

TaiLing Microelectronics has recently obtained the Bluetooth 5.3 certification issued by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group. This certification encompasses all core technical specifications at the controller level related to Bluetooth Low Energy Audio (LE Audio) and the latest features of Bluetooth Low Energy 5.3, making it one of the first chip manufacturers to fully support the LE Audio core specification certification. This certification is available to downstream customers in two forms: Bluetooth component (QDID: 195513) and Bluetooth subsystem (QDID: 188501), allowing customers to complete Bluetooth certification based on their specific needs. TaiLing’s Bluetooth Low Energy products and protocol stack currently provide the most comprehensive support for LE Audio and other latest Bluetooth Low Energy features, enabling audio device manufacturers to develop various new LE Audio terminal products, bringing an unprecedented auditory experience to end users.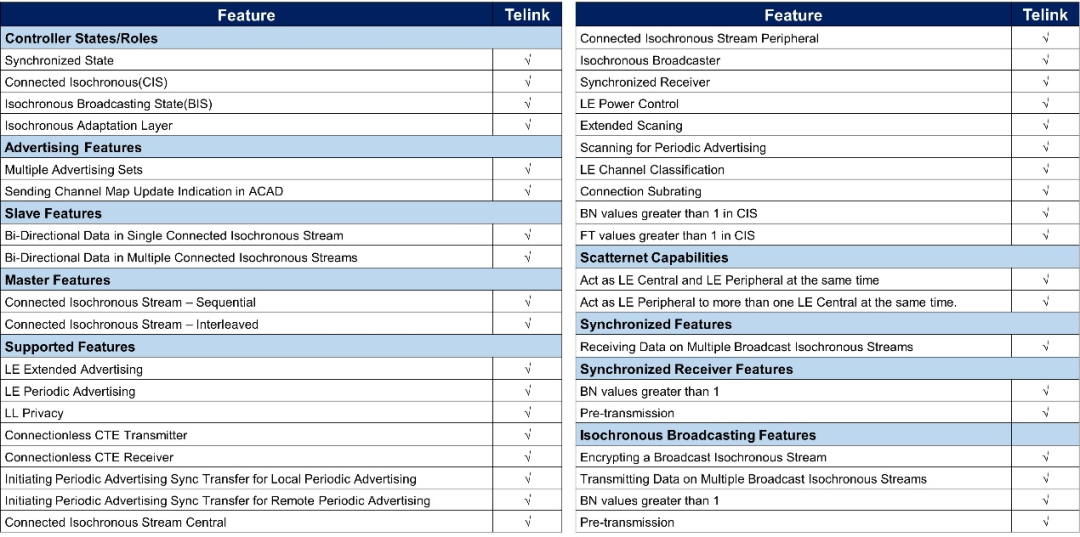 Next, let’s take a look at the main features of Bluetooth core specifications 5.2 and 5.3. The Bluetooth 5.2 specification introduces the concept of LE Audio, which represents a significant step forward in audio quality and functionality for Bluetooth audio, providing some revolutionary new features that were previously unattainable.Main Feature OneLE Isochronous Channels: Allows low-latency audio data to be transmitted to one or more devices while ensuring time-synchronized processing. It can be done through a connected mode (Connected Isochronous Stream) or broadcast (Broadcast Isochronous Stream) to an unlimited number of devices.
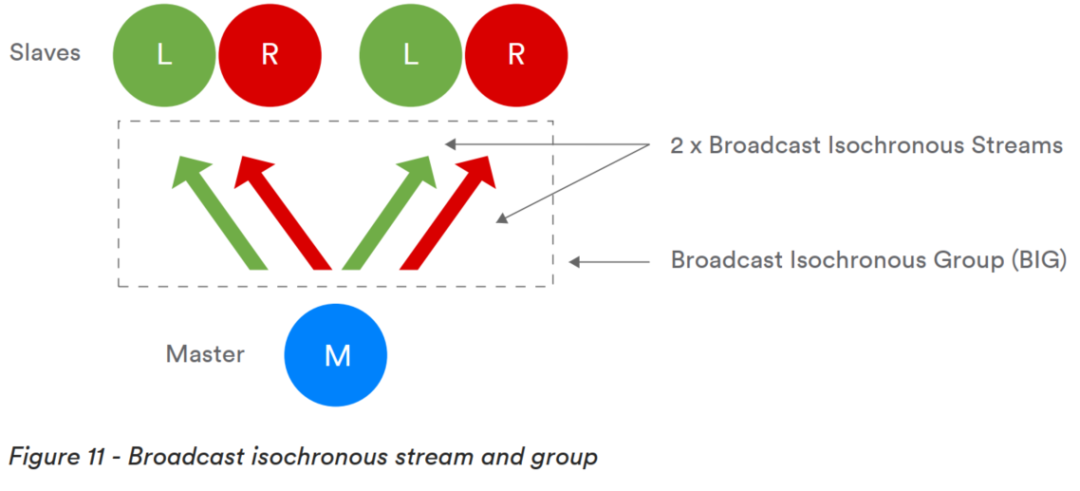
Next, let’s take a look at the main features of Bluetooth core specifications 5.2 and 5.3. The Bluetooth 5.2 specification introduces the concept of LE Audio, which represents a significant step forward in audio quality and functionality for Bluetooth audio, providing some revolutionary new features that were previously unattainable.Main Feature OneLE Isochronous Channels: Allows low-latency audio data to be transmitted to one or more devices while ensuring time-synchronized processing. It can be done through a connected mode (Connected Isochronous Stream) or broadcast (Broadcast Isochronous Stream) to an unlimited number of devices.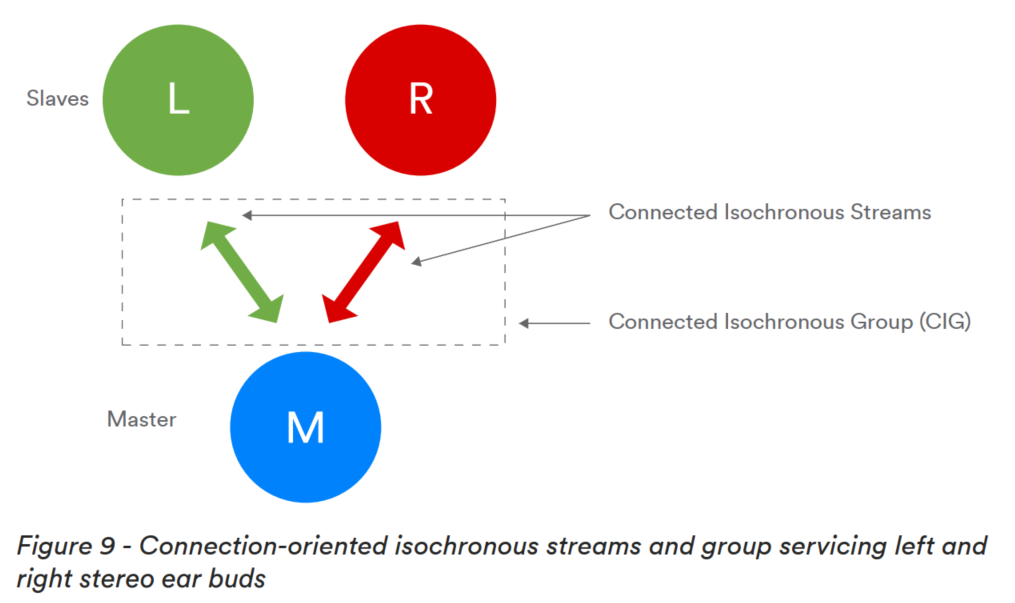
 Main Feature TwoIsochronous Adaptation Layer (ISOAL): Used for the segmentation and reassembly of synchronized data, as well as the segmentation and reassembly of upper-layer packets. Main Feature ThreeLE Power Control (PCL): LE power control ensures that the receiver always operates at the optimal state of transmission power and power consumption performance. The BLE 5.3 specification improves periodic broadcasting, connection updates, and channel classification in low-power Bluetooth, further enhancing communication efficiency, reducing power consumption, and improving wireless coexistence of Bluetooth devices.
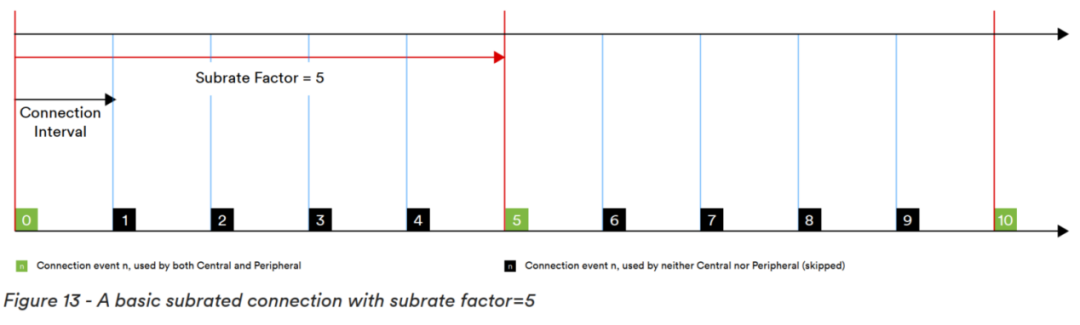
Main Feature TwoIsochronous Adaptation Layer (ISOAL): Used for the segmentation and reassembly of synchronized data, as well as the segmentation and reassembly of upper-layer packets. Main Feature ThreeLE Power Control (PCL): LE power control ensures that the receiver always operates at the optimal state of transmission power and power consumption performance. The BLE 5.3 specification improves periodic broadcasting, connection updates, and channel classification in low-power Bluetooth, further enhancing communication efficiency, reducing power consumption, and improving wireless coexistence of Bluetooth devices. Main Feature OneConnection Subrating: Through sub-rate connection mode, the duty cycle of Bluetooth devices can be quickly reduced to achieve power savings, while the normal connection rate can also be quickly restored to improve data throughput.
Main Feature OneConnection Subrating: Through sub-rate connection mode, the duty cycle of Bluetooth devices can be quickly reduced to achieve power savings, while the normal connection rate can also be quickly restored to improve data throughput.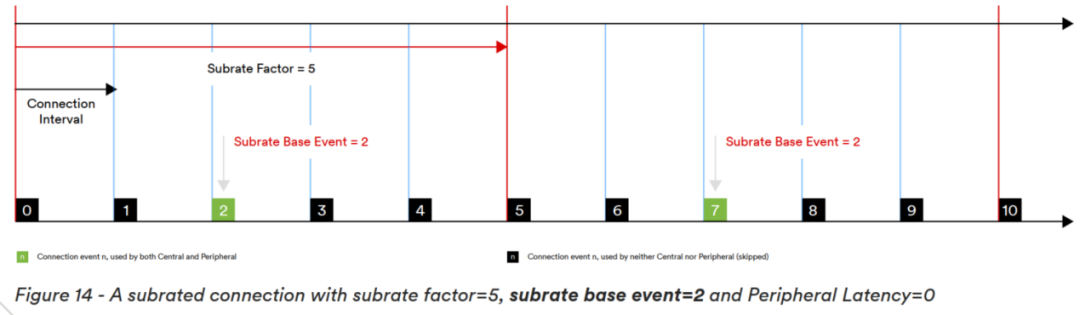
 Main Feature TwoChannel Classification: The LE channel classification feature can reduce interference between Bluetooth devices and other wireless devices, improving wireless communication coexistence. Before the core specification 5.3, the Bluetooth LE channel classification was only performed by the central device. However, if two connected devices are separated by a certain distance, the radio conditions of one device may differ from those of the other device. Therefore, when channel classification is only performed by the central device, the selected channel may include channels that are highly interfered with by peripheral devices, which is not a good choice for remote peripheral devices. This can lead to packet collisions and generally reduce throughput and reliability. The new channel classification feature effectively addresses these issues. Main Feature ThreePeriodic broadcast packets can now include the AdvDataInfo (ADI) field, which indicates whether the payload data in any periodic broadcast has changed, making the processing of redundant data more efficient and more conducive to low-power design.TaiLing Promotes the Development of Bluetooth LE Audio Audio DevicesBy combining the new ISO channel features with the efficient LC3 audio codec, Bluetooth LE Audio achieves high-quality audio transmission with lower power consumption and higher bandwidth utilization, significantly improving upon Bluetooth Classic audio. Supported by the Bluetooth 5.2 and 5.3 core specifications, Bluetooth LE Audio brings more new opportunities for audio device manufacturers. TaiLing’s latest TLSR9 series SoC chips support both Bluetooth LE Audio and Bluetooth Classic, enabling a seamless transition for audio devices from classic Bluetooth technology to Bluetooth Low Energy Audio, balancing market compatibility and technological leadership.
Main Feature TwoChannel Classification: The LE channel classification feature can reduce interference between Bluetooth devices and other wireless devices, improving wireless communication coexistence. Before the core specification 5.3, the Bluetooth LE channel classification was only performed by the central device. However, if two connected devices are separated by a certain distance, the radio conditions of one device may differ from those of the other device. Therefore, when channel classification is only performed by the central device, the selected channel may include channels that are highly interfered with by peripheral devices, which is not a good choice for remote peripheral devices. This can lead to packet collisions and generally reduce throughput and reliability. The new channel classification feature effectively addresses these issues. Main Feature ThreePeriodic broadcast packets can now include the AdvDataInfo (ADI) field, which indicates whether the payload data in any periodic broadcast has changed, making the processing of redundant data more efficient and more conducive to low-power design.TaiLing Promotes the Development of Bluetooth LE Audio Audio DevicesBy combining the new ISO channel features with the efficient LC3 audio codec, Bluetooth LE Audio achieves high-quality audio transmission with lower power consumption and higher bandwidth utilization, significantly improving upon Bluetooth Classic audio. Supported by the Bluetooth 5.2 and 5.3 core specifications, Bluetooth LE Audio brings more new opportunities for audio device manufacturers. TaiLing’s latest TLSR9 series SoC chips support both Bluetooth LE Audio and Bluetooth Classic, enabling a seamless transition for audio devices from classic Bluetooth technology to Bluetooth Low Energy Audio, balancing market compatibility and technological leadership.
Previous Recommendations