
Produced by Zhien Intelligent Chip
Renesas’ EE architecture material titled “NEXT GENERATION EE ARCHITECTURE CENTRAL GATEWAY AND ZONE CONTROL ECU SOLUTIONS” focuses on central gateways and zone controllers, providing practical insights.
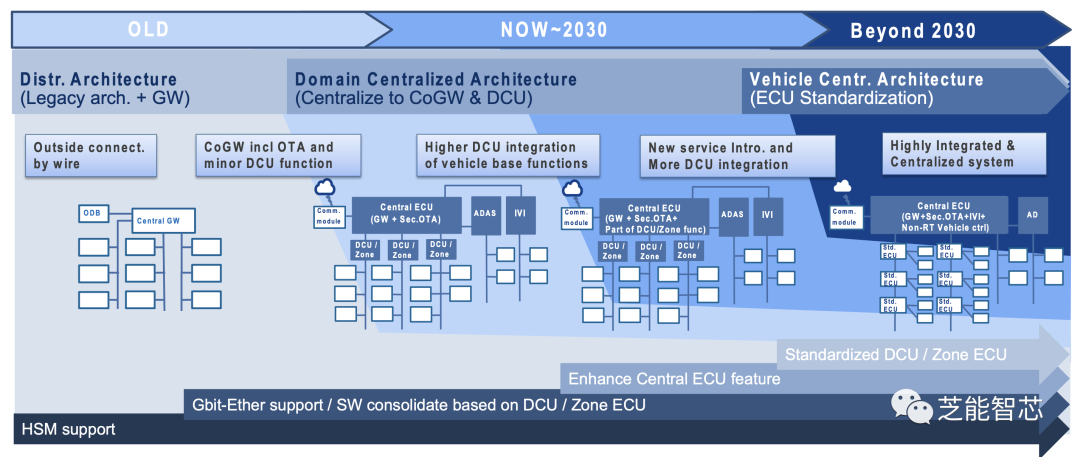
● Trends in Electronic and Electrical Architecture
The automotive industry’s electronic/electrical (E/E) architecture is evolving towards a more centralized trend. However, before innovative communication interfaces can improve latency, the situation of centralized ECUs may persist for a long time. This trend necessitates consideration of diverse communication interfaces to adapt to the changing E/E architecture.
As the E/E architecture evolves, various communication interface demands are emerging:
-
The latest automotive interfaces include Ethernet TSN (2.5G/1G/100Mbps), Ethernet T1S, CAN-XL, and I3C, to meet the needs for high-speed, low-latency communication.
-
Traditional automotive interfaces such as CAN/CAN-FD, LIN, UART, CXPI, SPI, I2C, and I2S still maintain their significance.
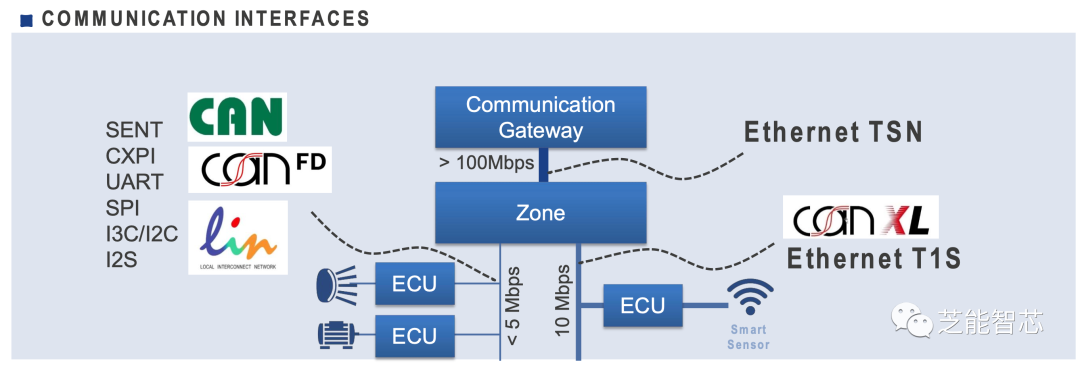
In implementing domain architecture, product mapping proposals play a crucial role. To meet the demands of future vehicles, several key MCU (Microcontroller Unit) products have been launched.
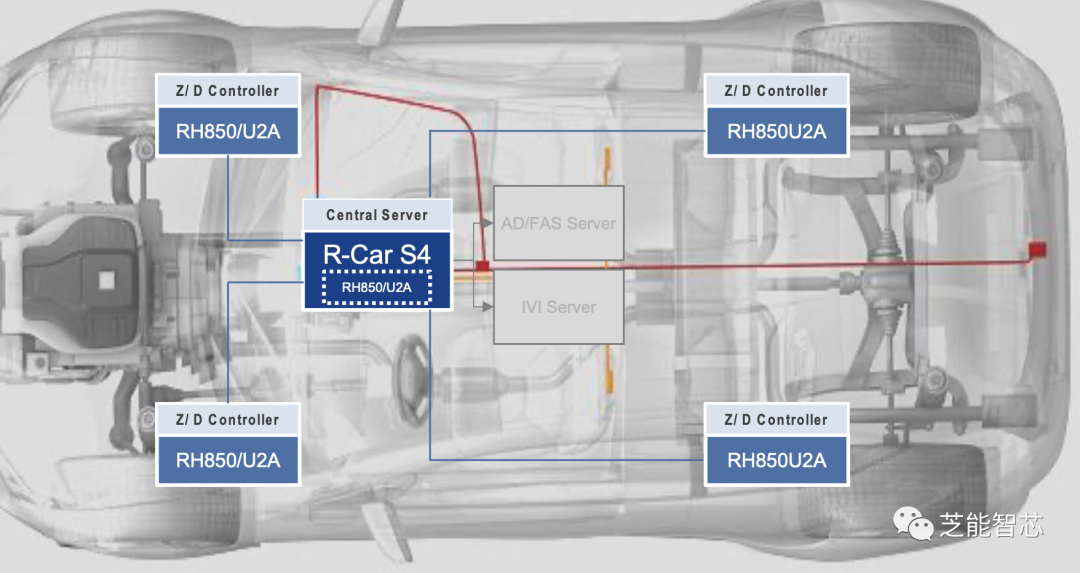
1) RH850
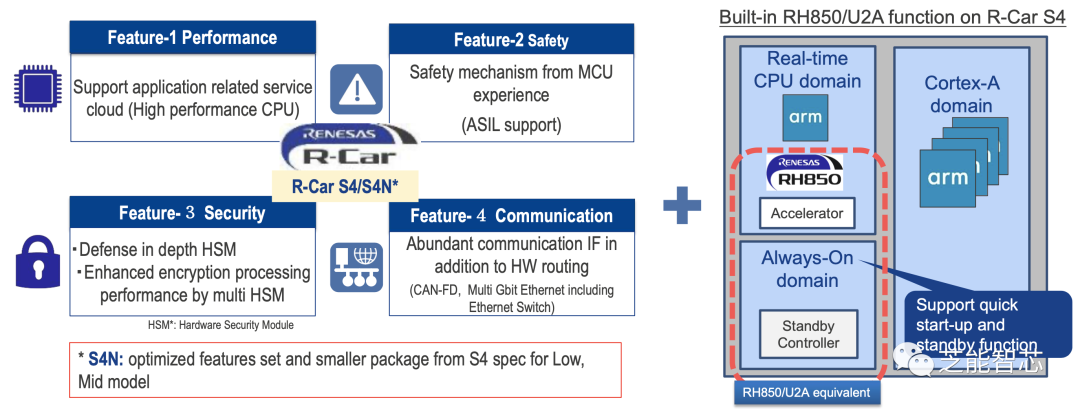
The ASIL-D series MCU features robust real-time performance, supports multi-core high performance, and provides reliable 28nm MONOS flash memory.
Hardware supports a super monitor program (FFI) and is embedded in the server SoC (R-Car S4) to achieve high software reuse.
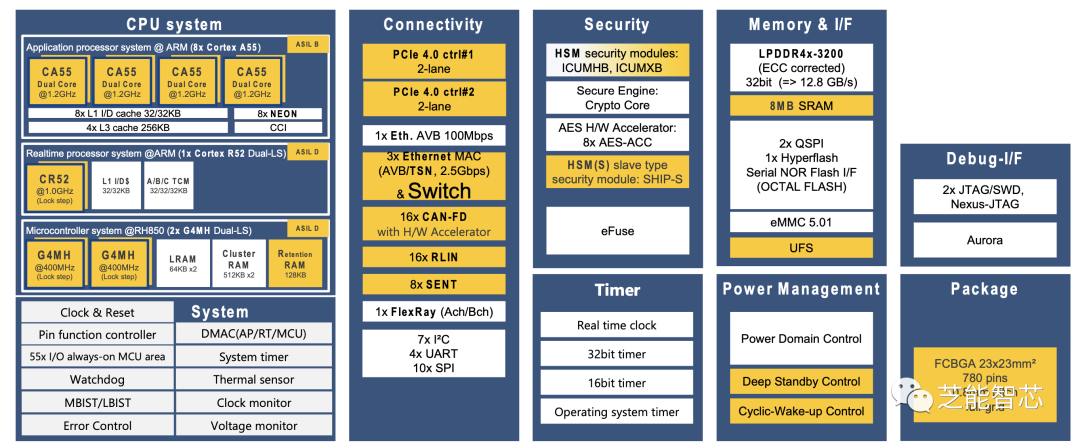
2) R-Car S4
The R-Car S4 series SoC/MCU also boasts excellent service performance, supporting single-chip ASIL-D HPC (High-Performance Computing), covering RH850 MCU, real-time and application cores, as well as high-speed Ethernet AVB/TSN switches, communication gateways, and in-vehicle servers. These products will enable developers to achieve high software reuse, thereby shortening development cycles and providing a solid foundation for future E/E architectures.
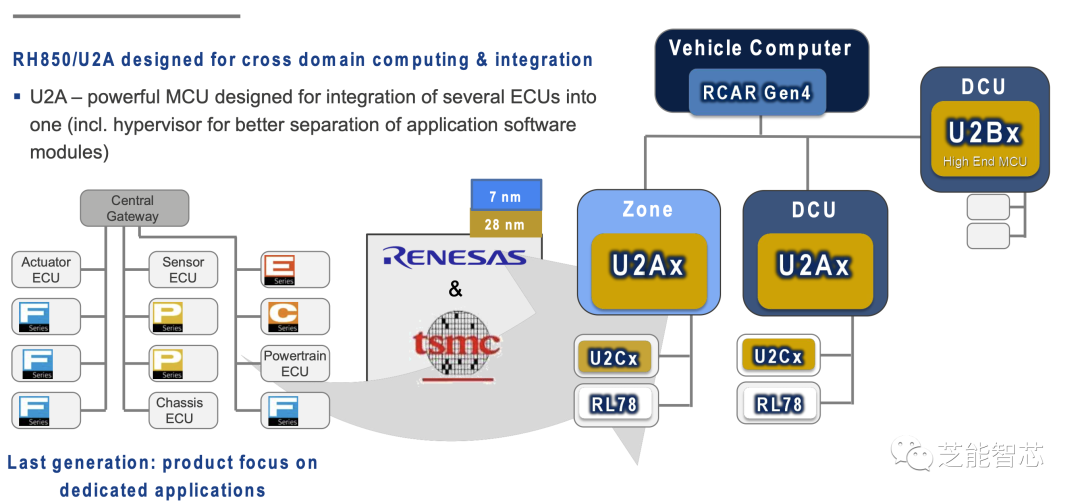
Vehicle computers also play a key role in this architecture, designed as an ideal platform for developing applications such as gateways, in-vehicle servers, and zone control to realize the next-generation E/E architecture.
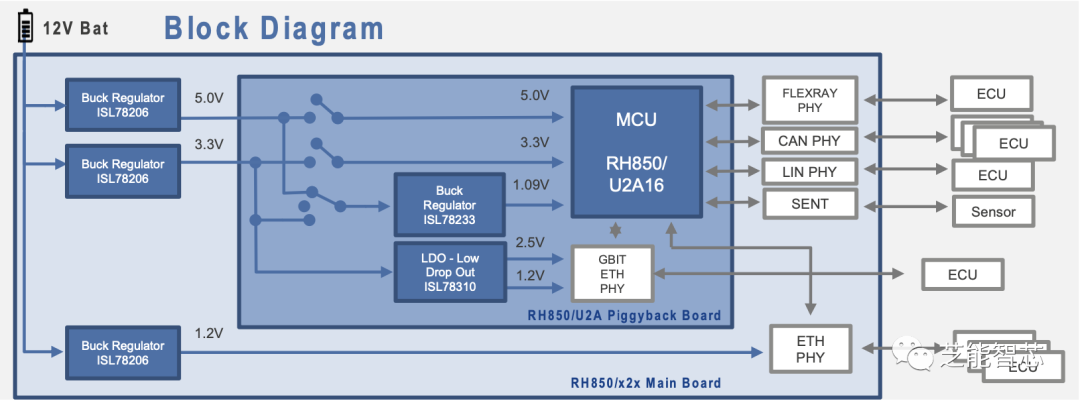
Vehicle computers support various automotive network technologies, including TSN Ethernet switches, 10BASE-T1S, 1000BASE-RH, and 2.5GBASE-T1, while also being compatible with traditional networks such as CAN, LIN, FlexRay, and SENT.
It also supports features such as analog input, wake-up, and real-time clock to enhance development usability. It provides ample computing power to accommodate the increasing user applications and allows designers to reuse 80% of the software code from the developed third-generation R-Car SoCs and RH850 MCU applications.
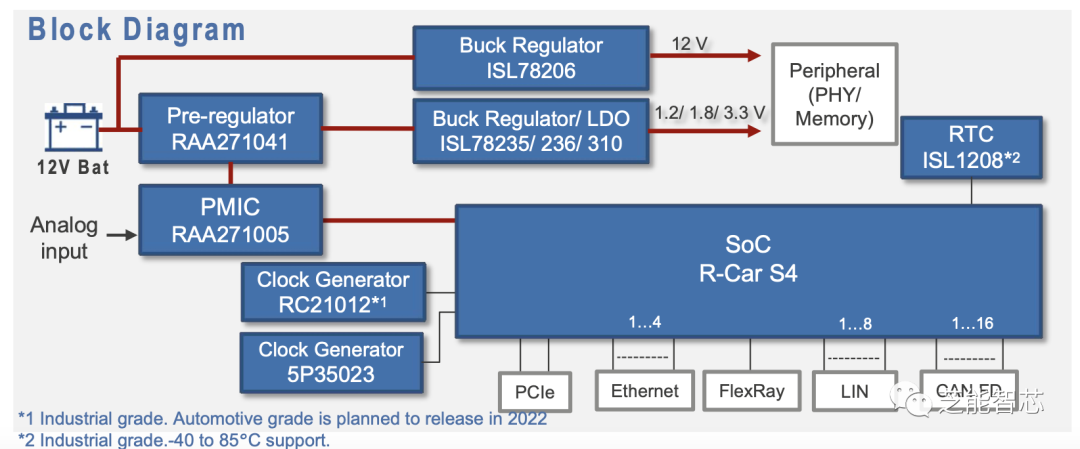
Through the combination of pre-regulators and PMIC developed for R-Car S4, vehicle computers can provide various power supply voltages to meet the functional safety requirements of ASIL D level in ISO26262 standards.
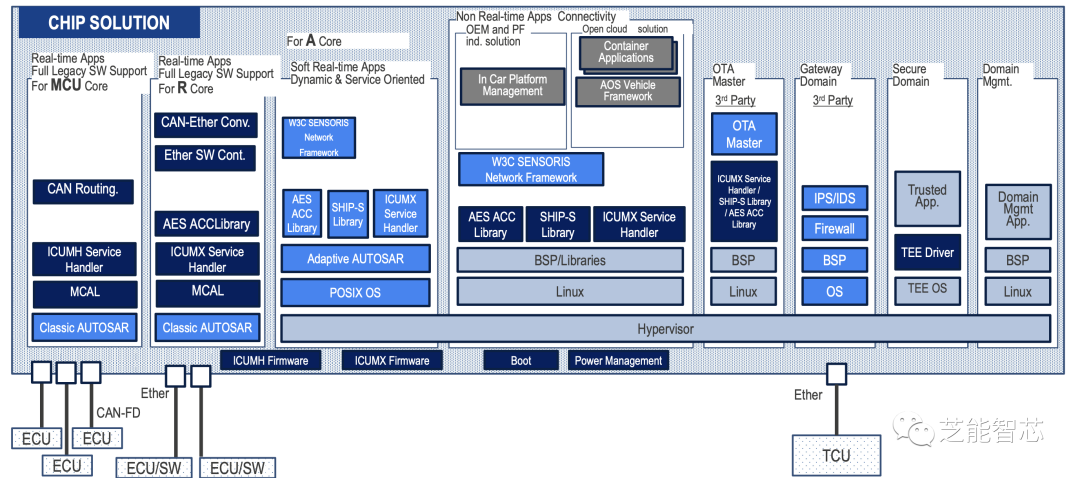
The development trend of automotive E/E architecture is moving towards a more centralized and high-performance direction, while also focusing on innovative communication interfaces and product mapping to meet the demands of future vehicles, which will bring more efficient, safer, and more flexible electronic systems to future smart vehicles.