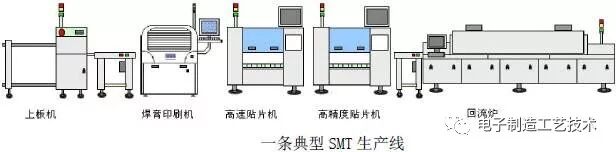
SMT stands for Surface Mount Technology, which is currently the most popular technology and process in the electronic assembly industry.
It is a circuit assembly technology that mounts surface-mounted components (referred to as SMC/SMD, known in Chinese as chip components) on the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs) or other substrates, using methods such as reflow soldering or wave soldering for assembly.
Understanding the production environment requirements and management specifications for SMT workshops
Many first-time users of SMT equipment are not very familiar with the environmental requirements for SMT production equipment. Therefore, Shenzhen Zhichi Technology has compiled some environmental requirements for reference. First, it is important to note that SMT production equipment is high-precision mechatronic equipment. The cleanliness, humidity, and temperature of the environment have specific requirements for the equipment and process materials. To ensure the normal operation of the equipment and the quality of assembly, the following environmental requirements must be met:
1. The load-bearing capacity, vibration, and noise requirements of the factory building: The load-bearing capacity of the factory floor should be greater than 8KN/m².
Vibration should be controlled within 70dB, with a maximum value not exceeding 80dB. Noise should be controlled within 70dBA.
2. Power supply
Generally requires single-phase AC220 (220±10%, 0/60Hz) and three-phase AC380 (380±10%, 50/60Hz). The power supply capacity should be more than double the power consumption.
3. Air source
Configure the air source pressure according to the equipment requirements. You can use the factory’s air source or configure a separate oil-free air compressor, generally with a pressure greater than 7kg/cm². Clean, dry purified air is required, so the compressed air must undergo oil removal, dust removal, and water removal treatment. Use stainless steel or pressure-resistant plastic pipes for air ducts.
4. Exhaust
Reflow soldering and wave soldering equipment must be equipped with exhaust fans. For hot air reflow ovens, the minimum flow rate of the exhaust duct should be 500 cubic feet per minute (14.15m³/min).
5. Lighting
The ideal illumination level in the factory is 800~1200LUX, with a minimum of no less than 300LUX. In areas for inspection, rework, and measurement, local lighting should be installed if the illumination is low.
6. Working environment
The factory should be kept clean and hygienic, free of dust and corrosive gases. The cleanliness level in the production workshop should be controlled at: 500,000 level.
The optimal environmental temperature for the production workshop is 23±3℃, generally between 17~28℃, with a relative humidity of 45%~70% RH. Appropriate temperature and humidity meters should be set according to the size of the workshop for regular monitoring, and facilities for adjusting temperature and humidity should be provided.
1. Purpose
To implement appropriate management of the working environment, comprehensively strengthenPCBAdaily operational control to ensure quality and ensure that the environment does not adversely affect product compliance.Enhance efficiency and create a good working environment.
2. Scope of application
Applicable toPCBAworkshop product realization process environmental management.
3. Responsibilities
PCBAworkshop all operational personnel
4. Environmental management items
①Workshop environmental management
②Anti-static work area
③Warehouse management
④Safety equipment management
Workshop environmental management
|
Illustration |
Operation description |
|
Figure 1
|
(1)Power supply The power supply voltage and capacity must meet the equipment requirements. Generally requires single-phase AC220V ± 10%, AC380 V, 50/60 Hz, and should generally use a three-phase five-wire connection method, with good grounding required. The power supply voltage must be stable; if it does not meet the requirements, a voltage stabilizer must be configured. The power supply capacity should be more than double the power consumption. For example, if the power consumption of the placement machine is 5 KW, a power supply of more than 10 KW should be configured. (2)Air source SMT equipment such as printers and placement machines require an air source for operation. Generally, the air source pressure should be greater than 686 KPa, and the air source must be clean and dry. Therefore, the air compressor generating the air source usually requires filters and condensers for dust and water removal. Air ducts should generally use stainless steel or pressure-resistant plastic pipes, and iron pipes should be avoided to prevent rust. Rust particles entering the pipes and valves can easily cause blockages and affect the normal operation of the machines. (3)Exhaust Reflow soldering and wave soldering equipment have exhaust requirements, and exhaust fans should be configured according to the equipment requirements. For hot air reflow ovens, the minimum flow rate of the exhaust duct is generally required to be 14.15m³/min. (4)Lighting and cleanliness SMT workshops should have good lighting conditions, with an ideal illumination level of 800×1200 lx. It should not be less than 300 lx. In areas for inspection, rework, and measurement, local lighting should be installed if the illumination is low. SMT workshops should be kept clean and hygienic, free of dust and corrosive gases, with an air cleanliness level of 105. Under air-conditioned conditions, ventilation should be conducted regularly to maintain a certain amount of fresh air, and the CO2 content should be controlled below 1000 mg/m³, and CO should be controlled below 10 mg/L to ensure human health. (5)Temperature and humidity A. The optimal control range for workshop environmental temperature is 23 ± 3℃. Generally, it is between 18~28℃, with limits of 15~35℃. B. The humidity in the workshop should be controlled at 40%~70% RH. |
Anti-static work area
1. Anti-static
a. The anti-static work area should be equipped with anti-static flooring, anti-static workbench mats, anti-static packaging bags, turnover boxes, PCB racks, etc.
b. Any personnel entering the anti-static work area must discharge static electricity and wear spare anti-static work clothes, hats, and anti-static shoes before entering.
c. Operators must wear anti-static gloves and anti-static wrist straps (the wrist straps must be checked for effectiveness daily). Before starting work, a static protection safety check must be performed, and only after passing can production commence.
d. The floors and seats in the production workshop must meet anti-static requirements.
e. The anti-static area should have clear anti-static warning signs to remind personnel to take protective measures.
f. Regular maintenance and checks of the effectiveness of anti-static facilities are required.
g. All anti-static wires and grounding wires must not be connected.
2. Anti-static measures and requirements
a. Set up anti-static areas according to anti-static requirements, divided into levels 1, 2, and 3 based on the electrostatic sensitivity of the devices used. Different protective measures should be formulated for different levels. Level 1 electrostatic sensitivity range: 0~1999V; Level 2 electrostatic sensitivity range: 2000~3999V; Level 3 electrostatic sensitivity range: 4000~15999V; above 16000V is non-static sensitive products.
b. The room temperature of the static safety area (point) is 23±3℃, and the relative humidity is 40~70% RH. Operations on SSDs (static-sensitive devices) are prohibited in environments below 30% humidity.
c. Regularly measure the surface resistance values of floors, tabletops, turnover boxes, etc.
d. Non-production items such as tableware, tea sets, bags, woolen fabrics, newspapers, rubber gloves, etc., are prohibited on the workbench in the static safety area (point).
e. When testing SSDs, take one piece from the packaging box, tube, or tray, test one, and place one, without stacking them on the table. Non-compliant devices should be returned to stock.
g. Inspectors should be familiar with the model, variety, and testing knowledge of SSDs and understand the basic knowledge of static protection.
3. Specifications for the use of static-sensitive devices (SSD) 1. Personnel involved in assembly, soldering, board repair, debugging, etc., must strictly follow static protection requirements during operations. 2. Printed circuit boards that pass inspection and testing should be sprayed once with an ion spray gun before packaging to eliminate any static charge that may have accumulated.
Warehouse management
Warehouse environmental requirements
a. The warehouse environment must be rainproof, moisture-proof, shockproof, and protected from direct sunlight, with anti-corrosion measures in place, and kept clean and tidy. The temperature in the component warehouse should be maintained at 20~28 degrees Celsius, with a relative humidity of 30%~70%, recorded in the “Temperature and Humidity Record Sheet.” The finished product warehouse should be maintained at 16~32 degrees Celsius, with a relative humidity of 30%~80%, also recorded in the “Temperature and Humidity Record Sheet.”
b. The warehouse must be ventilated and dry, with sufficient lighting to ensure that materials and products can be easily identified, and safety passages should be established.
c. The areas for placing materials and products in the warehouse must be organized neatly and not exceed the height limit.
d. Warehouse personnel must distribute relevant materials to the workshop according to the production schedule and carefully check the quantity, specifications, and models of the materials. All valuable materials used online must undergo strict handover procedures, and handover records must be kept.
e. During transportation, substrates must use anti-static turnover boxes or anti-static bubble bags or anti-static packaging boxes.
f. Detailed records of the entry and exit of materials must be maintained, recorded by order and model; including material requisition, distribution, replenishment, and storage.
Management specifications for humidity-sensitive components
1. Under normal conditions, all vacuum packaging materials must not be opened to check the components inside. The outer hard cardboard of the original vacuum packaging must not be removed to prevent air leakage from the vacuum package.
2. When incoming materials are loose or need to be unpacked for counting, the warehouse management should vacuum package the materials after counting and attach a tracking card for priority use in production.
3. For humidity-sensitive materials, the receiving center should promptly notify purchasing and customers for quick processing. Materials that cannot be processed in time should be transferred to a humidity-controlled storage area.
4. Warehouse management must confirm the packaging condition of received vacuum packaging materials for any damage or air leakage. If damaged or not vacuum packaged, the corresponding materials should be placed in a drying box (humidity ≦ 15% RH). Before distribution, materials should be baked according to the production schedule requirements.
Temperature and humidity record sheet
|
Warehouse number |
Record number |
Date |
|
Temperature range |
Humidity range |
|
|
Morning |
Afternoon |
Recorder |
|
Warehouse temperature |
||
|
Relative humidity |
||
|
Control measures |
||
|
After measures taken |
||
|
Warehouse temperature |
||
|
Relative humidity |
||
|
Control measures |
||
|
Measures taken |
||
|
Temperature |
||
|
Humidity |
Reviewed by: Compiled by:
Material number table
Year Month Day Page:
|
Material number |
Material name |
Material specifications and description |
Usage number |
Reviewed by: Created by:
Production safety management
(1) Production management
a. After optimizing the selection of component types, path settings, and position coordinates for a single device, the reasonable coordination of several devices should also be considered to avoid causing the entire production line to stop.
b. Production equipment must be well grounded, using a three-phase five-wire grounding method with independent grounding.
c. Implement the correct process plan according to different process requirements and continuously improve it.
d. Maintain production equipment properly and regularly perform maintenance on production equipment.
e. Operators must operate according to the corresponding work instructions, and they should also pay attention to their own safety, reduce material loss, and improve product quality.
(2) Safety management
a. During the SMT production process, solvents such as anhydrous ethanol and flux, as well as other flammable materials, must have fire safety equipment established in the production area and warehouse to ensure the safety of personnel.
b. Effective safety management measures should be established for valuable components and products, and a security system should be established to prevent product loss.
c. Regular training on static protection knowledge should be provided to relevant personnel.
d. Any place with sockets, plugs, and wires should have designated personnel check daily. If there is damage or exposed copper, it should be reported for repair immediately to avoid electric shock hazards to personnel in the working environment.
e. To prevent personnel from being injured by falling objects in the working environment, items must be neatly stacked, and stacking should not exceed 1.8 meters.
f. When working at heights, wear a safety helmet, and at least two people should be present, with at least one person holding the ladder for safety.
g. During breaks or downtime, the main power supply must be turned off to prevent electrical leakage, which could cause fire or personal injury accidents.

a. Ensure that all electronic materials are used in environments that comply with MSD component management;
b. Ensure that materials such as solder paste are used in environments that can stably exert their physical and chemical properties;
c. Ensure that all electronic materials are used in environments that comply with ESD protection standards;
3.1 Daily records and verification: Electronic warehouse and SMT workshop
3.2 Audit of temperature and humidity environment: Quality Assurance Department
3.3 Maintenance of temperature and humidity environment: Electromechanical Department
4.1 Regulations:
The temperature in the electronic warehouse/SMT workshop should be between 22~28℃, and the humidity should be between 30%RH~70%RH.
4.2 Management:
4.2.1 SMT:
4.2.1 Temperature and humidity measuring devices should be placed at SMT line 1s1 and line 3s2, and records should be made every day at 8 AM and 1 PM, recorded in the “Temperature and Humidity Record Audit Sheet.”
4.2.1.2 Two hours before SMT line starts, the facilities management department must restore the environment to meet the requirements of 4.1;
4.2.1.3 In case of abnormal temperature and humidity, fill out the “Temperature and Humidity Abnormal Feedback Form” to notify relevant personnel in the facilities management department for immediate improvement;
4.2.1 Electronic warehouse:
4.2.2.1 Temperature and humidity measuring devices should be placed in the electronic warehouse, and records should be made every shift, recorded in the “Temperature and Humidity Record Sheet.”
4.2.2.2 In case of abnormal temperature and humidity, immediately notify relevant personnel in the facilities management department for improvement;
“Temperature and Humidity Record Sheet”
“Temperature and Humidity Abnormal Feedback Form”

1. Entering the SMT workshop requires wearing anti-static clothing and shoes, and entering the workshop must be through the air shower door. When leaving the workshop, the door must be locked behind.
2. The team on duty must complete the 5S management of the workshop before the end of the shift.
3. The incoming team must check the materials, and quality personnel and operators must write inspection records.
4. Production consumables such as solder paste and solder wire must be properly stored and not thrown around or placed randomly. Solder wire must not be cut and left lying around.
5. Waste solder generated during maintenance must not be thrown into the trash can but should be placed in designated waste solder storage points.
6. PCB boards must not be placed randomly. At the end of the day, employees should clean their work surfaces. The duty person must clean the workshop and equipment and turn off all doors, windows, and power (during holidays). Otherwise, if theft or other accidents occur, the duty person and workshop supervisor will be held responsible.
7. In work and management activities, any behavior of ignoring advice, arguing, or bullying employees is strictly prohibited.
8. Employees must arrive on time for work (employees attending morning meetings should arrive 5 minutes early), and must not be late, leave early, or be absent without leave (in case of urgent orders, working hours will be arranged by management). If there is a need for leave, it must be handled according to the attendance management system.
9. During working hours, except for management personnel above the team leader level who need to move around the workshop for work, other personnel must not leave their posts without reason or switch positions.
10. After starting work, no one is allowed to leave their post for personal matters. If someone must leave, they must request leave in advance and obtain approval (bring the leave certificate). Anyone who leaves without approval will be fined 10 yuan each time.
11. Chatting, playing, fighting, leaving without permission, switching positions, eating snacks, etc., are prohibited in the workshop. Violators will be dealt with according to the employee reward and punishment system.
12. During working hours, visits and personal phone calls are not allowed to ensure product quality.
13. No one is allowed to bring prohibited items, dangerous goods, or unrelated items into the workshop; personal items must not be placed on the production line. Violators will be dealt with according to the employee reward and punishment system.
14. The workshop must strictly follow the production plan, organizing production carefully according to the equipment status and personnel. Production work is a collective effort, with the team’s interests as the ultimate goal. Each production team must complete production tasks with quality and quantity.
15. Employees must obtain materials through the material handler and must not take them privately. Operators must not misappropriate materials. Each team leader will organize items and materials within the workshop area in an orderly manner and label them to prevent mixing.
16. Once the production process is confirmed, no one may change it arbitrarily. If problems are found during operations (or if there are better improvement plans), the relevant department head should be notified for discussion, and changes can only be made with agreement and signatures.
17. During working hours, employees must comply with the work arrangements of management personnel and correctly use the instruments and equipment provided by the company. Idle production tools should be returned to designated areas; otherwise, it will be treated as a violation.
18. Workshop employees must maintain a civilized production environment and actively complete production tasks assigned by superiors. If temporarily reassigned due to work needs, they must comply with arrangements from supervisors at the team leader level or above, assist in work, and comply with the management of the employing department. Those who do not comply will be reported to the company for handling.
19. Employees are responsible for maintaining the cleanliness of the working environment, and spitting or littering is strictly prohibited. During production, attention should be paid to material conservation, and materials or tools should not be thrown around. Components that fall on the ground must be picked up immediately.
20. No one is allowed to take any company items out of the factory without permission (except in special circumstances with leadership approval). Anyone found doing so will be dismissed and have their salary for the month withheld. Malicious destruction of company property or theft (regardless of whether it is public or private property) will be handled by the company’s administrative department. Depending on the severity of the situation, dismissal without pay and compensation of twice the value of the stolen items or referral to the public security authorities will occur.
21. All SMT personnel must strictly adhere to the company and department regulations.

What others are reading
A diagram to understand the semiconductor industry chain
How does 5G affect industry?
Knowledge of cleaning equipment in the electronic circuit board industry is worth collecting and sharing
PCBA process flow
Investment and maintenance of PCB/FPC depaneling machines, worth collecting
Exciting introduction and configuration diagrams of SMT/DIP technology investment
PCBA appearance acceptance diagrams
Analysis of SMT soldering processes in the electronic manufacturing industry, with reliable case studies! Some good PCB wiring tips and techniques
Wave soldering and process manufacturing anomaly handling
Understanding the circuit board potting process technology with included videos
Collection of BGA rework operation techniques in electronic SMT manufacturing (essence version)
Six suggestions for controlling product quality from the valuable experience of a technical expert with 30 years of experience
What are the manifestations of damage to various electronic components?
[Classic] 100 PCB design tips Q&A
SMT solder paste printing steps and process guidelines, standards, and common defects
Basic design principles of printed circuit boards
Understanding the three-proof paint process technology in one article
Knowledge and common process issues related to three-proof coating worth collecting and sharing
Understanding optical communication module knowledge in one article (with included video) worth collecting
Understanding how to choose PCB cleaning equipment
Collection | 100 instruments – material performance and structural analysis testing
205-page PPT, looking at the next era led by 5G + AI!
Introduction to integrated circuit packaging and testing
Please collect! 268 PCB layout design specifications!
Common hidden dangers in factories, a comprehensive collection (350 pages)
100 experiences in 6S management!
Analysis of trace oxygen content in reflow soldering and wave soldering
Understanding knowledge of the robotics industry in one article
Technical experts teach you how to use a multimeter to test components
Refine, discard the dross, strengthen the foundation, and promote innovation
Disclaimer: This article is an original compilation of materials collected from the internet, and the copyright belongs to the original author. If reprinting is required, please indicate the source and mark the reprint source. If there are any issues with the works, please contact us.
If you need soft articles or image advertising business cooperation, please contact us.