


Infectious wound healing faces multiple clinical challenges such as bacterial clearance, tissue regeneration, and drug release control. Traditional therapies have significant limitations in addressing these complex issues.Recently, inspired by the hierarchical structure of crocodile teeth,Huanjun Li‘s team at Beijing Institute of Technology developed a3Dprinted photothermal responsiveMXene-based multifunctional eutectogel microneedle system (MF-MXene@MN), providing an innovative solution to the problem of infectious wound healing.
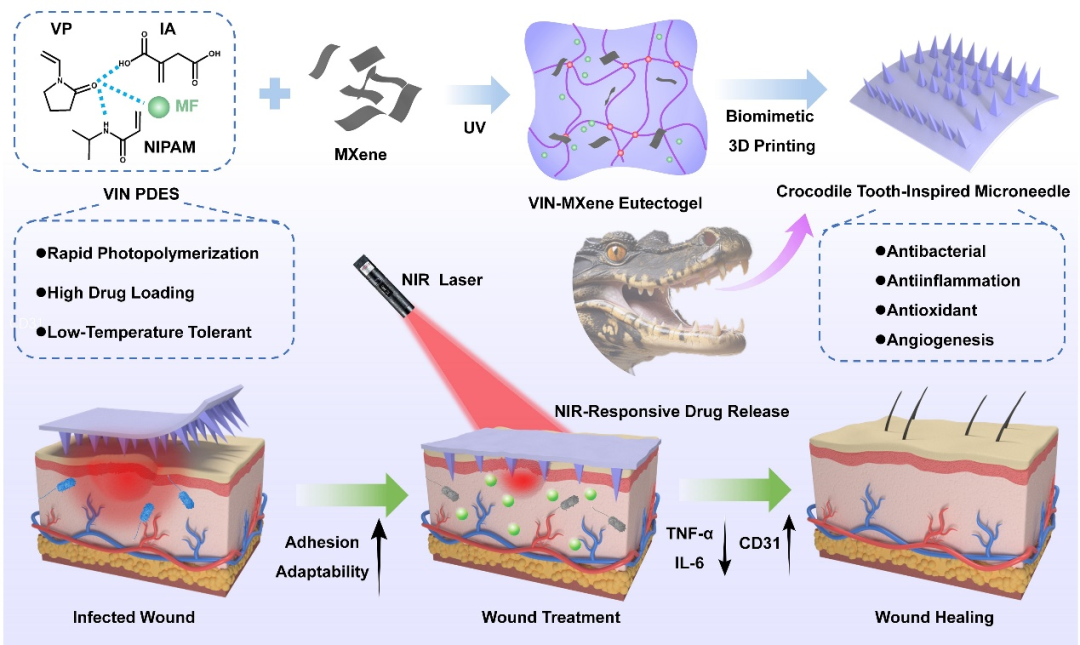
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the near-infrared responsive healing promotion of biomimetic 3D printed MXene-based eutectogel microneedles
The core of this microneedle system lies in the synergistic design of multidimensional functional materials. Vinyl pyrrolidone (VP), itaconic acid (IA), andN-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) were selected to construct a polymerizable eutectic solvent (PDES), forming a eutectogel network with temperature-responsive characteristics. Its lower critical solution temperature (LCST) is41.13℃, which is close to human physiological temperature, allowing for dynamic adjustment of drug release based on the inflammatory state of the wound. Additionally, the introduction ofMXene nanosheets endows the system with photothermal conversion capability, efficiently generating heat under near-infrared (NIR) light irradiation, which not only directly kills bacteria but also triggers drug release. Moreover, the inherent antioxidant properties ofMXene can eliminate excess reactive oxygen species (ROS) at the wound site, creating a favorable environment for tissue repair. Furthermore, the loaded natural polyphenolic component mangiferin (MF) possesses anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and wound healing-promoting effects, achieving efficient loading and controlled release through the solubilization effect ofPDES.
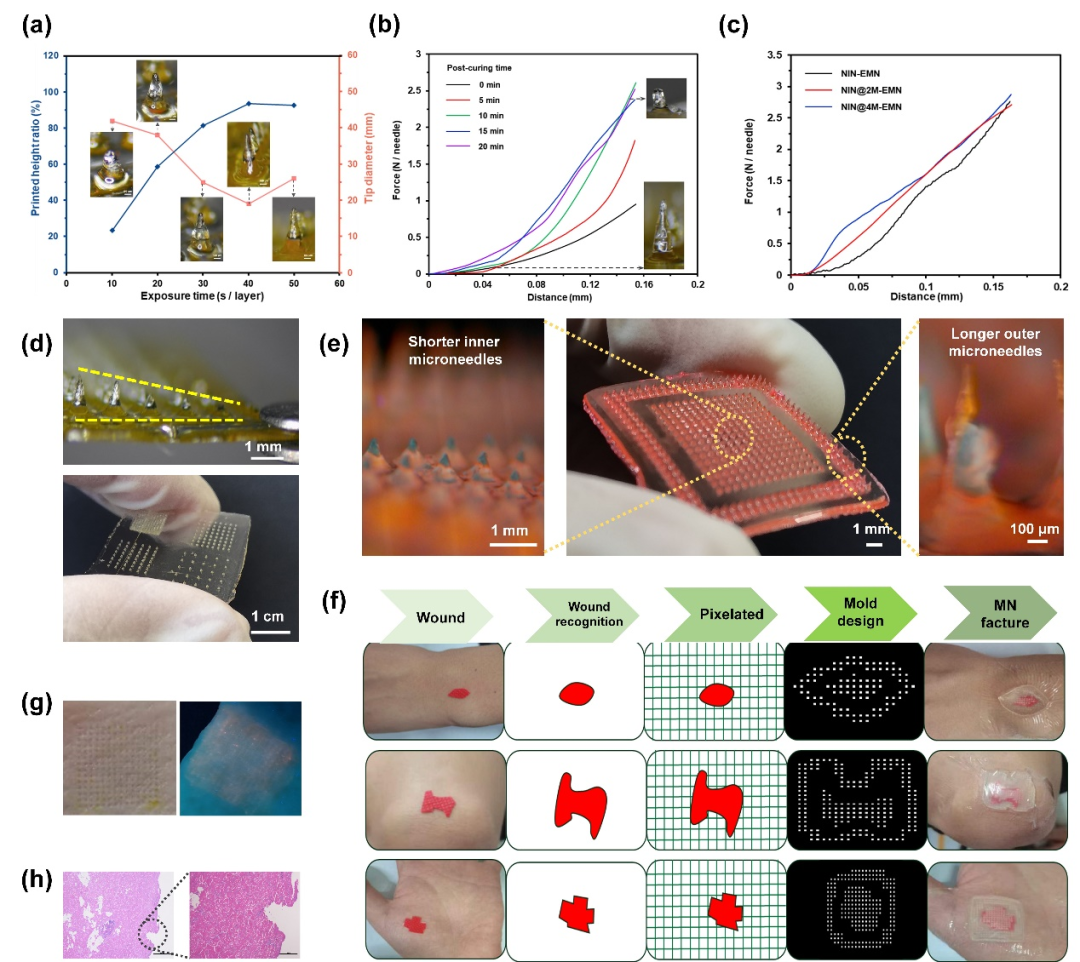
Figure 2. Parameter optimization, biomimetic structure, and personalized manufacturing of DLP 3D printed microneedles
UsingPDES as the printing ink, a digital light processing (DLP) 3D printing technology was utilized to construct a microneedle array with gradient heights. This biomimetic design mimics the hierarchical structure of crocodile teeth, significantly enhancing the adhesion of microneedles to tissues, achieving a functional partition of short needles inside and long needles outside—where the inner short needles are responsible for drug release control, and the outer long needles ensure tissue anchoring, addressing the poor tissue compatibility of traditional microneedles. More importantly, through the combination of ImageJ image recognition and TinkerCAD model design, microneedle patches can be quickly customized according to the specific shape and depth of the wound. The entire process from imaging to obtaining the patch can be completed within1 hour, meeting clinical timeliness requirements, with a printing resolution of<50μm, allowing precise control of microneedle parameters to adapt to irregular wounds.
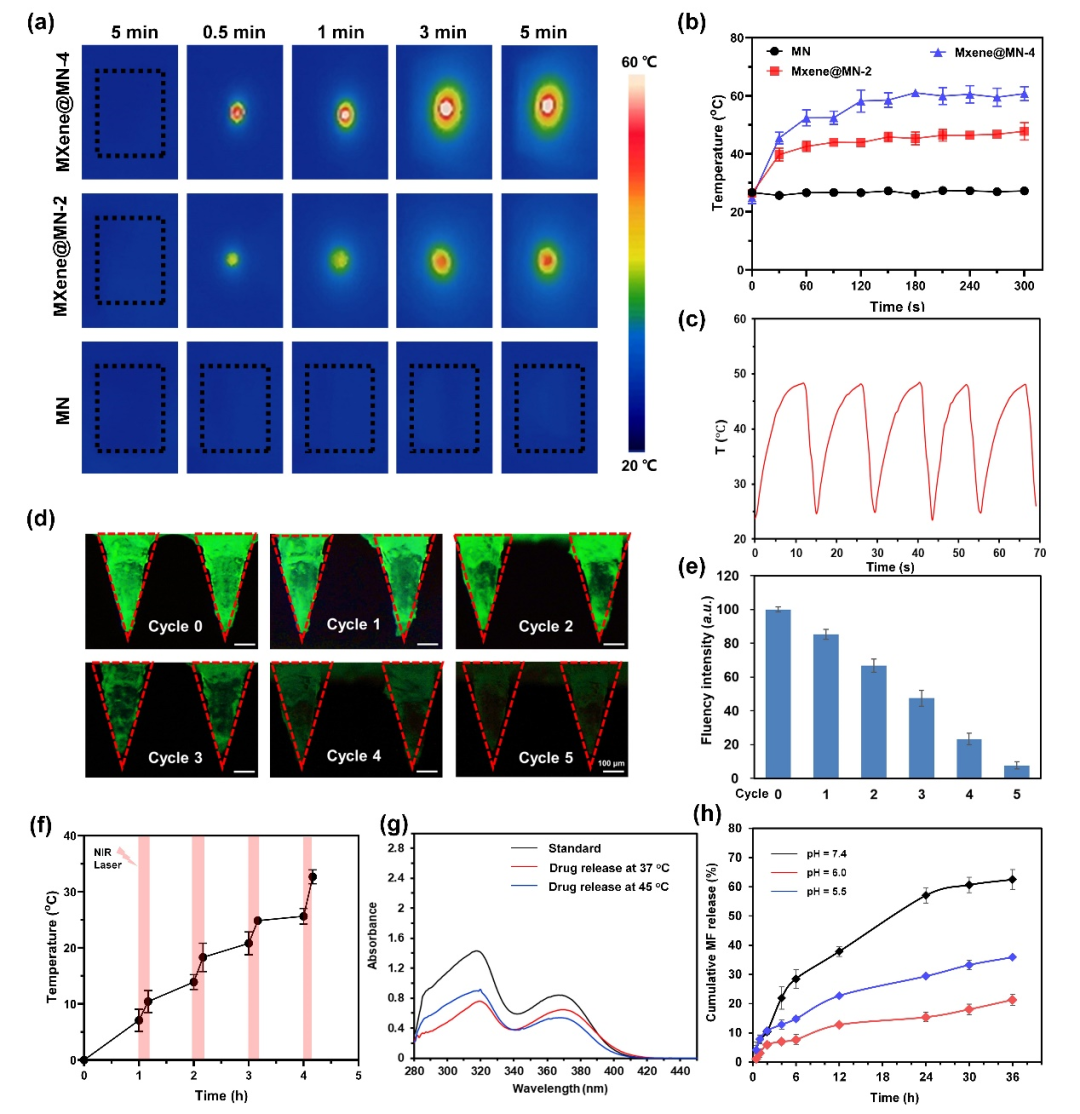
Figure 3. Characterization of the photothermal response and drug release characteristics of the microneedle system under near-infrared light
In terms of therapeutic mechanisms, this microneedle system exhibits a precise treatment mechanism with multimodal responses. In the dual response control of photothermal-temperature,MXene can raise the temperature to46.6℃ under 808nm NIR light irradiation, exceeding theLCST ofPDES, leading to accelerated drug release due to gel network contraction. Five cycles of experiments showed a cumulative drug release rate of88.3%; the pH-sensitive intelligent regulation characteristic allows the microneedles to slowly release drugs in the weakly acidic environment of healthy skin and accelerate drug release in the alkaline environment of infected wounds, achieving an “environmentally aware” precise drug release. In terms of the synergistic effects of antibacterial and antioxidant properties, the photothermal effect combined with the inherent antibacterial properties ofMXene achieved a bactericidal rate of67.41% and51.83% against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, respectively. The DPPH free radical scavenging rate of the composite system ofMF andMXene was48.72%, effectively reducing oxidative stress damage.
Subsequently, in vitro and in vivo experiments fully validated the excellent efficacy of this system. In vitro experiments showed a hemolysis rate of<4%, good compatibility with NIH-3T3 fibroblasts and HUVECs endothelial cells, and significantly promoted angiogenesis, with the vascular network length in tube formation experiments being3.2 times that of the control group. In the full-thickness skin infection model of SD rats, theMF-MXene@MN+NIR group achieved a wound closure rate of94.88% within10 days, with a bacterial load reduction of68%, abundant collagen deposition, increased density of new blood vessels, and significantly reduced expression levels of pro-inflammatory factors, demonstrating efficient healing capability and tissue repair quality.
In summary, this study achieved multiple breakthroughs in the treatment of infectious wounds through the deep integration of biomimetic design, smart materials, and3D printing. TheMF-MXene@MN system not only provides a new paradigm for the treatment of infectious wounds but also offers important references for other biomedical applications such as localized tumor treatment and chronic disease management. With further research, it is expected to become an important component of future precision medicine.
Paper Information:
Bioinspired 3D-Printed NIR-Responsive MXene-Based Multifunctional Eutectogel Microneedles for Personalized Infected Wound Healing
Huan Liu, Aminov Nail, Decheng Meng, Liran Zhu, Xiaohan Guo, Cong Li, Xiaoqing Ye, Huanjun Li*
Advanced Healthcare Materials
DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202501344
Click the lower left corner「Read the original text」 to view the original paper.
WILEY

MaterialsViews
Official WeChat platform of the materials science journal under Wiley
Follow the public account and video account
Push materials research news|Interview material experts and newcomers
Share writing and submission experiences|Follow the latest recruitment information

Click“Share” to give us some encouragement~