|
The following is a detailed design and implementation plan for smart locks and APP communication via Bluetooth BLE, covering protocol design, security mechanisms, development processes, and typical scenarios, helping developers quickly implement remote control and status management of smart locks: |
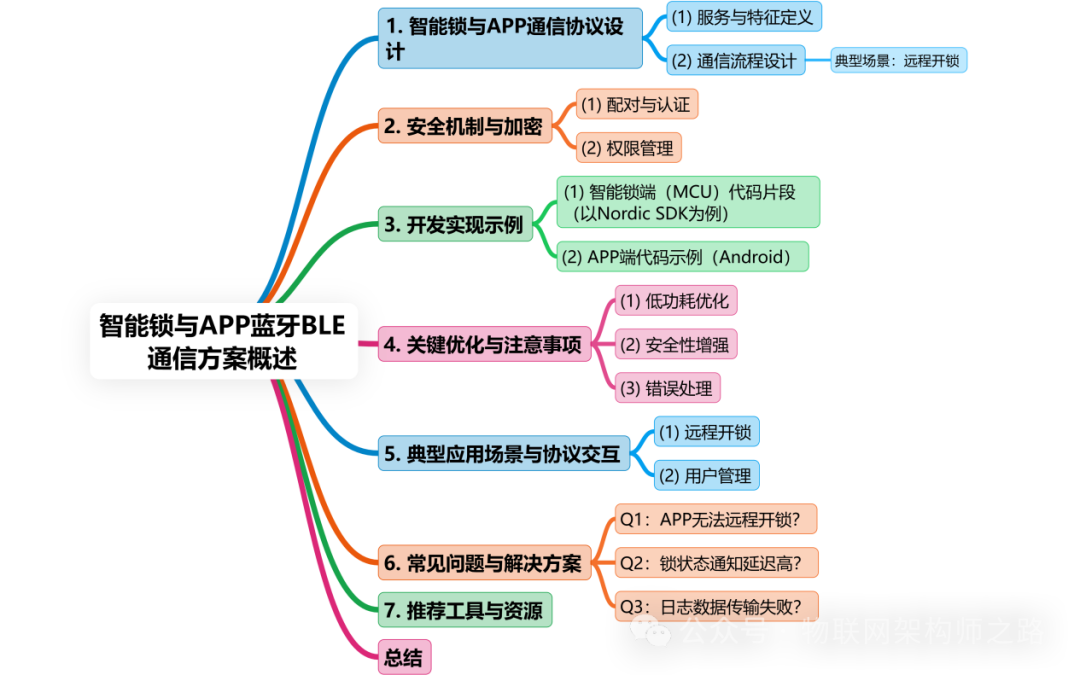
1. Smart Lock and APP Communication Protocol Design
(1) Service and Characteristic Definitions
Smart locks need to define core functions through GATT services, typically including the following services and characteristics:
|
Service |
Characteristic |
Function |
|
Smart Lock Service (Custom Lock Service) |
Lock Control |
Send unlock commands (e.g., fingerprint, password, remote unlock). |
|
|
Lock Status |
Return lock status (locked/unlocked, battery level, error code). |
|
|
User Management |
Add/remove user permissions (e.g., temporary passwords, user IDs). |
|
|
Log Record |
Read unlock logs (time, user ID, method). |
|
Security Service |
Secure Session |
Secure session key exchange and authentication (to prevent unauthorized access). |
|
Generic Service |
Firmware Update |
OTA firmware upgrade control. |
(2) Communication Process Design
Typical Scenario: Remote Unlocking
|
Plain Text 1. APP scans and connects to the smart lock (Peripheral). 2. APP discovers services: – Read `Lock Status` characteristic to get the current lock status. 3. Send unlock command: – Write to `Lock Control` characteristic (e.g., `0x01` indicates remote unlock). 4. Smart lock verifies the legality of the command (e.g., key authentication). 5. Execute unlock operation and return status: – Notify APP of unlock result (success/failure) through `Lock Status` characteristic. |
2. Security Mechanisms and Encryption
(1) Pairing and Authentication
•Secure Connections:
○Use ECDSA key exchange (Bluetooth 4.2+), ensuring a secure pairing process.
○After pairing, generate a Long-Term Key (LTK) for subsequent communication encryption.
•Application Layer Encryption:
○In the Secure Session characteristic, the APP and lock transmit data using AES-128 encryption.
○Example encryption process:
|
Plain Text 1. APP generates a random key, encrypts it, and writes it to the `Secure Session` characteristic. 2. Smart lock decrypts the key, and subsequent communication uses this key to encrypt data. |
(2) Permission Management
•User Levels:
○Set user permissions (e.g., admin, temporary user) through the User Management characteristic.
•Session Timeout:
○APP and lock need to re-authenticate after communication timeout.
3. Development Implementation Example
(1) Smart Lock Side (MCU) Code Snippet (using Nordic SDK as an example)
|
C // Define Smart Lock Service UUID static ble_uuid_t lock_service_uuid = {{0x12345678, 0x1234, 0x5678, {0x9a, 0xbc, 0xde, 0xf0, 0x12, 0x34}}, BLE_UUID_TYPE_VENDOR_BEGIN}; // Define Unlock Control Characteristic static ble_gatts_char_md_t lock_control_char = { .char_props = BLE_GATT_CHAR_PROPS_WRITE | BLE_GATT_CHAR_PROPS_NOTIFY, .p_char_user_desc = “Lock Control”, .p_char_pf = NULL, .p_user_desc_max_size = NULL, .p_user_desc_size = NULL }; // Handle Unlock Command void on_lock_control_write(ble_evt_t *p_ble_evt) { if (p_ble_evt->evt.gatts_evt.params.write.handle == lock_control_char_handle) { uint8_t cmd = p_ble_evt->evt.gatts_evt.params.write.data[0]; if (cmd == 0x01) { // Remote unlock command if (authenticate_session()) { // Verify session key unlock_door(); notify_lock_status(LOCK_STATUS_UNLOCKED); } } } } |
(2) APP Side Code Example (Android)
|
Java // Connect to Smart Lock and Discover Services BluetoothGattService lockService = gatt.getService(CUSTOM_LOCK_SERVICE_UUID); BluetoothGattCharacteristic controlChar = lockService.getCharacteristic(LOCK_CONTROL_UUID); // Send Unlock Command (must be encrypted) byte[] encryptedCmd = aes_encrypt(new byte[]{0x01}, sessionKey); controlChar.setValue(encryptedCmd); gatt.writeCharacteristic(controlChar); // Receive Lock Status Notification @Override public void onCharacteristicChanged(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) { if (characteristic.getUuid().equals(LOCK_STATUS_UUID)) { byte[] statusData = characteristic.getValue(); int status = parseLockStatus(statusData); // Parse status (unlocked/locked) } } |
4. Key Optimizations and Considerations
(1) Low Power Optimization
•Connection Interval Adjustment:
|
C // Increase connection interval to reduce power consumption (e.g., 1 second) ble_gap_conn_params_t params = { .min_conn_interval = 125, // 100ms units → 125×0.625ms = 78.125ms .max_conn_interval = 125, .slave_latency = 0, .supervision_timeout = 4000 // 4 seconds }; sd_ble_gap_conn_param_update(conn_handle, params); |
•Broadcast Strategy:
○Only broadcast basic information (e.g., device ID) when idle, reducing advertisement intervals.
(2) Enhanced Security
•Replay Attack Prevention:
○Add timestamps or random numbers to commands, APP and lock must verify validity.
•Log Encryption:
○Log data (e.g., unlock records) is transmitted after AES encryption.
(3) Error Handling
•Command Timeout Retry:
|
Java // Retry sending unlock command (up to 3 times) if (retryCount < 3) { gatt.writeCharacteristic(controlChar); retryCount++; } else { Toast.makeText(context, “Unlock failed, please try again”, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } |
5. Typical Application Scenarios and Protocol Interaction
(1) Remote Unlocking
|
Steps |
APP Operation |
Smart Lock Operation |
|
1. Connection |
Discover and connect to the device |
Broadcast advertisement packet, waiting for connection |
|
2. Authentication |
Exchange and encrypt session keys |
Verify key validity |
|
3. Send Command |
Write to Lock Control characteristic (encrypted) |
Decrypt command and execute unlock |
|
4. Return Status |
Receive Lock Status notification |
Send unlock result (success/failure) |
(2) User Management
|
Plain Text 1. APP writes new user information (e.g., temporary password) through `User Management` characteristic. 2. Smart lock verifies permissions and stores user data. 3. APP can read user list or delete users. |
6. Common Issues and Solutions
Q1: APP cannot unlock remotely?
•Reason: Session key not correctly exchanged or timed out.
•Solution:
|
Plain Text 1. Re-pair and generate session key. 2. Reduce command retransmission interval (e.g., from 5 seconds to 1 second). |
Q2: High delay in lock status notification?
•Reason: Connection interval too long or MTU too small.
•Solution:
|
C // Shorten connection interval to 20ms params.min_conn_interval = 32; // 32×0.625ms = 20ms |
Q3: Log data transmission failure?
•Reason: Insufficient MTU causing packet loss.
•Solution:
|
Java // Increase MTU to 247 bytes bluetoothGatt.requestMtu(247); |
7. Recommended Tools and Resources
•Development Tools:
○nRF Connect (Nordic): Simulate APP operations, debug services and characteristics.
○Wireshark: Capture BLE packets, analyze communication anomalies.
•Security Libraries:
○AES Encryption Library (e.g., Android’s javax.crypto).
○ECDSA Implementation (e.g., mbed TLS).
Conclusion
Smart lock and APP BLE communication must focus on:
1.Service Design: Implement core functions such as unlocking and status querying through custom services.
2.Security: Use key exchange, AES encryption, and replay attack prevention mechanisms.
3.Low Power Optimization: Properly set connection intervals and broadcast strategies.