Today, I will share some hardware-related commands that can be used for daily operations and troubleshooting.
Quick Reference Table for Hardware Commands
| Function | Command |
|---|---|
| CPU Information |
/ |
| Memory |
/ |
| Disk |
/ / |
| PCI Devices |
|
| USB Devices |
|
| Motherboard Information |
|
| Temperature Monitoring |
|
| Kernel Modules |
/ |
| Boot Logs |
|
1. CPU Information Troubleshooting
1.1
lscpu
lscpuQuickly view CPU architecture information, including the number of cores, threads, cache, etc.
lscpu
1.2
cat /proc/cpuinfo
cat /proc/cpuinfoView detailed information about each logical CPU at a lower level.
cat /proc/cpuinfo
2. Memory and Memory Module Information
2.1
free -h
free -hView the usage of memory and swap.
free -h
2.2
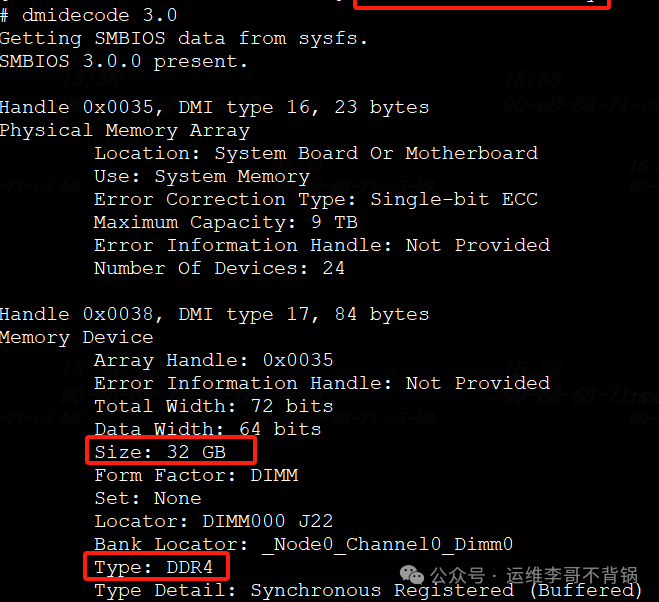
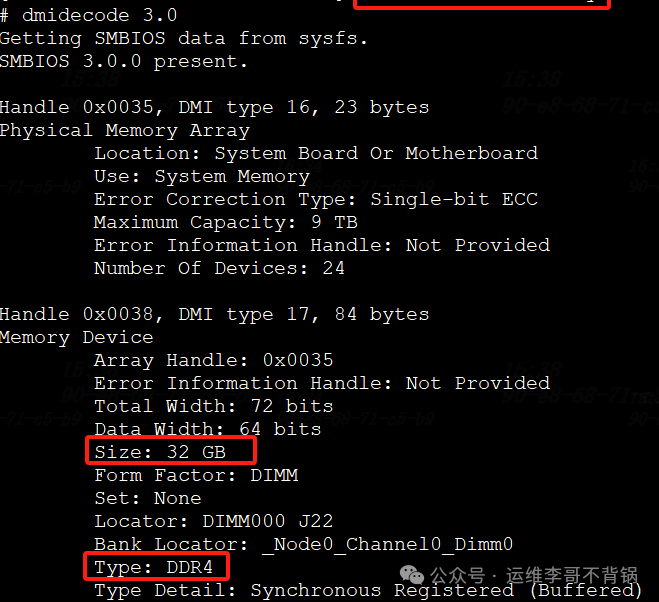
dmidecode
dmidecodeObtain information about physical memory modules, including slots, capacity, type, frequency, etc.:
dmidecode -t memory
3. Disk and Partition
3.1
lsblk
lsblkList all block devices (disks, partitions, mount points) in a tree structure.
lsblk
3.2
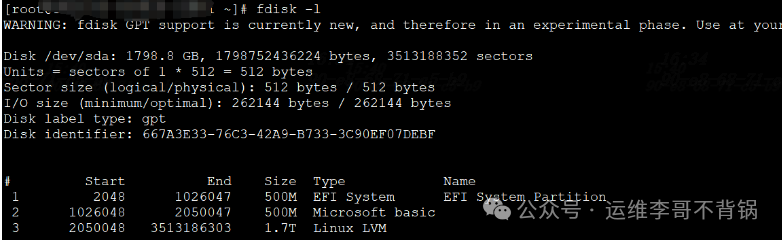
fdisk -l
fdisk -lList all disks and partition tables (MBR/GPT).
fdisk -l
3.3
blkid
blkidDisplay the UUID and filesystem type of disk devices, very useful for troubleshooting mount issues.
blkid
3.4
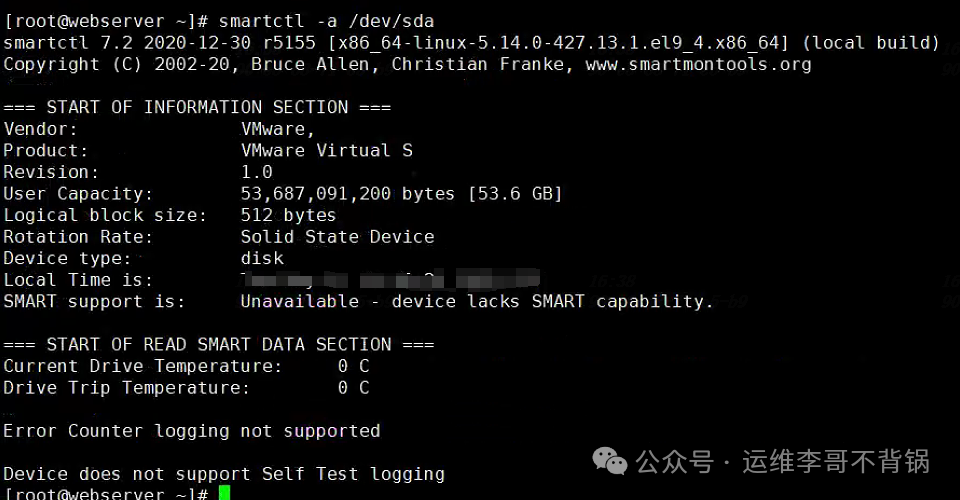
smartctl
smartctlRequires the
smartmontoolspackage to be installed, reads the S.M.A.R.T. status of the disk to determine if there are any hard drive failures.
smartctl -a /dev/sda
4. Graphics Card, Network Card, USB Devices
4.1
lspci
lspciList all PCI bus devices, including graphics cards, network cards, sound cards, etc.
lspci
Using the
-voption can display detailed information:
lspci -vnn
For example, to find the graphics card:
lspci | grep VGA
4.2
lsusb
lsusbList all USB devices, commonly used for peripheral identification issues.
lsusb
5. Motherboard and Basic Hardware Information
5.1
dmidecode
dmidecodeThis command is a universal hardware information viewing tool that can view information about the motherboard, BIOS, serial number, manufacturer, etc.:
dmidecode
Common types:
- BIOS:
dmidecode -t bios - Motherboard:
dmidecode -t baseboard - System Information:
dmidecode -t system
6. Temperature and Sensor Monitoring
6.1
sensors
sensorsRequires the
lm-sensorspackage to be installed, not all systems can install it, used to view CPU temperature, voltage, fan speed, etc.:
sensors
Installation command (Debian/Ubuntu):
sudo apt install lm-sensors
sudo sensors-detect
7. Kernel Modules and Drivers
7.1
lsmod
lsmodView the currently loaded kernel modules (drivers) in the system:
lsmod
# Generally combined with grep for filtered output
lsmod |grep vmx
7.2
modinfo
modinfoView detailed information about a specific module (version, dependencies, etc.):
modinfo e1000e
7.3
dmesg
dmesgThis command is very important. View the system boot logs and hardware loading information, very suitable for troubleshooting driver loading failures and other issues:
dmesg | grep -i error
Mastering the above commands will greatly enhance your efficiency in locating and resolving hardware issues.
Feel free to share! If there are any errors or omissions, please correct me! If you find it useful, don’t forget to like 👍 and follow 🌟~
We undertake various operational technical support and implementation of operational solutions, with a mature team to solve your problems professionally. If interested, please add WeChat, and you are welcome to join the discussion group: lige_linux
Previous Excellent Articles:
Detailed Summary of K8S Commands [Personal Collection]| Undertaking operational technical support and implementation of operational solutions | K8S Certificate Renewal for Ten Years | K8S Deployment of Prometheus | Rancher Deployment and Management of K8S |Jenkins Installation and Deployment | Gitlab Installation and Deployment | Service Mesh Istio Installation and Practice |Building an Enterprise-Level Harbor Repository | K8S Integration with Harbor Repository | Common Docker Commands Summary |Solutions for Docker Image Download Issues | Three Methods to Install Docker | Summary of Basic Docker Concepts |