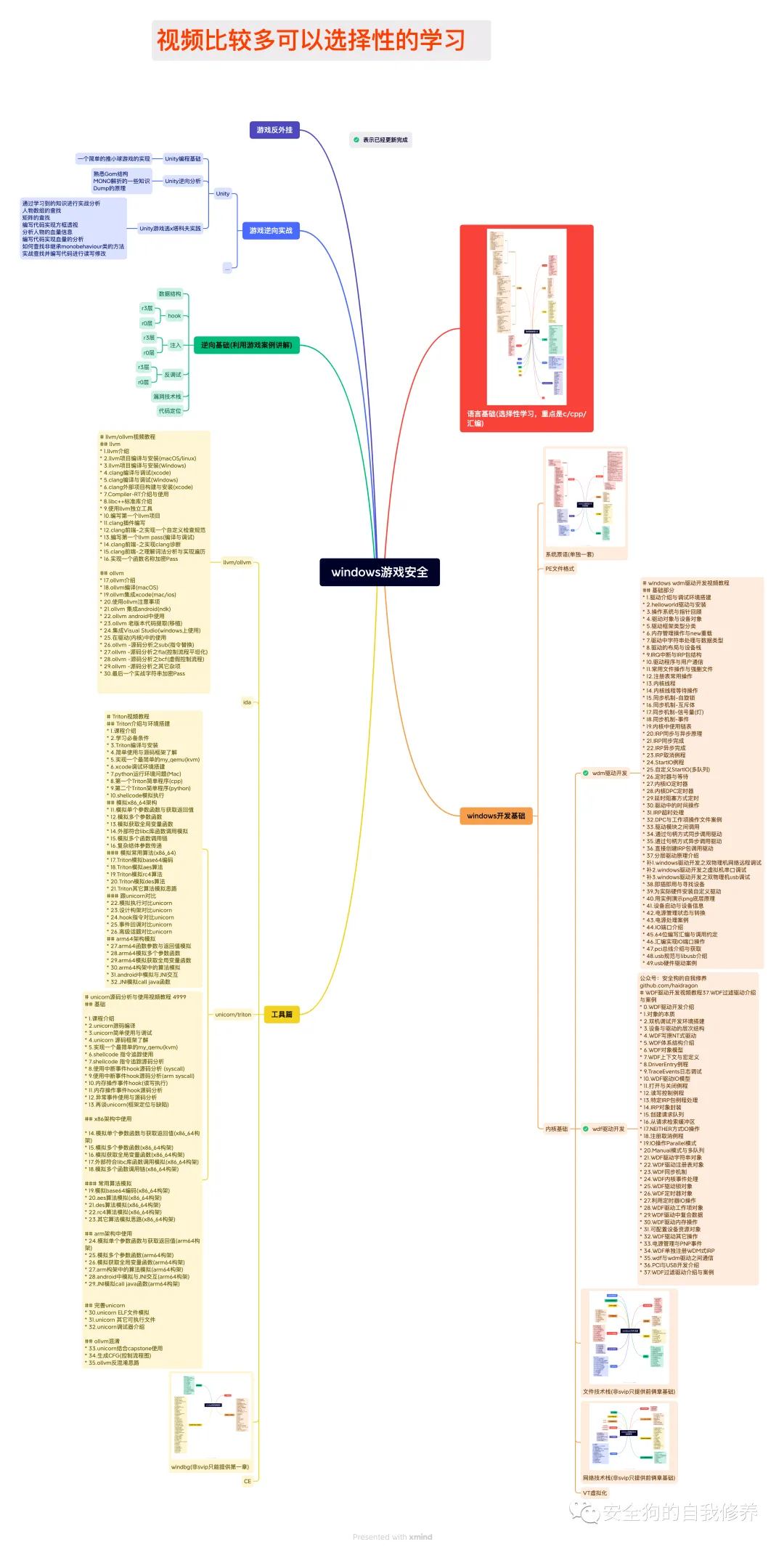
-
ios逆向
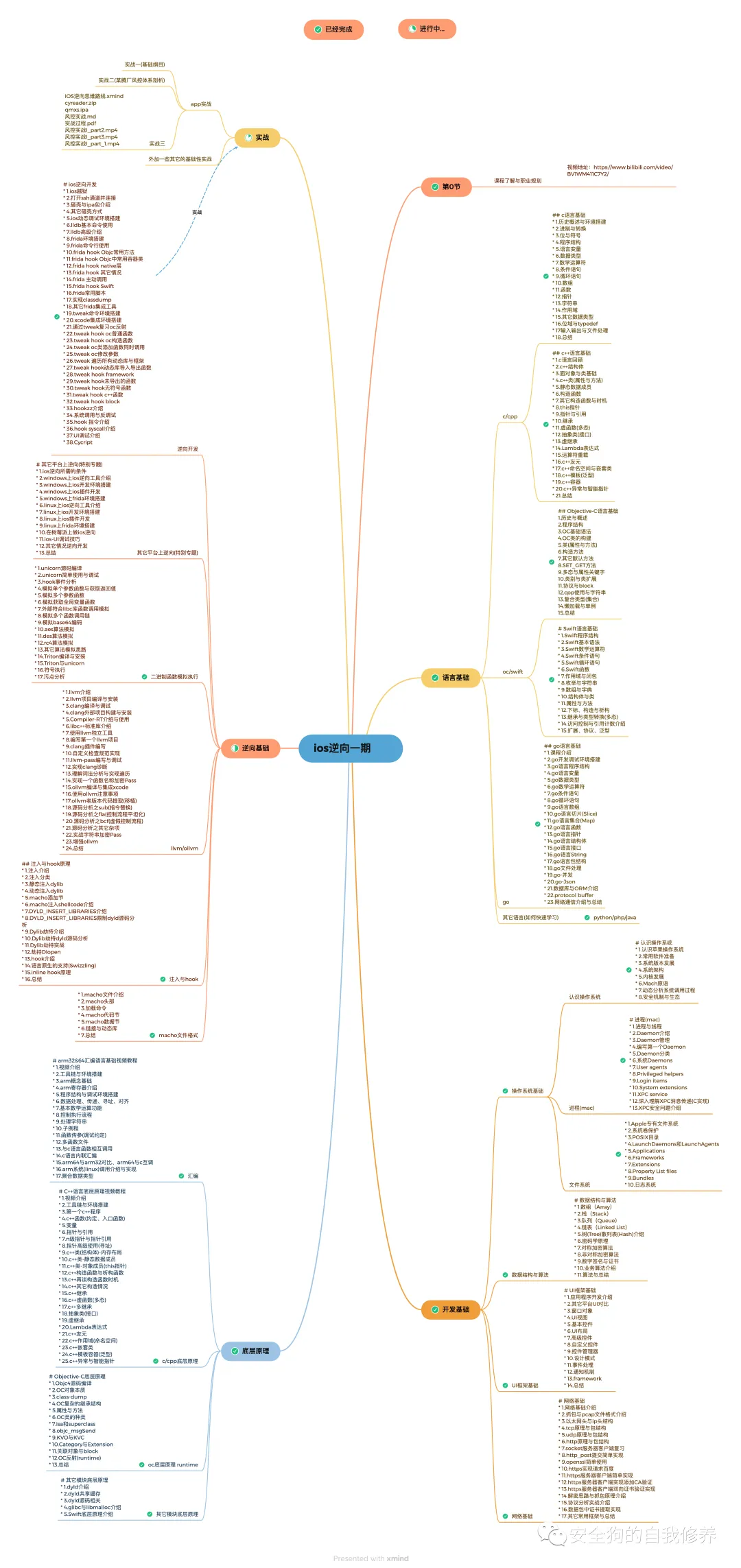
-
windbg
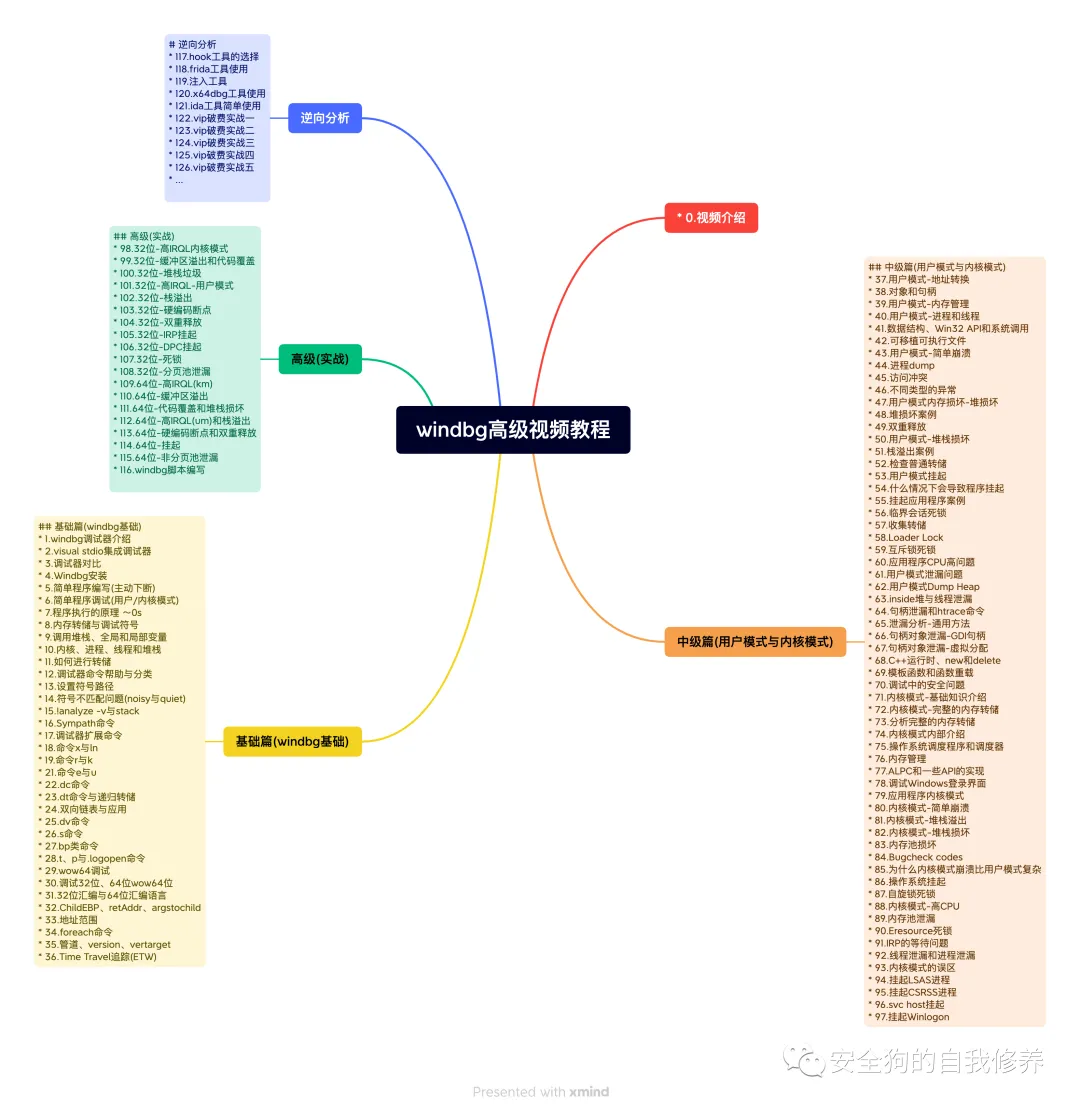
-
还有很多免费教程(限学员)
-

-
-
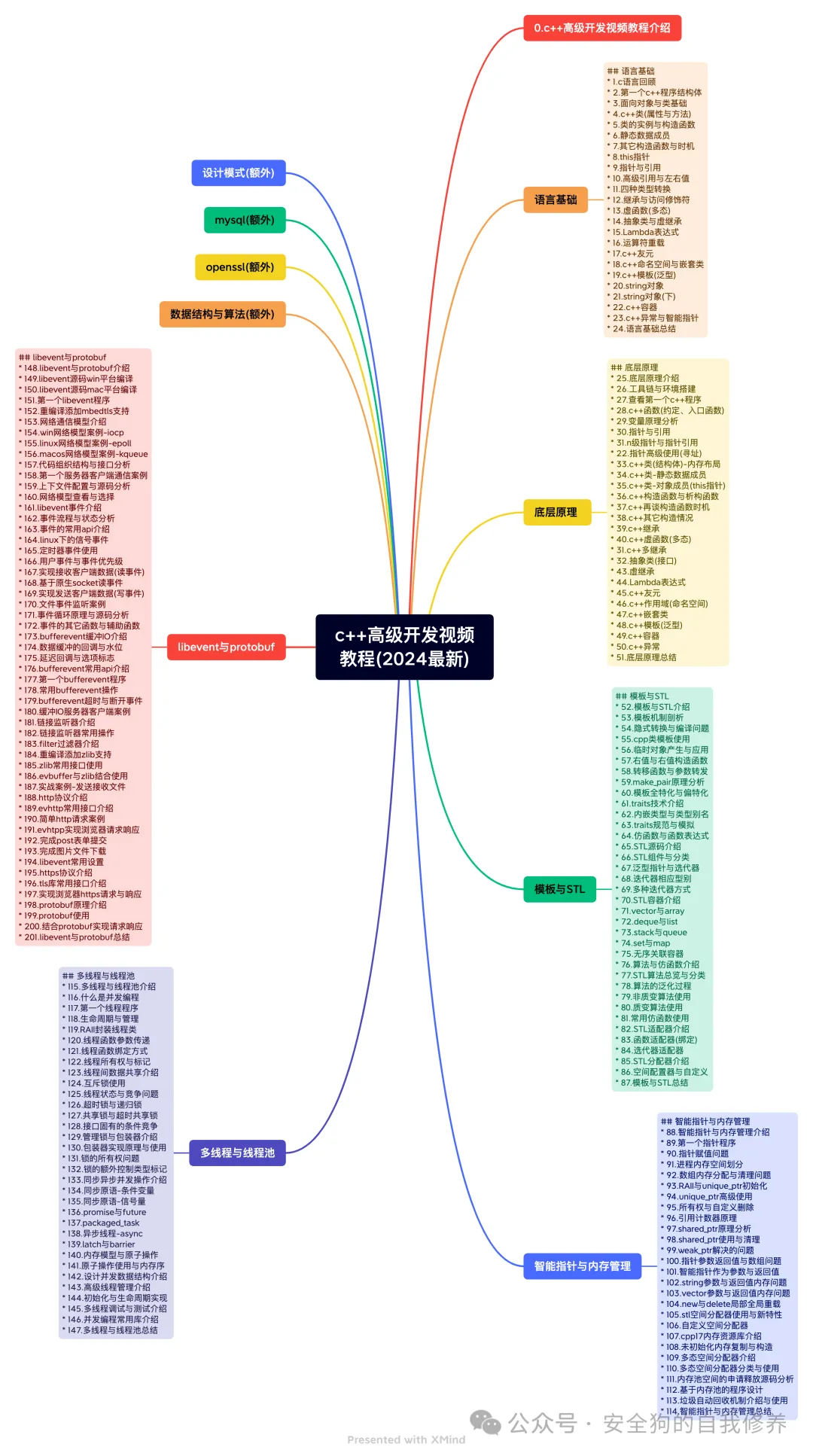
Windows Malware Development and Countermeasures Video Tutorial