With the opening of the Mi Home platform, many BLE devices have been integrated, such as sensors (temperature and humidity meters, door/window sensors, water immersion sensors, etc.), toothbrushes, water cups, fascia guns, and more. BLE devices typically have several notable characteristics: battery-powered/low power consumption, and direct communication with mobile phones over short distances. When integrating these devices into Mi Home, it is essential to understand the basic principles, limitations, and specifications of Mi Home BLE devices to prevent rework due to non-compliance with standards, which could disrupt product development and launch plans.Mi Home BLE devices are divided into standard devices and high-security devices (such as door locks and scooters). This article mainly focuses on standard devices, while high-security devices will not be discussed.1. Mi Home BLE Principles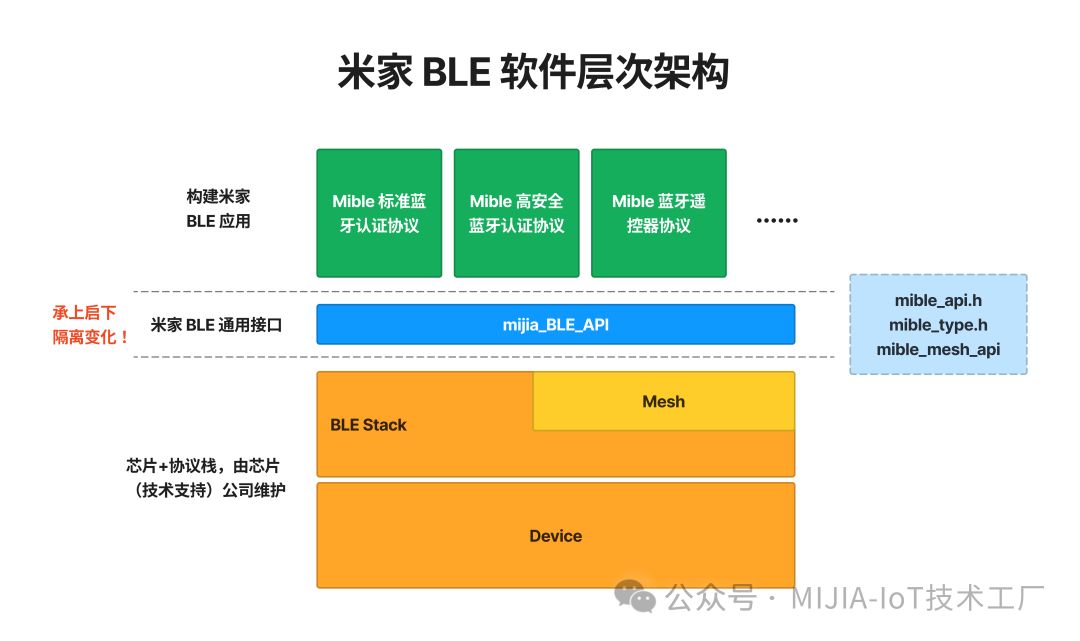 Mi Home BLE is based on the Bluetooth standard BLE protocol, combined with the protocol requirements of Mi Home format, while still operating on the SIG BLE layer. It is essentially a customized application layer private protocol for Xiaomi. What functionalities does this private protocol mainly implement?
Mi Home BLE is based on the Bluetooth standard BLE protocol, combined with the protocol requirements of Mi Home format, while still operating on the SIG BLE layer. It is essentially a customized application layer private protocol for Xiaomi. What functionalities does this private protocol mainly implement?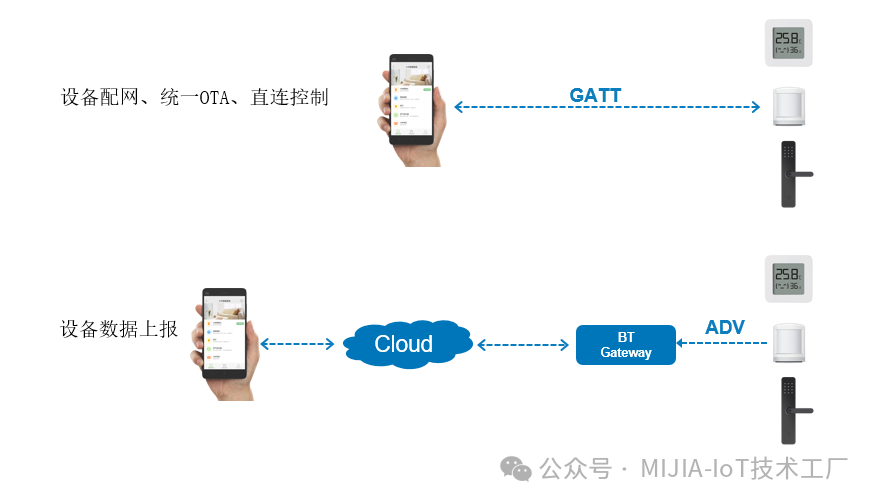 As seen in the above image, Mi Home BLE devices achieve direct GATT communication with mobile phones (for regular communication and OTA upgrades) and data reporting to gateways through broadcasting.It is important to note that when integrating, BLE devices can only complete remote datareporting (via Bluetooth gateways) and near-field direct control and settings. Currently, remote control is not supported (Tip: It is said that Xiaomi is researching BLE remote communication functionalities, which may be supported in the near future). If bidirectional remote data communication is desired, other communication methods (such as WiFi or BLE Mesh) need to be selected.2. Supported BLE Chips/Modules for IntegrationMi Home BLE devices support integration through Xiaomi modules and also support integration through Xiaomi-certified chips, meaning it is not mandatory to use Xiaomi modules for integration. For manufacturers that already have BLE chip supplies and whose chips have been certified by Xiaomi, this is a very good integration method. Below are the modules/chips that have been certified by Xiaomi; if the images are unclear, you can refer to the Xiaomi developer platform:https://iot.mi.com/v2/new/doc/embedded-dev/ble-sdk/quickstart
As seen in the above image, Mi Home BLE devices achieve direct GATT communication with mobile phones (for regular communication and OTA upgrades) and data reporting to gateways through broadcasting.It is important to note that when integrating, BLE devices can only complete remote datareporting (via Bluetooth gateways) and near-field direct control and settings. Currently, remote control is not supported (Tip: It is said that Xiaomi is researching BLE remote communication functionalities, which may be supported in the near future). If bidirectional remote data communication is desired, other communication methods (such as WiFi or BLE Mesh) need to be selected.2. Supported BLE Chips/Modules for IntegrationMi Home BLE devices support integration through Xiaomi modules and also support integration through Xiaomi-certified chips, meaning it is not mandatory to use Xiaomi modules for integration. For manufacturers that already have BLE chip supplies and whose chips have been certified by Xiaomi, this is a very good integration method. Below are the modules/chips that have been certified by Xiaomi; if the images are unclear, you can refer to the Xiaomi developer platform:https://iot.mi.com/v2/new/doc/embedded-dev/ble-sdk/quickstart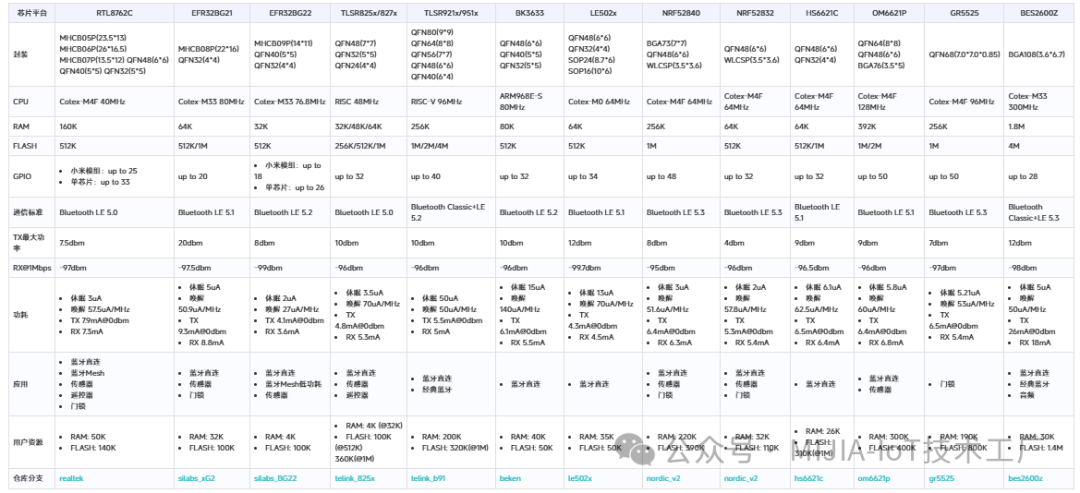 As can be seen, Xiaomi has adapted multiple BLE chips to meet the needs of various industry manufacturers. It is important to note that chips that have not been certified by Xiaomi are not supported for integration, and different chips have varying capabilities and applicable directions, so please choose carefully based on your needs!If you want to import your commonly used BLE chips, you need to contact Xiaomi’s business side to discuss the import matters. They usually focus on whether the chip’s usage range is broad, whether the integration volume is sufficient, and whether the chip’s performance meets the requirements.3. Specification RequirementsDifferent product types will have variations in UED specifications. Below are some common specification requirements; developers are advised to read the detailed specification requirements for different product types on the Xiaomi developer platform documentation center:https://iot.mi.com/v2/new/doc/introduction/solution/standard/category/sensor_ht.3.1 HardwareDevices must have a button (new products are generally required to have this) for resetting the device and triggering Bluetooth broadcasting.3.2 Software
As can be seen, Xiaomi has adapted multiple BLE chips to meet the needs of various industry manufacturers. It is important to note that chips that have not been certified by Xiaomi are not supported for integration, and different chips have varying capabilities and applicable directions, so please choose carefully based on your needs!If you want to import your commonly used BLE chips, you need to contact Xiaomi’s business side to discuss the import matters. They usually focus on whether the chip’s usage range is broad, whether the integration volume is sufficient, and whether the chip’s performance meets the requirements.3. Specification RequirementsDifferent product types will have variations in UED specifications. Below are some common specification requirements; developers are advised to read the detailed specification requirements for different product types on the Xiaomi developer platform documentation center:https://iot.mi.com/v2/new/doc/introduction/solution/standard/category/sensor_ht.3.1 HardwareDevices must have a button (new products are generally required to have this) for resetting the device and triggering Bluetooth broadcasting.3.2 Software
- The Bluetooth broadcasting transmission power of the device must be strictly set to 7 dBm (to ensure messages can be scanned by the gateway).
- In an unbound state, the device will send unconfigured network broadcasts at intervals of 200ms. If the device has not completed the binding operation for more than 30 minutes, it will turn off broadcasting to save power.
- Button-triggered broadcasting: In an unbound state, users can re-trigger unconfigured network broadcasting through the device button.
- Reset-triggered broadcasting: Long press 7s to reset and trigger unconfigured network broadcasting.
- The device must broadcast at least once every 50 minutes (30 packets: e.g., a 30ms broadcast interval lasts about 1s) for keep-alive purposes. For example, once every 50 minutes (30 packets) with battery level broadcasting. If the device needs to connect directly to a mobile phone, it can trigger the device to send a quick broadcast via the button to facilitate rapid connection.
- The device needs to support the unified OTA upgrade capability of the Mi Home SDK.
4. Precautions/Pitfall Guide
-
Only standard attributes/events under certain standard services can be reported through the gateway, with a clear characteristic: at this time, the piid/eiid >1000, and gateway permissions will be generated during configuration.
-
The total number of standard attributes + events supported for gateway reporting must be ≤ 7.
- To avoid repeated reporting of the same data to the server when the BLE device data has not been updated, thereby reducing server pressure, the gateway has set reporting rules for the device’s reporting permission attributes/events, including interval and delta (change amount/difference). Reporting can occur if either condition is met (e.g., if a temperature sensor continuously sends a temperature of 10°C every second, and if the interval==10min, the gateway will only report the temperature to the cloud every 10 minutes): If the default rules do not meet product requirements, modifications can be requested online.
- If the device does not have reporting requirements through the gateway and only requires direct connection, do not load and define the supported reporting functionalities, so it will not display under any gateway and will not show the device as offline.
- If the currently selected BLE chip does not support sending broadcast data reporting while directly connecting, and if you want to report attribute data to the cloud during direct connection (to trigger automation), the plugin side can call the reportPropChanged interface to report attribute data after obtaining data during direct connection.
- Not every Xiaomi-certified BLE chip supports the Mi Home Bluetooth remote control; currently, only RTL8762C,TLSR825x/827x are supported.
5. ConclusionIn summary, Mi Home BLE is a layer of Xiaomi’s custom private protocol encapsulated based on the SDK of the chip manufacturer, achieving BLE and Mi Home Spec protocol conversion, including capabilities such as mibeacon, secure network authentication, and connection encryption. If you are considering integrating BLE devices into Mi Home, I hope this article helps you understand Mi Home BLE! If you encounter related issues during development,feel free to leave a message for discussion!

