| We will continue to update various technical analyses of robot competitions. At the end of the article, there is a technical exchange group for everyone to happily connect with the future of intelligence. We welcome everyone to follow and communicate.
1.Overview of Basic Competition Information
| Project | Description |
|
Competition Name |
Robot Task Challenge (Smart Pharmacy) |
|
Affiliated Event |
China Robot and Artificial Intelligence Competition |
|
Organizing Body |
Chinese Association for Artificial Intelligence National Computer Education Research Association of Higher Education |
|
Competition Area |
Nationwide |
|
Competition Type |
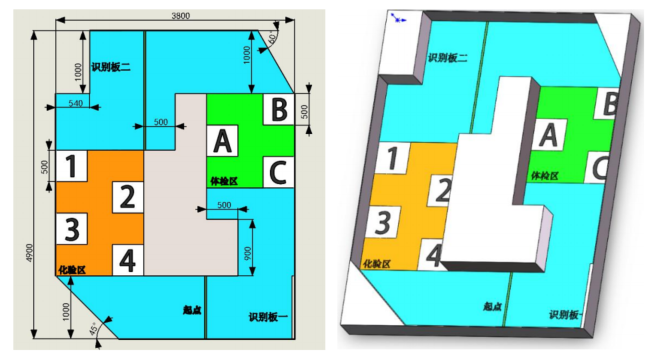
Task competition. Simulating a medication delivery scenario, where the vehicle needs to pick up and drop off medication at designated points within a closed map. The vehicle is an Ackermann steering car approximately 270*210mm in size. |
|
Competition Official Website |
https://www.caairobot.com/html/robot2025/44921.html |
|
Rules Link |
https://www.caairobot.com/html/robot2025/44956.html |
2. Task Overview
|
Main Competition Content |
Design a small car based on an Ackermann chassis to simulate the hospital testing and delivery process. It needs to recognize QR codes to determine task order and flow. During the overall operation, there are no path planning markers on the ground, and it needs to navigate to specific target locations using SLAM. Vehicle dimensions: Length * Width * Height not less than 270mm * 210mm, height between 140~250mm. Controller requirements: CPU ≤ 4 cores 1.5GHz; GPU/BPU ≤ 5T (INT8) or 0.5T (FP16); Memory ≤ 4GB;
|
| Competitiveness |
Completion of the task. |
| Robot Configuration |
Chassis: Ackermann structure; |
| Performance Parameters |
Total vehicle weight: No restrictions, but it is recommended to be as light as possible to ensure sufficient speed; Load: No specific requirements; Robot dimensions: Length * Width * Height not less than 270mm * 210mm, height between 140~250mm; Controller requirements: CPU ≤ 4 cores 1.5GHz; GPU/BPU ≤ 5T (INT8) or 0.5T (FP16); Memory ≤ 4GB; Robot speed: The main task should be implemented smoothly, speed is not a primary concern. |
| Control Functions | Car control: High precision required for distance and angle, closed-loop control, speed + position cascade PID + gyroscope angle loop; QR code recognition: scanning module or visual camera module; full-field positioning: SLAM navigation positioning; voice broadcasting: text-to-speech TTS module or embedded development board calling API interface; |
3. Analysis of Robot Chassis Solutions
3.1 Reference Configuration
| Configuration | Schematic Diagram | Reference Physical Diagram |
| Ackermann Steering Chassis | 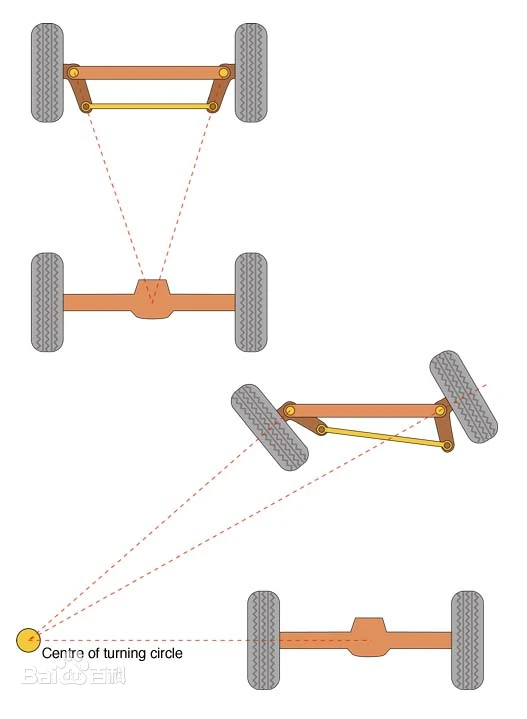 |
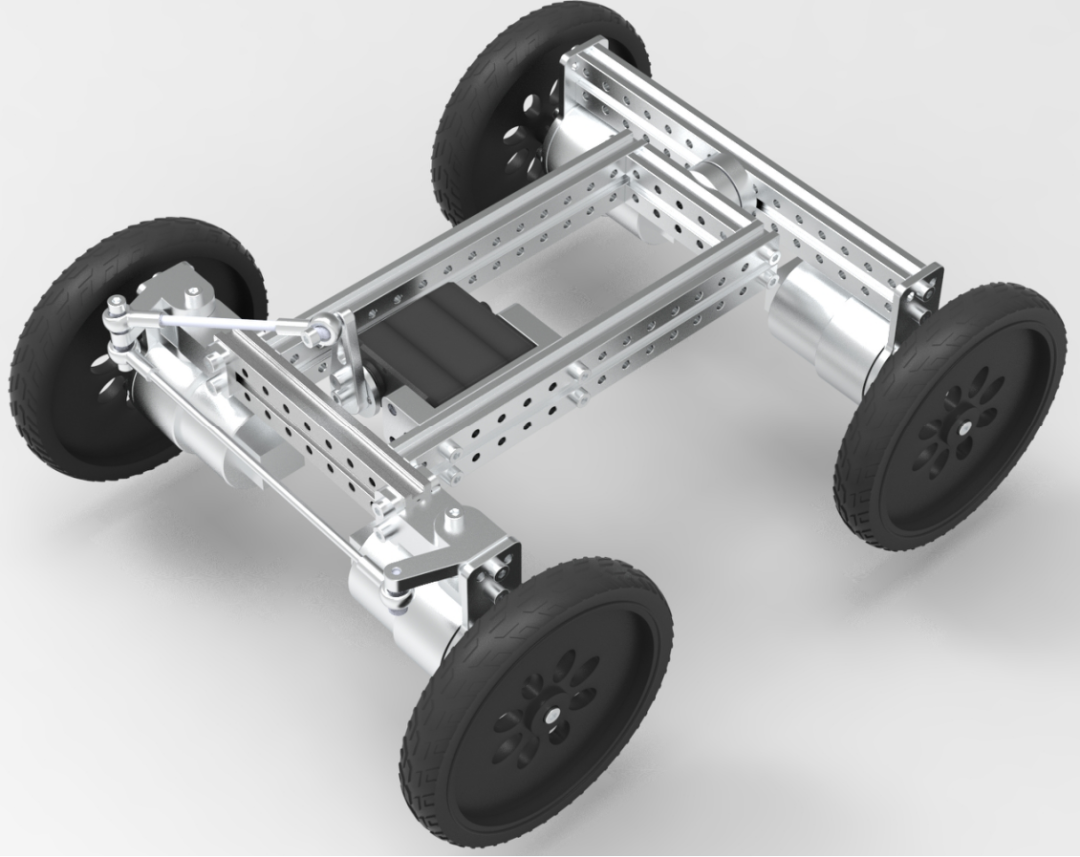 |
3.2 Hardware Selection
| Type | Name | Description |
| Drive Scheme | Chassis Scheme 1: 42-stepper motor + closed-loop driver board (e.g., Taobao Zhang Datou driver board); |
Advantages: Simple control of chassis drive, no need to design PID controller or tune parameters; Disadvantages: The torque output of the 42-stepper motor is relatively small, and it may not be able to carry a heavy chassis, and the hardware procurement cost is relatively high. |
|
Chassis Scheme 2: Encoded DC motor; |
Encoded motor using photoelectric or Hall encoding, 12V, reduction ratio recommended between 10-30; Advantages: Large output torque and relatively low cost; Disadvantages: Requires designing a PID controller, and precision is highly dependent on PID parameters, tuning for high precision can take a long time. |
|
| Ackermann Steering: Swing using PWM or bus servo; | Here, the precision requirement is very low, using a standard PWM servo is sufficient; if data feedback is needed, consider using a bus servo. | |
| QR Code Recognition | Scheme 1: Scanning module; |
Advantages: Low cost, small structure size, simple control, basic parameters can be used directly, high detection efficiency; Disadvantages: Requires writing a decoding program. |
| Scheme 2: K210, OpenMV, MaixCAM and other modules; |
Advantages: Good recognition accuracy, and algorithms are available for direct use; Disadvantages: Software deployment has certain difficulties, larger size needs to consider installation space, camera resolution is low. There are certain cost requirements, with K210 having a low frame rate but low cost, while OpenMV and MaixCAM have higher frame rates but also higher costs. Overall, they can meet usage requirements. |
|
| Scheme 3: Embedded development board + camera, such as RDK X3. |
Advantages: High recognition accuracy, high accuracy rate, high recognition speed, camera resolution can be selected, and the hardware can be used for visual SLAM. Disadvantages: Requires embedded basics, relatively high cost. |
|
|
Comprehensive Suggestion: If you have not yet contacted vision, it is recommended to consider using the scanning module directly; if you want to try vision, consider the K210 integrated vision module or MaixCAM integrated vision module; if you are familiar with ROS for robot operating systems, consider the RDK + Zbar library vision scheme. |
||
| Voice Broadcasting | TTS text-to-speech module | The module itself is low cost, and deployment difficulty is low, can directly communicate with the microcontroller via TTL serial, but cannot reuse hardware with other functions. |
| Embedded development board + speaker module | The mainboard can be shared with the navigation positioning mainboard, but deployment requires a good software foundation, can call AI model API interfaces, such as Volcano Engine, but there are calling costs, and in simple text playback scenarios, real-time performance may be relatively poor. | |
| Robot PositioningNavigation | Laser SLAM |
Advantages: The system is relatively simple, with low performance requirements for the controller; Disadvantages: In this competition, there are no particular disadvantages, can meet competition requirements, requires pre-mapping. |
| Visual SLAM |
Advantages: Can share hardware with QR code recognition; Disadvantages: High performance requirements for the controller, recognition accuracy is poor, easily affected by light interference. |
|
| Laser-Visual Fusion SLAM |
Advantages: Relatively better positioning accuracy; Disadvantages: High performance requirements for the controller, system control is relatively complex, engineering implementation difficulty is high. |
|
| Controller (Choose One) | Microcontroller – Arduino | Consider using the Arduino Mega2560 board with many pins and interrupts. Arduino has standard libraries, programming is relatively simpler. |
| Microcontroller – STM32 | Choose based on pin selection, generally recommended to choose between STM32103 and STM32407, requires a good foundation in STM32. | |
| Embedded Development Board | For this competition, both the RDK X3 of the sweet potato robot and the Raspberry Pi 4b can meet the competition requirements. If you want better performance in vision, it is recommended to choose RDK X3. |
4. Some Learning Reference Materials
| Project | Learning Link |
|
DC Motor PID Control |
https://unirobot.yuque.com/org-wiki-unirobot-gr9ewx/bebdzr/nfpr4fqgl7aqg0n5?singleDoc# “Experiment 2 PID Control of DC Motor Speed” |
| Servo Drive |
https://unirobot.yuque.com/org-wiki-unirobot-gr9ewx/bebdzr/xkqdpc8vakm6cvtc “Experiment 3 PWM Drive Servo” |
| Visual QR Code Recognition |
https://unirobot.yuque.com/org-wiki-unirobot-gr9ewx/bebdzr/tvbmrqgn2ztcvq44 “4.5 QR Code Recognition and Data Acquisition” |
| Laser SLAM Navigation and Positioning | https://unirobot.yuque.com/org-wiki-unirobot-gr9ewx/uni_wr2 “UNI-WR2 Navigation Practice” |
| ROS Learning – Wiki |
https://wiki.ros.org/cn “ROS Development Documentation” https://docs.ros.org/en/humble/Tutorials/Beginner-Client-Libraries/Creating-A-Workspace/Creating-A-Workspace.html “ROS2 Development Documentation” |
| More References | https://unirobot.yuque.com/org-wiki-unirobot-gr9ewx/bebdzr?# “GX-MAT-09 Design and Development Manual” |
| Technical Communication |
Partners interested in robot technology can join the QQ group for communication:811348489 |