
—— Xi Jinping
The new round of technological revolution has led to a new round of industrial revolution. This premise is very important, meaning that without this round of technological revolution, there would be no industrial revolution.
Xiumi is a mobile content creation and publishing platform that provides rich templates and a user-friendly experience, allowing you to quickly create highly innovative content that impresses you.What is Industry 4.0?Industry 4.0 will be the first breakthrough of Internet+.What is Industry 4.0?If you miss Industry 4.0, you miss this era.The essence of “Industry 4.0” isthe industrial Internet. The integration of “Internet+ manufacturing” is a revolution of the era, a disruption and self-disruption. In fact, over the past 15 years, I have not only witnessed the transition from automation to the Internet but also the technological changes brought about by the Internet of Everything. “Industry 4.0” is the last industrial revolution of human society. To quote Miao Wei, the Minister of Industry and Information Technology: “Internet+” is a huge concept, and “Internet+ manufacturing” is the most qualified. “Industry 4.0” will also become the first breakthrough field of “Internet+”. What is Industry 4.0?
The path of Industry 4.0 has just begun, but it has given us a general direction. In the future, enterprises will become data-driven, innovative, integrated, and rapidly changing enterprises. For the entire manufacturing industry, this is a huge disruption, and it is not an exaggeration to call it an industrial revolution.
What is Industry 4.0?
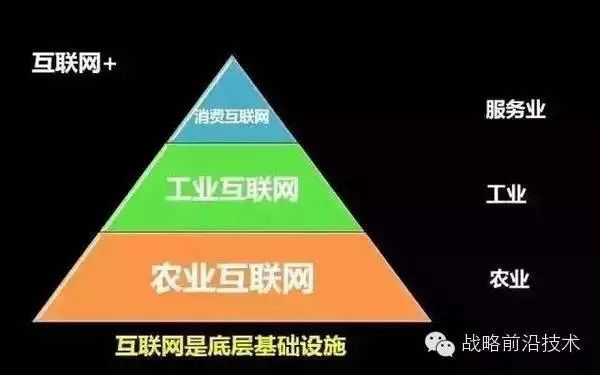
In the past 15 years in China’s mobile Internet field, all resources and funds have been concentrated in the tertiary industry, namely the service industry, which we call the consumer Internet. Now the mobile Internet has reached the secondary industry, manufacturing, and the primary industry, agriculture. According to Jack Ma, the Internet is the top-level infrastructure of our society today, like water, electricity, coal, and highways. Therefore, with the disruption and invasion of the mobile Internet into the industrial and agricultural fields, I personally believe that the entire mobile Internet has entered a stage of deep reconstruction and re-creation of efficiency. This is also the core meaning of the “Internet+” proposed by the Chinese government.
“Industry 4.0” is an immensely vast concept, and its core is “smart manufacturing”.It has a huge impact on the entire industry in China. Because China is a major manufacturing country in the world, “Industry 4.0” not only affects China’s economy but also influences the future development of the entire country. I personally believe it will impact employment in China, as there are over 80 million employees in the manufacturing sector. Secondly, it will affect China’s economic exports. Thirdly, it will impact China’s military defense. It affects all our product production, manufacturing, processes, and supply chains, so “Industry 4.0” is disrupting the entire production model of traditional industries.
The Three Major Benefit Areas Brought by Industry 4.0
I often mention in many places, including government departments in China and many large enterprises, that “Industry 4.0” has just begun since 2013. In my personal view, it will continue for 30 to 40 years. Therefore, “Industry 4.0” is an immensely vast market worth trillions. In the field of “Industry 4.0”, there will be more than 300 listed companies in the capital market in the next 10 years. Many students ask what categories of companies will have more opportunities. My understanding is as follows:
The first category is smart factories.It can be divided into two subcategories: 1. Traditional factories transforming into smart factories. 2. Factories that are born as smart factories.
The second category is technology solution companies.These companies provide “Industry 4.0” solutions for the manufacturing industry, including smart factories, top-level design, transformation roadmaps, and integrated hardware and software facilities, acting as general integrators. In fact, there are 4 million traditional manufacturing enterprises in China, and in the next 10 years, or even 20 years, they will gradually transform into “Industry 4.0” factories in steps. Therefore, there is a huge market facing this.
The third category is the nine major technology suppliers in the process of transforming China’s manufacturing industry into “Industry 4.0”, including industrial IoT, industrial cybersecurity, industrial big data, cloud computing platforms, etc.
In the “Industry 4.0” solutions, both software and hardware are included.Software includes industrial IoT, industrial cybersecurity, industrial big data, cloud computing platforms, MES systems, virtual reality, artificial intelligence, and automation support for work. Hardware includes robots (including high-end components), sensors, RFID, 3D printing, machine vision, smart logistics, AGV, PLC, data collectors, industrial switches, etc.

If you miss Industry 4.0, you miss this era.
There are two core signs from Industry 3.0 to 4.0.
The first is the transition from containers in the 3.0 era to express delivery today, which answers why express companies like SF Express have become immensely significant in the Internet era. In the industrial era, the role of EMS was not as great. Therefore, the core sign of the industrial era is containers, while the core sign of the Internet era is express delivery.
The second sign is the transition from molds to data. This is the title of a new book I recently wrote. We know that in the industrial era, the most typical company in global manufacturing is Foxconn. Terry Gou has also mentioned that molds are the mother of industry, and IE is the father of industry. Therefore, Foxconn, BYD, and Toyota have all regarded molds and IE as core capabilities, which can also be considered as the hallmark of the industrial era or 3.0 era. In the 4.0 era, according to Jack Ma from Alibaba, it is called DT, which stands for data technology. Therefore, the core sign from 3.0 to 4.0 is the transition from molds to data. This is a massive industrial revolution; missing “Industry 4.0” means missing this era.
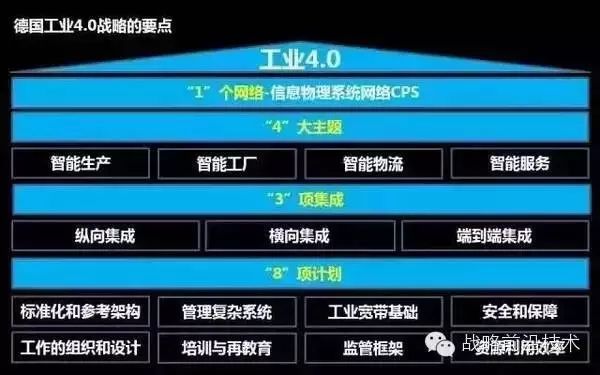
The German government defines Industry 4.0 in Germany as a framework structure composed of one information, one network, four major themes, three integrations, and eight plans. The overall framework proposed by the German government for Industry 4.0 has many differences from China’s actual national conditions, and there is still a certain distance in operation.
Background and Overview of German Industry 4.0
The first industrial revolution is marked by the invention of the steam engine by Watt in 1784, which originated in the UK and lasted for 86 years.
The second industrial revolution occurred in 1870, marked by the invention of electricity in Cincinnati, USA, and lasted for 99 years;
The third industrial revolution began in Silicon Valley in 1969 and has lasted for 44 years, with an expected continuation of 10 to 20 years.
The fourth industrial revolution is marked by the announcement in 2013 in Hannover, Germany, that this round of work revolution is centered on smart manufacturing. The fourth industrial revolution is expected to last for about 30 to 40 years, so the disruption, reconstruction, and integration of Industry 4.0 and the mobile Internet in China’s industry have just begun.
The first camp: the USA and Germany
The new round of global industrial revolution is actually the integration of industry and the Internet. The USA has proposed industrial Internet standards, hoping to focus on equipment interconnection, data analysis, and business insights based on data. Their focus on traditional industrial Internet interconnectivity is on big data and cloud computing.
Germany has launched Industry 4.0, hoping to redirect the global manufacturing trend, which is also the main symbol of Germany’s desire to lead the fourth industrial revolution. Whoever leads this industrial revolution will become the leader of this industrial revolution, can set the standards, and can become the king of this revolution, potentially saving the decline of the EU and restoring Germany’s status as a world power.
Germany’s proposal for Industry 4.0 is backed by strong mechanical manufacturing technology, advanced embedded and control equipment capabilities, and a keen focus on the profound changes in the intelligence and virtualization of production processes.
Industry 4.0 represents the struggle for dominance in this industrial revolution between Germany and the USA, with two major goals: one is smart manufacturing, and the other is smart factories. The essence of the fourth industrial revolution is the competition for future industrial standards led by Germany and the USA, advancing according to their own logical paths and expressions.
The second camp: China and Japan
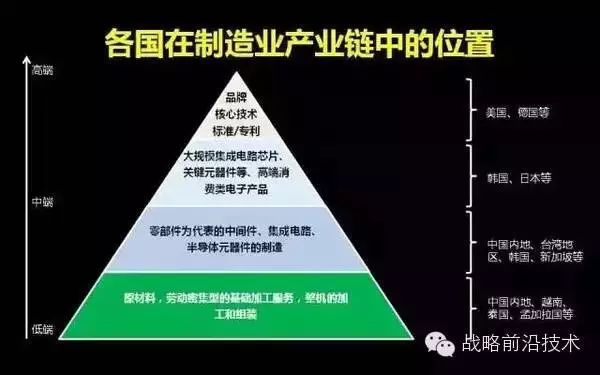
In the fourth industrial revolution, Germany and the USA are competing for global standards. China is a follower of standards, and the Chinese government has chosen the German standard, launching “Made in China 2025” to transition from a manufacturing power to a strong manufacturing nation. The Chinese Academy of Engineering leads this initiative, with the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology participating, providing top-level design and path selection. The core of “Made in China 2025” is to accelerate the deep integration of a new generation of technologies with manufacturing, focusing on promoting smart manufacturing.
Why is Japan absent in this round of industrial revolution? Japan has fallen behind in this process due to its lagging information technology. Germany can become the proposer of this round of industrial revolution because it has strong software companies, such as SAP, KUKA Robotics, and Siemens, which have strong R&D capabilities.
China lacks such strong industrial software and robotics companies. Therefore, in this round of industrial revolution, Germany and the USA hold the dominant position, while China and Japan are in the second camp.
Of course, in the future of Industry 4.0, Japan will still have a place. Because Japan has a deep accumulation in new materials research and technology, it will still hold some position but cannot become a standard setter.
It can be seen that the industrial Internet of the USA and Industry 4.0 of Germany have opposite implementation paths and logic, but their goals are the same. The USA, supported by companies like GE and IBM, focuses on connecting hardware from a software perspective; Germany, led by Siemens, KUKA, and SAP, hopes to connect software from a hardware perspective.
Whether from software to hardware or from hardware to software, the goal of both is the same: to achieve smart manufacturing and the integration of mobile Internet and industry.
The Reasons for China’s Choice of German Standards
First, the Chinese government believes that the German path is easier to achieve than the American path; second, the USA’s industrial hollowing out is severe. IT companies face significant challenges in implementing Industry 4.0 due to a lack of infrastructure. Germany has strong industrial technology, being a manufacturing base with suppliers of production equipment and IT business solution providers. In the strategic choice of the fourth industrial revolution, the Chinese government’s strategy is to closely follow the trend of a new round of industrial development, choose Industry 4.0, launch the Chinese version of “Made in China 2025”, and seek opportunities for leapfrogging and proactive measures.
Can China become a winner in this round of industrial revolution? The conclusion is affirmative. Because in the strategic choice race of starting, China has always been able to take the lead. From China’s start in mobile Internet and the tertiary industry, we can see that China’s mobile Internet and e-commerce have far surpassed Silicon Valley.
Industry 4.0 is a brand new era, and the first phase has just begun, with an expected development time of 30 to 50 years. According to the Minister of Industry and Information Technology, Germany has transitioned from Industry 3.0 to Industry 4.0, while China is parallelly transitioning from 2.0 and 3.0 to 4.0.
Due to the disparity between coastal and inland areas, the foundation is different. China is generally at the stages of 2.0 and 3.0, so for Chinese enterprises, 4.0 is a relatively long-term vision that requires a long journey. It requires a down-to-earth approach, advancing step by step according to their actual situation.
The Two Major Goals of Industry 4.0: Smart Manufacturing & Smart Factories
The first goal is smart manufacturing, and the second is smart factories. In the past, there were several definitions of smart manufacturing: first, digital manufacturing; second, intelligent manufacturing; these expressions are not accurate. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and the Chinese Academy of Engineering define the core goal of the Chinese version of Industry 4.0 as smart manufacturing, which is a very accurate term. Extending from smart manufacturing to specific factories means smart factories.
Smart manufacturing is the core of Industry 4.0. As a broad concept, smart manufacturing includes five aspects. Only after achieving intelligence in these five aspects can the large concept of smart manufacturing be realized.
Smart manufacturing is a giant system, and Industry 4.0 means that a super complex giant system is forming. The machines in the workshop are like smartphones, achieving functional upgrades through operating system updates and various functions through industrial apps, continuously expanding the manufacturing ecosystem through APIs.
All machines, products, components, personnel, raw materials, all R&D tools, testing and verification platforms, virtual products and factories, all product management, production management, and operation management processes, all R&D, production, management, and sales employees, all levels of suppliers, and thousands of customers will be important components of this system. A complex information system based on the cloud, pipelines, and end-to-end is forming, where the machines in the workshop are like smartphones, and the entire operation will form an immense giant system.
In smart factories, the Germans hope to achieve two conceptual goals. The first is machines producing machines, or self-production. The second is unmanned factories, or dark factories, or 100% fully intelligent factories, coexisting with intelligent machines. Smart factories represent a new stage in the development of modern factories, utilizing IoT technology and equipment monitoring technology to enhance information and services.
The Three Major Characteristics of Smart Factories
The first characteristic of smart factories is that the information infrastructure is highly interconnected, including production equipment, robots, operators, materials, and finished products.
The second is that manufacturing process data is real-time, with production data having a stable rhythm and flow, and data storage and processing also being real-time.
The third is the ability to use stored data for data mining and analysis, with self-learning capabilities, and the ability to improve and optimize manufacturing processes.
The development trend of smart factories is from flexibility to agility to intelligence and then to informatization.
The Five Characteristics of Industry 4.0
Interconnectivity
The core of Industry 4.0 is connectivity. Today, the entire world of mobile Internet is centered on connectivity, just like Baidu connects people and information, and Tencent connects people with people. Industry 4.0 aims to closely link devices, production lines, factories, suppliers, products, and customers.
Data
When sensors are ubiquitous, smart devices are everywhere, smart terminals are everywhere, and connectivity is everywhere, the inevitable result is that data is everywhere.
Industry 4.0 connects product data, equipment data, R&D data, industrial chain data, operational data, management data, sales data, and consumer data.
From last year to this year, Jack Ma mentioned that Alibaba is essentially a data company, and Lei Jun also stated that Xiaomi is fundamentally a data company. From IT to DT, the entire society is transforming into a big data society.
From Industry 3.0 to Industry 4.0, I propose my own viewpoint: it is actually a transition from molds to data. The industrial 3.0 era is centered on molds, while the industrial 4.0 era is based on data, and all factories will become data factories.
Integration
Integration is a keyword of Industry 4.0 and also a keyword for China to promote the integration of the two industries. Industry 4.0 will form an intelligent network through ubiquitous sensors, embedded terminal systems, intelligent control systems, and communication facilities via CPS.
This intelligent network enables connections between people and people, people and machines, machines and machines, and services to services, achieving high levels of horizontal, vertical, and end-to-end integration.
Innovation
The implementation process of Industry 4.0 is a process of innovative development in manufacturing. Innovations in manufacturing technology, products, models, business formats, and organizations will emerge endlessly, from technological innovation to product innovation, to model innovation, and finally to organizational innovation.
Transformation
For China’s traditional manufacturing industry, transformation is essentially from traditional factories, from 2.0 and 3.0 factories to 4.0 factories. The entire production form is shifting from mass production to personalized customization. Three years ago, Alibaba proposed that the entire manufacturing process should shift from B2B and B2C to C2B. They keenly observed this direction, and the entire production process is becoming more flexible, personalized, and customized. This is a very important feature of Industry 4.0.
Industry 4.0 is transitioning from production-oriented manufacturing to service-oriented manufacturing. In the future, the boundaries between production and service will become increasingly blurred. According to the entire framework of German Industry 4.0, future factories may shift from centralized production to distributed production. 3D printing will be rapidly utilized, and the concept of future factories may be entirely new, not what we see today with hundreds or thousands of people and equipment. The future factory may be in the customer’s living room, where the customer can print the rice cooker using a 3D printer based on the design drawings sent from the Guangdong rice cooker company. This means that the living room has become a production workshop, so the concept of future factories needs to refresh our imagination.
For example, in the past, producing a rice cooker might involve manufacturing in Guangdong, China, and then shipping it to Africa for the customer. However, in the future, during the Industry 4.0 era, the Guangdong rice cooker company only needs to send the design drawings to the customer’s computer, and the customer can print the rice cooker using a 3D printer in their living room, meaning that the living room has become a production workshop. Therefore, the concept of future factories needs to be reimagined.
Industry 4.0 is transitioning from factor-driven to innovation-driven. In the past, it was based on demographic dividends, large-scale production, and low exchange rates, which led to factor-driven development, often at the expense of the environment. In the future, the era of Industry 4.0 will see the manufacturing industry transition to 4.0 factories, driven by innovation, with increasing technological content, and a dramatic reduction in factory personnel. In the past, blue-collar workers will transition to black-collar workers, operated by computer operators managing the entire machinery. The workshop will increasingly utilize low-cost automation equipment and industrial robots, enabling machines to achieve self-production as defined by Germany’s 4.0.
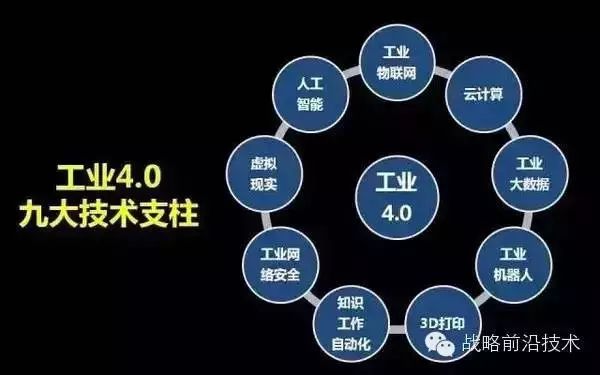
The Nine Major Technological Pillars of Industry 4.0
The nine major technological pillars of Industry 4.0 include industrial IoT, cloud computing, industrial big data, industrial robots, 3D printing, knowledge work automation, industrial cybersecurity, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence. Countless business opportunities and listed companies will emerge from these nine pillars.
Industrial IoT
Industrial IoT is the core foundation of Industry 4.0, with ubiquitous sensors. Once these sensors are interconnected, they generate vast amounts of data, which return to a digital hub for data cleaning, organization, and mining, adding value to the data. In the past, big data was more commonly used in service enterprises, while many data in industrial enterprises were not fully mined. Now a new market is forming, which is the value generation through the vast amounts of data created by industrial IoT, making industrial IoT the first technological field.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is divided into public cloud and private cloud. In the past, many large enterprises in China and globally hoped to establish their own cloud computing platforms. This trend has emerged in China, with China Telecom and China Bank wanting to build their own cloud computing platforms, while small and medium-sized enterprises use public clouds.
In the past three years, Citibank in the USA has gradually laid off its IT team of over a thousand people, transitioning its public cloud to Amazon or IBM’s private cloud. This trend is also emerging in China, where cloud computing is becoming the infrastructure of the Internet, akin to water, electricity, coal, and highways. A company does not need to maintain a large IT team, and for security defense, it cannot achieve enterprise-level security. Therefore, outsourcing to professional cloud service infrastructure providers is the best choice.
In the USA, Amazon has secured many contracts with the US Department of Defense, surpassing IBM. Alibaba in China also provides excellent cloud computing services. Therefore, in the cloud computing field, observing global trends, everyone is storing their data in the cloud for processing. Thus, cloud computing based on big data is also the core ID technology of Industry 4.0. The strongest technologies in this area are found in Silicon Valley.
From the above cases, it can be seen that while Industry 4.0 originated in Germany, it is inseparable from Silicon Valley. The big data, cloud computing, and future technologies like artificial intelligence and virtual reality from Silicon Valley also have a huge impact on the integration of industry and the Internet.
Industrial Big Data
Jack Ma mentioned to reporters about industrial intelligence that in the future, all enterprises will become data enterprises, and we are transitioning from IT to DT, which is data technology. Industrial big data is also a crucial technological field within Industry 4.0. Many new industrial big data companies in Silicon Valley and Germany provide analysis, collection, and data collection services. This industrial data will be stored in the cloud, and through industrial data analysis, we can reanalyze machine operations and efficiency improvements.
Four years ago, I met a Taiwanese professor, Li Jie, from the University of Cincinnati, who was consulting for Haier, studying intelligent equipment management. Many machines today are maintained and serviced reactively, while they are researching intelligent machines that analyze parameters and performance, such as when they might fail or when faults might occur.
Boeing sponsored his research because they wanted to know how long an aircraft could operate before a fault might occur, potentially leading to a crash. Therefore, in the era of big data, analyzing when a machine might fail is an application of big data in machine operation.
Industrial Robots
China has 80 million workers in the manufacturing industry, while Japan has 11 million. In 2013, Masayoshi Son, the president of SoftBank in Japan, suggested to the Japanese government that by 2040, Japan should increase its industrial robots to 50 million, allowing these robots to work in factories, combined with 11 million workers, resulting in about 60 million usable labor forces. He believes that this will enable Japan’s manufacturing industry to regain its status as the world’s strongest manufacturing power.
About two weeks ago, Jack Ma from Alibaba and Terry Gou from Foxconn jointly invested in a Japanese service robotics company. In February, President Xi Jinping emphasized the importance of robots in a document, and in March and April, over 170 new robotics companies emerged in China. In the future, the breadth and depth of industrial robot applications in factories will be vast. Some provinces and cities, such as Dongguan and Zhejiang, have proposed “replacing humans with machines,” with government incentives.
There are three major companies in the global industrial robotics market: the first is KUKA from Germany, the second is ABB from Sweden, and the third is FANUC from Japan. Currently, the best company in China’s industrial robotics field is the Shenyang Institute of Automation under the Chinese Academy of Sciences, which has been listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange with a market value of nearly 70 billion.
Therefore, in the field of Industry 4.0, there will be many outstanding listed companies. In the future, investing in hardware and software companies related to Industry 4.0 has enormous development prospects in China. The future ten years of Industry 4.0 will be a market worth tens of trillions for smart manufacturing transformation, supported by national policies and the necessity of mobile Internet transformation. This area is just beginning to be explored as a gold mine.
3D Printing
3D printing is the greatest technological breakthrough in manufacturing history. There have been many new technological breakthroughs in 3D printing in the USA and Germany, with applications in clothing, automobiles, and even heart stents.
In the past, 3D printing had drawbacks: first, the printing speed was too slow; second, the realism was still distant from actual objects. However, technology is advancing rapidly, transitioning from 3D printing to rapid 3D printing and then to 4D printing. In the field of 3D printing, there will be significant breakthroughs in technology. In January of this year, I attended the CES electronics show and saw many technological breakthroughs; the era of rapid application of 3D printing will soon arrive.
The rapid development of 3D printing aligns with the logic behind the “maker” movement promoted in China, providing countless individual creators with possibilities. Therefore, many one or two-person factories will emerge. The future will see a coalition of freelancers, posing new challenges to organizational structures and large companies, but this trend has already been established.

Knowledge Work Automation
In the past, we emphasized the standardization of production processes and the automation of production equipment. In the future, society will be an era of collaborative knowledge workers, and the work of knowledge workers will become increasingly automated, representing a new market worth trillions. The management models and theories of the industrial era will largely disappear in the Internet era, and management models for the Internet have yet to be established. The forms and standards of knowledge workers have not yet been formed.
The industrial production processes and value chains formed in the 3.0 era will be destroyed, and new management models and value chains have not yet been established. Borrowing from Li Shanyou’s words: the future is uncertain, and we are only using uncertainty to determine the uncertainties of the future.
Through the sharing economy, we can see that the boundaries of organizational employment are becoming blurred. Many people are becoming freelancers, no longer employed by a single company, but gathering for a project and separating once the project ends. This may be a significant direction for the transformation of the entire enterprise in the future.
Industrial Cybersecurity
In the past, we could see that in the service industry, there were enterprise-level cybersecurity measures with certain prevention and security indices. However, in industry, past data was based on PC interconnectivity, while in the future, machine-to-machine interconnectivity will present compatibility issues. Secondly, as data is stored in the cloud, the security of data becomes a crucial choice. Therefore, industrial cybersecurity is a very important aspect of Industry 4.0 technology and one of the fastest-growing service sectors in China in recent years.
Virtual Reality
Currently, many companies in Silicon Valley, including Boeing, are working on augmented reality and virtual reality. They are exploring how to incorporate virtual scenarios into R&D and testing before new production. In the past, we used blueprints to produce products and then iterated and improved them continuously. In the future, through virtual reality, products can undergo millions of improvements on the computer before production, dramatically increasing production efficiency.
Artificial Intelligence
A futurist in Silicon Valley predicts that by 2045, machine intelligence will surpass human intelligence. Therefore, 2045 is designated as the singularity, and Singularity University has been established in Silicon Valley. 2045 is a unique year; if machine intelligence surpasses human intelligence, it means that machine intelligence will overturn human mechanization. When machine intelligence exceeds human intelligence, the entire social structure, production methods, lifestyles, and production relationships will undergo tremendous changes.
Currently, Baidu is focusing its future strategy on two points: one is establishing connections between people and information, and the other is artificial intelligence. Keda Xunfei in Anhui is also focusing its entire business scope on artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence is a trillion-dollar market. Many artificial intelligence companies are emerging in Silicon Valley and Canada. In the past, humans operated machines, but after machines become intelligent, they can lead and command production, and artificial intelligence will bring about significant changes to the world.
In the future of Industry 4.0, is software more important than hardware? The answer is very simple: software determines everything; software defines machines. All factories are software companies and data companies, and all industrial software is crucial in the era of Industry 4.0. Therefore, software defines everything.
This round of industrial revolution is driven by technological revolution. In China’s “Internet+”, Industry 4.0 is a component of “Internet+ manufacturing”, which is the German version of Industry 4.0, also known as “Made in China 2025”.
(Reprinted from Strategic Frontier Technology)
