The Perfect Partnership of Modbus Protocol and RTU

RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) serves as the “nerve center” for data acquisition and control in the field of industrial automation, while the Modbus protocol is its most reliable “communication language”.
The design philosophy of Modbus is “simple, efficient, and practical”. It employs a master-slave communication model with a straightforward communication frame structure, supporting both serial communication (Modbus RTU) and Ethernet communication (Modbus TCP). This adaptability allows RTU to flexibly interact with PLCs and SCADA systems while maintaining low costs and high stability in various complex field environments.
So the question arises: why does Modbus appear so powerful in RTU? The answer lies not only in the advantages of the protocol itself but also in its efficient implementation and optimization techniques within RTU.
Why is Modbus the Best Communication Assistant for RTU?

- Simple and Easy to ImplementThe frame format of Modbus is clear, mainly consisting of address field, function code field, data field, and checksum. By flexibly parsing the function code and managing data through RTU’s internal registers, the implementation of Modbus communication is not complex.
- Strong ExpandabilityModbus supports not only point-to-point communication but also a one-to-many master-slave model, allowing easy integration of multiple slave devices. For complex field control systems, combining Modbus with TCP networks further breaks the limitations of traditional serial communication, expanding communication capabilities.
- High Reliability and StabilityThe Modbus protocol has a built-in CRC check mechanism, which means that even if data is affected by noise during transmission, it can ensure accuracy through verification. Coupled with RTU’s inherent real-time design, the robustness of communication is further enhanced.
Core Implementation Technologies of RTU Based on Modbus Protocol
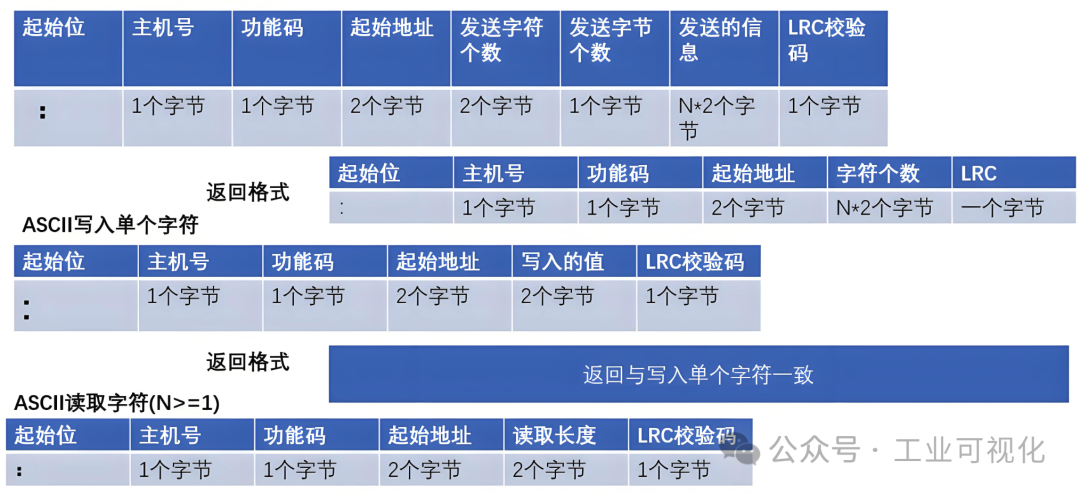
- Communication Frame Construction and ParsingRTU processes requests based on function codes. For example,
<span>0x03</span>is used to read holding registers. After the master station sends the starting address and the number of registers, RTU reads data from the internal register mapping table and packages it into a response frame. Conversely,<span>0x10</span>is used to write multiple registers, requiring RTU to parse the data and store it properly. In this process, efficient frame parsing and data mapping are key to achieving communication performance. For instance, optimizing address mapping through table lookup or using caching techniques to reduce repeated processing. - Synchronization Mechanism and Data ConsistencyMost Modbus slave devices need to support polling requests from the master station to maintain real-time updates. However, processing delays or conflicts from multiple master stations can easily lead to data inconsistency issues. In this case, RTU should ensure consistent task order through locking mechanisms (such as mutex locks) or by introducing priority task queues to avoid read-write conflicts.
- Error Detection and Fault ToleranceThe most common issues in Modbus communication are timeout errors or checksum failures. An ideal RTU firmware should design a comprehensive exception mechanism. For example, if the master station does not receive a response for an extended period, the slave should record the number of retransmissions and explicitly notify the master station of errors for quick resolution.
Optimization Solutions and Cases for Modbus Protocol in RTU
- Optimizing Communication Efficiency: For complex application scenarios, a caching mechanism should be introduced to improve communication efficiency. For example, frequently used register data can be stored in a cache to save processing time for the master station’s frequent queries while reducing the memory and CPU load of RTU.
- Dynamically Adjusting Timeout: In industrial environments with severe interference, it is recommended to dynamically configure the timeout for RTU. For instance, extending the retry interval when communication quality is poor can reduce resource waste caused by repeated requests.
- Combining TCP/IP for Cross-Protocol Transmission: By integrating Modbus RTU with Modbus TCP protocol, RTU can overcome the limitations of traditional physical distances and achieve remote data monitoring. For example, in a smart grid project, the development team designed a protocol gateway module within RTU that can translate Serial data into TCP packets in real-time, enhancing response speed and significantly improving the overall system’s scalability.
Case Analysis:
In an energy management project at a chemical plant, RTU devices connected dozens of smart meters and the master station system via the Modbus protocol. Initially, due to long device response times, the system often experienced communication lags. The optimization solutions included:
- Introducing a data buffer pool to store fixed register data in RAM for quick access by the master station;
- Adjusting communication timeout based on polling frequency to reduce unnecessary retries;
- Simultaneously supporting Modbus RTU and TCP protocols to expand overall throughput capacity.
After optimization, the system communication efficiency improved by approximately 57%, and on-site debugging time was reduced by nearly 30%.
Conclusion: Why is Modbus So Powerful in RTU?
The core advantages of Modbus lie in its simplicity, expandability, and high reliability. The strong performance of this protocol in RTU relies on the technical team’s lean implementation and targeted optimizations. From the efficient construction of communication frames to the ultimate optimization of data mapping, and to higher-level protocol extensions, Modbus provides RTU with stable and flexible communication assurance.
In summary, the strength of Modbus in RTU comes not only from its inherent protocol advantages but also from the optimization measures that combine software and hardware, enabling it to handle various complex industrial scenarios.
Recent Popular Articles:
| Don’t Understand Protocol? Don’t Mess with the Host Computer!!!What!!! You Haven’t Even Seen a DCS System?Why!!! Industrial Control Prefers Modbus Over???Industrial Control Experts!!! Decoding RS-485Essentials!!! Can’t Tell the Difference! RTU and TCP Fully Explained |